Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare form of cancer that develops in the bile ducts, which are small tubes that transport bile from the liver to the small intestine. Several risk factors may increase...
Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare form of cancer that develops in the bile ducts, which are small tubes that transport bile from the liver to the small intestine. Several risk factors may increase an individual's chance of developing cancer of the bile duct such as chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, exposure to certain chemicals or toxins as well as age. The symptoms of bile duct cancer may include fever, jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, weight loss, fatigue, etc. The treatment of bile duct cancer depends on the stages and spread of the bile duct cancer to other organs.
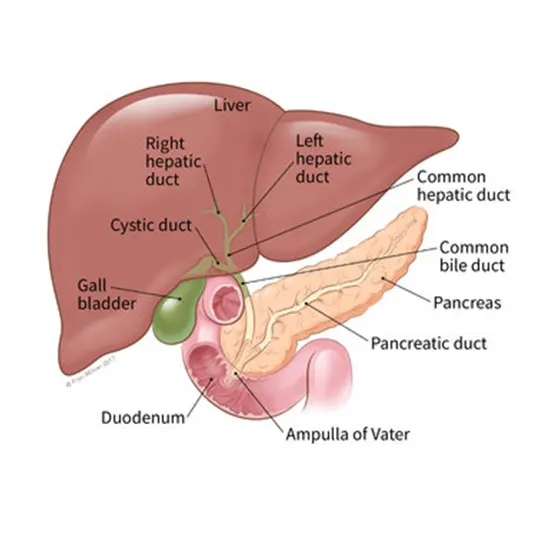
Types of Bile Duct Cancer
There are three main types of Bile Duct Cancer
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
- Distal cholangiocarcinoma
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: This cancer typically occurs in small bile ducts inside the liver. This is the least common type of bile duct cancer, which accounts for only 10-20% of cases of bile duct cancer.
Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: This is also known as hilar cholangiocarcinoma; this cancer typically occurs in the bile duct and presents at the junction of both left and right hepatic ducts. This type of cancer is very common and accounts for about 50-60% of cases of bile duct cancer.
Distal cholangiocarcinoma: This type of bile duct cancer develops in the part of the bile ducts that are closest to the small intestine. It is less common than perihilar cholangiocarcinoma, accounting for about 20-30% of all cases.
There is also a rare type of bile duct cancer called intraepithelial neoplasia, which is a pre-cancerous condition that can sometimes develop into cholangiocarcinoma.
Stages of Bile Duct Cancer
Bile duct cancer, like other cancer, is staged according to the extent to which it has spread from its original location. The staging of bile duct cancer helps doctors determine the best course of treatment for every patient. The staging system commonly used for bile duct cancer is the TNM system, which takes into account the tumor size, whether it has spread to surrounding nodes (lymph nodes), and whether it has.
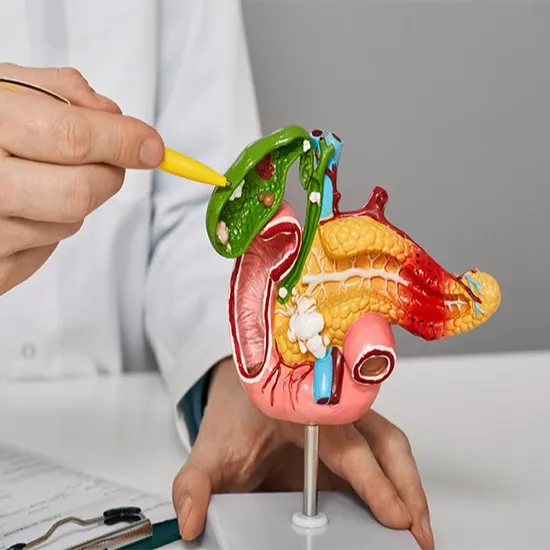
The stages of bile duct cancer are as follows:
Stage 0: This stage refers to a very initial form of bile duct cancer, in which abnormal cells are found only in the inner lining of the bile ducts.
Stage I: At this stage, the cancer is limited to the bile ducts neither it has spread to nearby nodes nor distant tissues. It has grown through the inner lining and into the deeper layers of the ducts.
Stage II: At this stage, cancer has grown beyond the bile duct and into nearby blood vessels, tissues, or organs. But not yet spread to either nearby lymph nodes or distant tissues.
Stage III: Cancer has spread to close lymph nodes or other organs, but has not yet spread to distant parts of the body.
Stage IV: Cancer has metastasized (spread) to distant organs or tissues, such as the lungs, bones, or liver.
The treatment options and prognosis for bile duct cancer depend largely on the stage of cancer at the time of diagnosis, as well as other factors such as the patient's age, overall health, and personal preferences.
Symptoms of bile duct cancer
The signs or symptoms of bile duct cancer can vary depending on the location and stage of cancer.
But in some cases, there may be no signs until cancer has advanced. Some common signs or symptoms of bile duct cancer may include:
- Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, often accompanied by itching, dark urine, and pale stools.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort: A dull ache or sharp pain in the upper abdomen, often accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
- Unexplained weight loss: A loss of weight without trying to lose weight.
- Fatigue: A feeling of tiredness or weakness that doesn't go away with rest.
- Fever: A low-grade fever that persists for several days or weeks.
- Loss of appetite: A decreased desire to eat or drink.
The mentioned above symptoms can also be caused by other health conditions, so, if you are experiencing any of the mentioned symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis of your health issues. Early detection and treatment of bile duct cancer can improve outcomes and increase the chances of a successful recovery.
Causes of Bile Duct Cancer
Several factors increase there that increase the
- Chronic inflammation: Chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, usually caused by conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis or chronic hepatitis B or C infections, is a major risk factor for bile duct cancer.
- Bile duct abnormalities: Abnormalities in the bile ducts, such as congenital cysts or choledochal cysts, can increase the risk of bile duct cancer.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver is damaged and scarred, often due to chronic alcohol use or viral hepatitis. People with cirrhosis are at an increased risk of developing bile duct cancer.
- Age: Bile duct cancer is more common in people over the age of 50.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop bile duct cancer than women.
- Exposure to toxins: Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, a contrast agent that was used in X-rays many years ago, may increase the risk of bile duct cancer.
- Family history: A family history of bile duct cancer or other liver diseases may increase the risk of developing bile duct cancer.
Prevention of bile duct cancer
Here are some steps that you need to take to prevent cancer of the bile duct.
Practice good liver health: Maintaining good liver health by avoiding alcohol or drugs that can harm the liver, getting vaccinated against hepatitis B and C, and treating underlying liver diseases such as cirrhosis, can help reduce the risk of bile duct cancer.
Maintain a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and low in saturated and trans fats, can help reduce the risk of bile duct cancer.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Avoid exposure to toxins: Avoiding exposure to chemicals or toxins that may harm the liver or bile ducts, such as pesticides or industrial chemicals, may help reduce the risk of bile duct cancer.
Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups and screening tests can help detect bile duct cancer at an early stage when it is more treatable.
Benefits of early detection of bile duct cancer
Bile duct cancer early detection can provide many benefits, including:
Better treatment options: If bile duct cancer is detected at an early stage, there are more effective treatment options to detect cancer at an early stage.
Increased chances of survival: Early detection of bile duct cancer can increase the chances of survival. The five-year survival rate for people with early-stage bile duct cancer is around 40-50%, compared to around 5-10% for people with advanced-stage cancer.
Improved quality of life: Early detection of bile duct cancer can also improve a person's quality of life, as they can receive treatment earlier and avoid more aggressive treatments that may have more side effects.
Reduced need for aggressive treatments: When bile duct cancer is detected at an early stage, it may be possible to avoid more aggressive treatments such as liver transplantation or extensive surgery.
Increased awareness and education: Early detection of bile duct cancer can increase awareness and education about this rare cancer, leading to an improved understanding of risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options.
Diagnosis of Bile Duct Cancer
The diagnostic procedures for bile duct cancer may vary depending on the location and stage of cancer, but some common tests and procedures that may be used to diagnose bile duct cancer include:
Blood tests: Blood tests such as Liver Function Test (LFT), CEA and CA19-9, and Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) may be performed to evaluate liver function and check for abnormal levels of certain substances that may indicate the presence of bile duct cancer.
Imaging tests: Imaging tests such as whole abdomen ultrasound, CT scan, MRI scan, and Whole body PET scan may be performed to visualize the bile ducts and look for signs of cancer.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): ERCP is a procedure that involves passing a flexible tube down the throat, through the stomach, and into the small intestine to inject dye into the bile ducts. the radiologist will take an X-Ray to identify any abnormalities.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP): MRCP is a non-invasive imaging test that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the bile ducts and identify any blockages or abnormalities.
Biopsy: A biopsy may be performed to remove a sample of tissue from the bile duct for examination under a microscope to determine whether cancer is present.
Brush cytology: Brush cytology involves inserting a thin brush into the bile duct during an ERCP procedure to collect cells for examination under a microscope.
Laparoscopy: Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a small camera and instruments through small incisions in the abdomen to examine the bile ducts and surrounding tissues.
The choice of diagnostic procedure may depend on the individual patient's condition, the location and stage of cancer, and other factors. Your healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate diagnostic tests and procedures for your individual situation.
Conclusion
Bile duct cancer is a rare but serious form of cancer that occurs when cancer cells develop in the bile ducts, which are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. There are different types of bile duct cancer, and the symptoms and treatment options may vary depending on the location and stage of cancer. While the exact causes of bile duct cancer are unknown, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing this disease, such as liver disease, chronic inflammation, and exposure to certain toxins.
Early detection of bile duct cancer is important for improving outcomes and increasing the chances of successful treatment. Diagnostic procedures such as blood tests, imaging tests, and biopsies may be used to diagnose bile duct cancer, and treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or liver transplantation.
If you have any concerns about your health or are experiencing any symptoms, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Ganesh Diagnostic offers Bile Duct Cancer Screening Package for early detection and addressing the bile duct cancer when treatment of the disease can be curative and complications can be prevented. If you have any queries about bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) diagnostic procedures, contact our expert healthcare executives.









