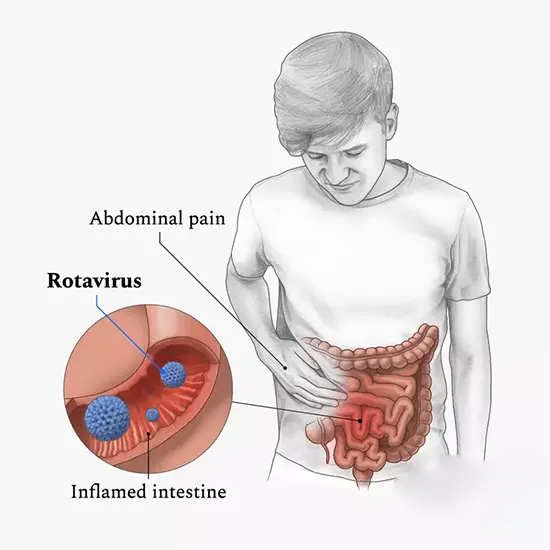
Rotavirus contamination is an extraordinarily contagious viral contamination that reasons extreme diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, and stomach ache in babies and younger children.
Rotavirus contamination is an extraordinarily contagious viral contamination that reasons extreme diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, and stomach ache in babies and younger children. The virus is transmitted through the faecal-oral route and can unfold unexpectedly in crowded locations like daycare centres, schools, and hospitals.
The ailment is most frequent in youngsters under the age of 5, however, can additionally affect adults. In some cases, rotavirus contamination can lead to extreme dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and even death, specifically in creating international locations the place gets entry to easy water and clinical care is limited.
However, rotavirus contamination can be avoided through vaccination and true hygiene practices.
What is Rotavirus Infection?
Rotavirus contamination is a kind of viral contamination that motivates infection of the belly and intestines, ensuing in signs and symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, and stomach pain.
It is induced via a crew of viruses referred to as rotaviruses, which are especially contagious and can unfold without problems from man or woman to person. Rotavirus contamination is most frequent in toddlers and younger children, however, can additionally affect adults.
The virus is transmitted through the faecal-oral route, with the ability it can unfold through contact with contaminated faeces or objects, or through ingesting contaminated meals or water.
The incubation length for rotavirus contamination is commonly between 1-3 days, and the sickness can last for various days.
Explore the Epidemiology of Rotavirus Infection
Rotavirus contamination is a frequent cause of diarrhoea in babies and younger youth worldwide.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), rotavirus is accountable for an estimated 128,500 deaths yearly in kids under the age of 5 years.
The incidence of rotavirus contamination varies geographically and seasonally.
In developed countries, rotavirus infections happen especially for the duration of the icy months, whilst in growing countries, rotavirus infections manifest year-round.
In the United States, earlier than the introduction of the rotavirus vaccine, rotavirus used to be accountable for an estimated 400,000 outpatient visits, 200,000 emergency branch visits, 55,000 to 70,000 hospitalizations, and 20 to 60 deaths per year in teens below the age of 5 years.
Since the introduction of the rotavirus vaccine, the incidence of rotavirus contamination has reduced considerably in the United States and different international locations where the vaccine is automatically used.
However, rotavirus contamination continues to be a great public fitness problem in many components of the world, especially in growing nations where access to easy water, sanitation, and scientific care is limited.
Learn About the Pathophysiology of Rotavirus Infection:
Rotavirus contamination mainly affects the cells lining the small intestine. The virus infects the cells in the small intestine, causing them to die and shed from the intestinal lining.
This leads to infection of the intestines, which can end in signs and symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, and stomach pain.
Rotavirus infects cells in the small gut by binding to unique receptors on the floor of intestinal cells.
Once the virus enters the cells, it replicates and spreads to adjoining cells, inflicting similar injury to the intestinal lining.
As the virus damages the cells in the small intestine, it disrupts the everyday manner of nutrient absorption and fluid balance.
This can lead to diarrhoea, which can be extreme and can also end in dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
In extreme cases, rotavirus contamination can lead to intestinal obstruction, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Rotavirus can additionally motivate extraintestinal manifestations such as respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and seizures, even though these are much less common.
The immune response to rotavirus contamination performs a vital position in the pathophysiology of the disease.
The body's immune gadget produces antibodies towards the virus, which assist to clear the virus from the
physique and forestall reinfection.
However, in some cases, the immune response can be excessive, leading to infection and tissue damage.
Overall, the pathophysiology of rotavirus contamination is complicated and includes an aggregate of viral replication, immune response, and disruption of intestinal function.
Types of Rotavirus Infection
There are several kinds of rotavirus, which are categorized based totally on the antigenic houses of their outer capsid proteins.
The two most frequent kinds of rotavirus that cause sickness in human beings are referred to as Group A and Group B rotaviruses.
Group A rotaviruses are accountable for the majority of rotavirus infections in human beings worldwide.
They are quite contagious and are accountable for epidemics of extreme gastroenteritis in kiddies and younger children.
Group A rotaviruses are in addition categorized into specific lines primarily based on the antigenic homes of their outer capsid proteins.
Group B rotaviruses are much less frequent than Group A rotaviruses and are especially discovered in Asia and Africa.
They can cause moderate to extreme diarrhoea in kids and adults, however, are less regularly related to outbreaks of extreme gastroenteritis.
Other much less frequent sorts of rotavirus that can cause sickness in human beings encompass Group C and Group D rotaviruses.
These kinds of rotavirus are much less well-studied than Group A and B rotaviruses, however, have been related to sporadic instances of gastroenteritis in teenagers and adults.
Overall, Group A rotaviruses are the most sizable kind of rotavirus in phrases that affect public health and are the predominant goal of rotavirus vaccines.
Signs and Symptoms of Rotavirus Infection
The symptoms and signs and symptoms of rotavirus contamination usually show up 1-3 days after publicity of the virus and can vary from slight to severe.
Infants and younger youngsters are most normally affected, though the contamination can additionally appear in adults.
The most frequent symptoms and signs of rotavirus contamination include:
- Water Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal ache or cramping
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
Dehydration (dry mouth, sunken eyes, diminished urination, letdiarrhoeaDiarrhea and vomiting can be severe, mainly to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. In some cases, diarrhoea may also be so extreme that it leads to hospitalization.
The period of the sickness can vary, however, most humans with rotavirus contamination will get better within a few days to a week.
In some cases, however, signs may additionally persist for longer, especially in immunocompromised individuals. In addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, rotavirus contamination can additionally cause extraintestinal manifestations such as respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and seizures, even though these are much less common.
Diagnosis of Rotavirus Infection
The analysis of rotavirus contamination is normally made based totally on the scientific presentation of signs and proven with the aid of laboratory testing.
Laboratory checking out includes the detection of rotavirus in stool samples.
The most oftentimes used take a look at is the enzyme immunoassay (EIA) test, which detects the presence of rotavirus antigens in stool samples.
This look is rather speedy and handy to function and can furnish consequences within a few hours.
Another take-a look that can be used to diagnose rotavirus contamination is polymerase chain response (PCR) testing.
This check detects the presence of rotavirus RNA in stool samples and is surprisingly touchy and specific.
In some cases, a stool subculture can also be carried out to rule out different reasons for gastroenteritis, such as bacterial or parasitic infections.
It is vital to be aware that laboratory testing for rotavirus contamination is no longer constantly necessary, as the prognosis can frequently be made based totally on the scientific presentation of symptoms.
However, laboratory checking out can also be advocated in instances where the prognosis is unsure or if there is a want to verify the presence of rotavirus for public fitness purposes.
Complications of Rotavirus Infection
Complications of rotavirus contamination can occur, particularly in infants, younger children, and immunocompromised individuals.
The most frequent complication is dehydration, which can manifest due to extreme
Diarrhoea and vomiting.
Dehydration can be life-threatening if left untreated, particularly in younger children.
Other viable problems of rotavirus contamination include:
Electrolyte imbalances: diarrhoea diarrhea and vomiting can lead to an imbalance in electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. This can cause weakness, fatigue, and in extreme cases, can lead to seizures, coma, or even death.
Intussusception
In uncommon cases, rotavirus contamination can motivate intussusception, a situation in which one component of the gut telescopes into some other portion, inflicting a blockage.
This can cause extreme stomach pain, vomiting, and bloody stools and can also require emergency surgery.
Malnutrition
Chronic or recurrent episodes of rotavirus contamination can lead to malnutrition, specifically in creating nations the place gets entry to easy water and desirable vitamins might also be limited.
Secondary infections
Rotavirus contamination can weaken the immune system, making it more inclined to different infections, such as bacterial infections, respiratory infections, and urinary tract infections.
It is necessary to seek clinical interest if any problems are suspected, as an early cure can assist stop serious or life-threatening complications.
Treatment of Rotavirus Infection
There is no unique therapy for rotavirus infection, as the sickness is normally self-limited and will unravel on its own within a few days to a week.
Treatment is targeted at managing signs and stopping complications, such as dehydration.
The following measures might also be advocated for treating rotavirus infection:
Oral rehydration therapy
This includes consuming fluids containing water, salts, and sugars to substitute the fluids misplaced due to diarrhoea and vomiting. Oral rehydration solutions, such as Pedialyte, are advocated for younger teenagers and infants. In some cases, intravenous fluids might also be integral to controlling extreme dehydration.
Medications
Anti-diarrheal medications, such as loperamide, are now not endorsed for the remedy of rotavirus infection, as they can gradually reduce the removal of the virus from the body.
However, antiemetics, such as ondansetron, may additionally be used to manipulate vomiting in some cases.
Nutritional support
Infants and younger teens might also require a greater diet to assist stop malnutrition all through the illness. Breastfeeding or component feeding ought to proceed as usual, and stable ingredients can also be step by step reintroduced as tolerated.
Monitoring
Infants and younger youth with rotavirus contamination must be intensely monitored for signs and symptoms of dehydration, such as dry mouth, sunken eyes, reduced urination, and lethargy.
Seek clinical interest if any symptoms of dehydration or different issues are present.
Antibiotics are no longer wonderful in treating rotavirus infection, as it is a viral sickness and antibiotics are solely fantastic in opposition to bacterial infections.
Additionally, overuse of antibiotics can lead to the improvement of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Rotavirus contamination is a notably contagious sickness that influences infants, younger children, and immunocompromised individuals. It unfolds via contact with contaminated faecal counts or objects. If you or your infant are experiencing signs of rotavirus infection, are seeking clinical interest for suitable analysis and treatment.
Rotavirus prevention - A small step for your child, a giant leap for their health!















