Neurons make up the electrical circuitry that powers brain activity, and astrocytes give neurons the support and structure they need to function properly. The brain is made up of a variety of different types of cells. The most...
Neurons make up the electrical circuitry that powers brain activity, and astrocytes give neurons the support and structure they need to function properly. The brain is made up of a variety of different types of cells. The most prevalent type of brain tumor in adults is called an astrocytoma, which develops from astrocytes. Each year, 15,000 new cases of astrocytomas are diagnosed in the US. A ratio of 1.3/1 indicates that men are marginally more impacted than women.
Tumor Grading and Its Meaning
Astrocytomas are classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as either grade 1 (the most benign) or grade 4 brain tumors. (Most malignant). The following characteristics are used to grade the tumor cells after being examined under a microscope:
1) The cells' level of abnormality (atypia)
2) Their growth rate (mitosis)
3) The tumor has newly formed blood vessels. (Vascular proliferation).
The genetic characteristics of the tumor, or the DNA analysis of the tumor cells, are further integrated into this. Except for forde1 tumors, which are most prevalent in children, most astrocytomas typically affect adults over the age of 40. Astrocytomas with higher grades are also more likely to develop in elderly patients.
Grade 1
Pilocytic A well-defined tumor with slow growth is an astrocytoma. The cerebellum, or the area of the brain situated in the rear of the head, right above the neck, is where the condition is most prevalent. Since it doesn't spread to the surrounding brain when it is entirely removed it is considered cured and neither chemotherapy nor radiotherapy is needed.
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma typically develops in the temporal lobes and is frequently linked to seizures. Its cells are pleomorphic, which means they can take on a variety of forms, although they often lack proliferative characteristics. Surgery is typically therapeutic.
Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma (SEGA) is most common within the more youthful populace, more often than not in affiliation with a commonplace disorder called tuberous sclerosis. It characteristically develops the interior of the ventricles, which are fluid-filled spaces profound into the brain and can frequently square the typical surge of this liquid, hence causing hydrocephalus. Surgical resection is ordinarily corrective
Grade 2
Diffuse Astrocytoma is an invasive tumor, so there's no clear partition from the encompassing brain, and surgery itself might not be sufficient for its remedy (this depends on a few other components portrayed underneath). The tissue appearance is as it were decently distinctive from a typical brain, but cells show up irregularly beneath the magnifying lens and marginally expanded in number.
Grade 3
Anaplastic Astrocytoma is considered a more dangerous advancement of an already lower-reviewed astrocytoma, which has obtained more forceful highlights, counting a better pace of development and more attack into the brain. Histologically, it shows a better degree of cellular variations from the norm, and proves cell proliferation (mitosis), in comparison to grade 2 tumors. Surgery is never considered healing for these tumors and must be taken after by radiation and nearly continuous chemotherapy.
Grade 4
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the foremost dangerous, forceful, and common (60%) frame of astrocytomas. Histologically, it is characterized by exceptionally abnormal-appearing cells, expansion, zones of dead tissue, and arrangement of unused vessels. GBM can show either as a threatening movement from an already existing lower review astrocytoma (more often than not in 10% of cases) or start specifically as a review 4 tumor (90% of cases). The previous situation is most common in more youthful patients, whereas the last mentioned is most common after age 60. In any case of its presentation, this tumor could be an exceedingly forceful cancer, with articulated brain intrusion and devastation and exceptionally quick movement.
Imperative Organic Highlights
Over the past 15 long times, there have been important strides in understanding this illness, basically inferred from noteworthy progresses within the capacity to think about its hereditary and biological underpinnings.
IDH1 mutation is a crucial feature that characterizes a subgroup of astrocytes with half a quality, called isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1). This quality is included in providing energy to the cells. Its change comes about in the generation of a chemical called 2-HG, which, over time, builds up the interior of the typical astrocytes and sets them off track, causing astrocytomas. More than fair another laboratory finding, this change is crucial since it characterizes nearly 100% of moo review astrocytomas and is related altogether.
MGMT quieting needs to do with the methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) protein included in repairing DNA after it has been harmed by chemotherapy, hence securing the tumor against the activity of these drugs. Certain astrocytomas have this enzyme turned off, and, as a result, they react altogether superior to chemotherapy with TMZ.
Immunologic elude implies that tumors escape the watching immune system, which ordinarily devastates anything that's recognized as “abnormal”. Astrocytomas are among the tumors with the foremost created capacity to elude this observation. They do this by enacting multiple genes that can turn the safe framework off. There's consensus that checking this safe elude will result in critical restorative benefits.
Risk Factors
Astrocytomas are, for the most part, intermittent tumors, meaning that they happen by chance, or at the slightest, it isn't however known why these happen. There are as it were two circumstances with demonstrated proof to cause the tumor:
- Genetic disorders (i.e., caused by acquired DNA transformations)
Li-Fraumeni:
Due to changes in tumor suppressor quality p53 and characterized by the youthful onset of different tumors, counting breast cancer, bone cancers, leukemias, and astrocytomas.
Turcot:
Due to changes in a few tumor silencer qualities, counting APC and MMR, and characterized by early onset of colon cancer and astrocytomas.
Neurofibromatosis 1:
Due to the change of tumor silencer NF1, capable of early onset of astrocytomas, peripheral nerve tumors, skin freckling, and light-brown patches within the skin.
Tuberous sclerosis:
Maybe an uncommon hereditary clutter related to mental hindrance and early onset of subependymal monster cell astrocytoma (SEGA).
Ionizing radiations:
Introduction to ionizing radiations has been associated with the deferred onset of astrocytomas. People at specific hazards are those uncovered to helpful radiotherapy to the head and neck locale amid childhood (i.e. for treatment of leukemias or other brain tumors). The interim between exposure to radiation and astrocytoma onset can be as long as 20-30 a long time.
Fighting chemicals:
There's a yet problematic doubt that introduction to Operator Orange amid the Vietnam War might be dependable for the deferred onset of astrocytomas in veterans.
Cellular phones:
Despite a few suspicions, particularly related to heavy use, there's no information supporting a causative hazard for astrocytomas.
Indications
The clinical introduction of astrocytomas depends much more on their area within the brain in their biological characteristics. There are locales of the brain that can suit exceptionally huge tumors some time recently they become symptomatic (for example, the districts within the forehead), whereas there are other areas where even a little tumor can cause problems early on, like limb shortcoming or trouble with discourse or vision.
Generally, low-review astrocytomas tend to be of greater measure some time recently they become symptomatic, as compared to more forceful, higher-review astrocytoma lower-review tumors tend to uproot the brain rather than pulverize it, and since they are related to less brain swelling than dangerous ones.
Common side effects of astrocytomas are the following:
- Determined migraines.
- Migraines which are more awful in the morning or cause awakening from rest ( a sign of expanded intracranial weight)
- Twofold or obscured vision
- Discourse issues
- Diminished cognitive capacities.
- Get a handle on appendage shortcomings.
- Modern seizures
Imaging
Routine MRI:
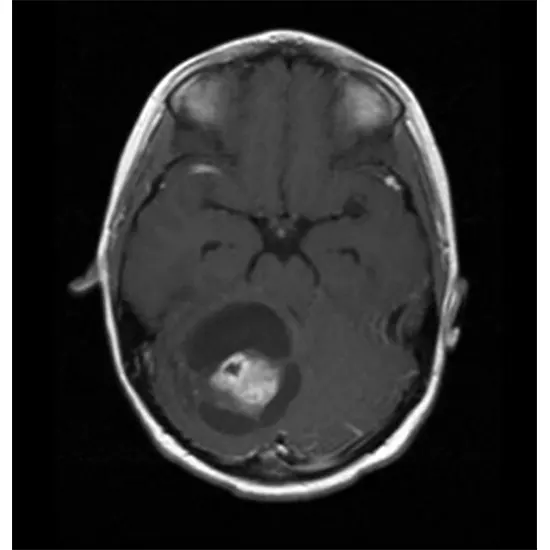
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the foremost imperative imaging considered for astrocytomas. Often, pictures are acquired both sometime recently and after the organization of IV differentiates. As a run show of thumb, on the off chance that the tumor picks up the difference (i.e. gets to be shining in pictures), it is a sign of a better-grade astrocytoma.
Other imaging arrangements give clues as to tumor cellularity, brain swelling, and brain infiltration.
Pivotal T1-weighted MRIs after IV gadolinium administration:
Low-review tumors ordinarily don't take differentiate (cleared outboard), whereas review 4 tumors show solid contrast enhancement and visit central rot (right board)
MRI spectroscopy (MRS):
It is an imaging instrument, based on MRI, which gives data on the chemical composition of the tumor, and works based on the truth that certain chemicals are abundant within the typical brain (for case, NAA), while others are plentiful in tumors (for illustration, choline). The yield of this imaging methodology is a chart appearing the sum of each chemical within the region of the brain beneath examination:
In case the sum of NAA is more than choline, that proposes an ordinary brain (see underneath). The opposite raises suspicion of a tumor. This technique can be considered non-invasive tissue testing, even though it is not as exact or conclusive as a standard biopsy.
Functional MRI (fMRI):
fMRI could be a valuable method to imagine in genuine time which parts of the brain get to be actuated when the persistent is asked to perform a certain task. Usually crucial to characterize the regions of the brain which, on the off chance that harmed, would cause issues to the patient. The enacted brain appears as a yellow/red flag superimposed on an otherwise standard MRI. For tumors that are localized within the nearness of critical regions (discourse centers, engine cortex, or visual cortex) fMRI provides imperative aid, especially regarding surgery.
Treatment
Surgery
Surgery is the primary step for the treatment of astrocytomas, as it gives two vital benefits:
To begin with, it obtains tumor tissue to set up a conclusion. Furthermore, it offers the plausibility to expel as much tumor as securely conceivable to calm mass impact, decrease swelling and encourage reaction to adjuvant treatments, when indicated. The choice of whether to perform a basic biopsy or a full resection depends on different components, especially on the clinical and medical conditions of the quiet, as well as the anticipated extent of respectability of the tumor.
Vital devices to maximize proficiency and security of surgery are:
Neuronavigation:
It is, in essence, a GPS for the brain, and permits the specialist to visualize in genuine time on the MRI his/her localization inside the patient's brain. This significantly increases precision and minimizes the hazard of harming ordinary brains.
Surgery:
This method is especially valuable to resect tumors found in speech ranges, conjointly when r to the primary motor cortex reciprocally. The patient is kept calm but not intubated, so that he/she can talk and execute commands when asked to. In this way, the surgeon can persistently assess the patient's capacities whereas evacuating the tumor.
Mapping amid general anesthesia:
The districts of the brain controlling movement can be moreover fortified with an electrode even on the off chance that the persistent is snoozing. A simulator is utilized to apply streams straightforwardly to the brain cortex, and muscle reactions are recorded. Positive responses are deciphered as brain structures that ought to be saved from resection.
Fluorescent colors:
Tumors, particularly those of higher review, have the characteristic of eagerly absorbing certain colors that are given IV to the understanding just before surgery. In this way, the tumor tissue becomes colored by a particular color, while the ordinary brain does not. This permits a much more exact definition of what ought to be resected and what should be cleared out untouched. Among the most reliable dyes are 5-ALA, which colors the tumor violet, and Fluorescein, which colors the tumor yellow.
Built-up adjuvant therapies
Steroids:
Dexamethasone is the medication of choice to relieve side effects due to the brain swelling that's regularly related to the tumor. It is a very viable medicate, which acts rapidly and reliably. Shockingly, it does not have any activity against the tumor, and it is associated with critical side impacts when utilized for an extended duration than 2-3 weeks:
- Weight picks up, high blood sugars, hypertension, expanded hazard of contamination, fractiousness.
Chemotherapy with TMZ:
Temozolomide (TMZ) may be a drug that is taken by mouth and works by marginally adjusting the DNA of tumor cells. This impact on the DNA triggers its breakage and resulting death of the cell unless DNA repair mechanisms abrogate the damage. TMZ is presently a well-set-up first-line treatment for each astrocytoma which is either review 3 or 4 and is every so often utilized too for grade 2 tumors. It is often taken day by day for 5 days, taken after by a rest period of 3 weeks, time recently beginning another cycle.
Radiotherapy:
Radiation has been the premise of the treatment of astrocytoma for a long time, and it is greatly compelling, at the very least for a few months after treatment. Radiation, as well, works by harming the DNA of the tumor cells, thus inducing their passing. Beneath standard protocols, the treatment consists of small doses of radiation within the area of the tumor, 5 days a week for 6 weeks. Side impacts are neighbourhood hair misfortune (as a rule transitory), and weariness. Long-term side impacts are a corruption of the brain around the treated locale and cognitive difficulties.
Bevacizumab (Avastin):
Bevacizumab is a drug that pieces the tumor's ability to enroll blood vessels so that they can bolster themselves and keep growing. Avastin has been endorsed by the Nourishment and Sedate Administration (FDA) in 2013 for its use in repetitive glioblastomas. It is exceptionally successful in lessening the swelling associated with the tumor and frequently makes a difference in improving symptoms. In this sense, its capacities as a powerful elective to steroids. Unfortunately, in an unexpected way from radiation and TMZ, it does not essentially drag out survival.
Antiseizure Drugs:
Levetiracetam (Keppra) is the foremost broadly utilized medication for this reason.
Exploratory Therapies
Astrocytomas, and in particular glioblastomas, are the target of serious investigation and each year a few clinical trials are conducted to discover unused methodologies which would improve survival.
The foremost strong field of examinations is the taking after:
Focused on treatments:
These days, most treating centres perform a nitty-gritty hereditary investigation of any tumour tissue expelled at the surgery to get patient-specific advice on the finest medication for that tumour.
Immunotherapy:
A debilitated, resistant reconnaissance is essential for the advancement and movement of astrocytomas. For this reason, expansive exertion is now underway to find techniques to boost the safe framework against the tumour. Usually, this is done with the utilise of antitumor antibodies, the utilization of hereditarily altered resistant cells that are managed to the patient by intravenous mixture, or the utilization of drugs that strengthen the resistance framework's actuation.
Infection treatment:
A promising and ever-growing approach is the utilization of infections which, once managed to patients (often specifically infused by the neurosurgeon into the tumor), can specifically contaminate and annihilate tumor cells without hurting the encompassing normal brain.









