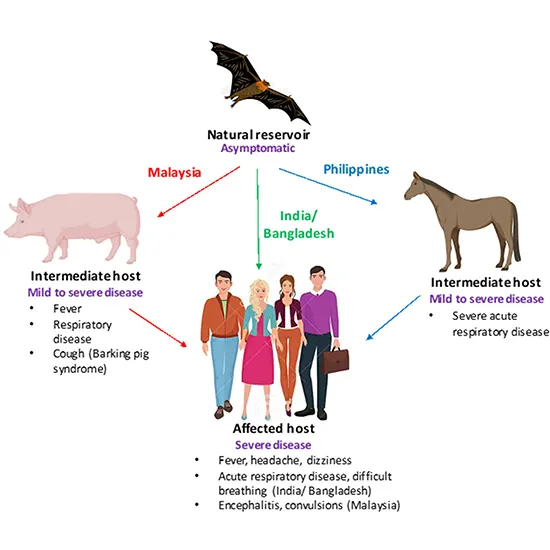
Following an outbreak in horses and people in the Brisbane suburb of Hendra, the Hendra virus (HeV), a deadly and uncommon virus, was first discovered in Australia in 1994.
Following an outbreak in horses and people in the Brisbane suburb of Hendra, the Hendra virus (HeV), a deadly and uncommon virus, was first discovered in Australia in 1994. The neighbourhood where the first outbreak happened is where the virus gets its name. Because the virus is a zoonotic virus, it can spread from animals to people. The virus is mostly present in fruit bats, sometimes known as flying foxes, and it is thought that bats are where it first appeared.
Transmission of Hendra Virus
Fruit bats are the main source of Hendra virus transmission to horses, who ultimately spread it to humans.
The virus can contaminate equine food sources since it is shed in bat saliva, urine, and faeces.
Horses can catch the Hendra virus by consuming contaminated food or water or by interacting with infected bats or their bodily fluids.
Horses that have the virus can shed it into their bodily fluids and potentially spread it to people.
Veterinarians and horse trainers are two examples of people who have acquired the Hendra virus via being in close contact with sick animals or their bodily fluids.
It is thought unlikely that the Hendra virus will spread from person to person.
People who work with horses or bats should take steps to minimise virus exposure, such as wearing personal Chest X-Ray protective equipment and avoiding direct contact with sick animals or their bodily fluids, to lessen the risk of transmission.
Horse owners need to be aware of the symptoms and signs of the Hendra virus in horses, and they should get in touch with a vet if they think their horse might be affected.
Signs and symptoms of Hendra Virus in Humans
variety of mild to severe symptoms, such as:
Flu-like illness: Hendra virus infection can produce symptoms such as fever, headache, chills, and muscular pains that are comparable to the flu.
Symptoms of the respiratory system: Hendra virus infection can cause coughing, sore throats, and shortness of breath in certain people.
Neurological signs and symptoms: In some situations, an infection with the Hendra virus can result in neurological signs and symptoms such disorientation, vertigo, and seizures.
Gastrointestinal symptoms: Hendra virus infection may also cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea.
Rapid progression of illness: People infected with the Hendra virus may become gravely ill within a few days after infection.
In severe situations, infection with the Hendra virus can lead to severe respiratory distress, which may necessitate the use of mechanical ventilators to support breathing.
Death: The Hendra virus infection may occasionally result in death. Human infection with the Hendra virus has a 50% death rate.
Precautionary measure to prevent virus infection
Vaccine is not proper cure for the Hendra virus in humans, prevention is the key when it comes to infection. The following precautions can be followed to avoid contracting the Hendra virus:
- Avoid handling bats, and do not come in contact with their saliva, faeces, or urine.
- Reduce your exposure to horses by using personal protection equipment, such as gloves, a mask, and other protective clothing, if you deal with horses.
- Horses who are ill should be isolated, and you should consult a veterinarian right away if you have any reason to believe that a horse may be infected with the Hendra virus.
- After handling horses or other animals, wash your hands carefully with soap and water to maintain proper hygiene.
- Maintain order in your surroundings: Remove any bat urine, droppings, or nesting materials from the area around your home or place of business.
- Use insect repellent to prevent mosquito bites because the Hendra virus can be spread by mosquitoes.
- Learn more about the Hendra virus and infection prevention techniques.
It's important to remember that, although various precautions can aid in lowering the danger of Hendra virus infection, they cannot provide CECT Chest absolute security. Get medical help right away if you suspect you may have been exposed to the Hendra virus or if you are showing symptoms.
Diagnosis of Hendra virus
Various tests that may be carried out, ranging from simple to complex ones, to assist detect Hendra virus infection:
Clinical examination : A clinical examination performed by a medical expert can assist in identifying typical signs of Hendra virus infection, such as fever, headache, muscle aches, and respiratory symptoms.
Blood tests : Blood tests, like complete blood count (CBC) and liver function tests, can assist in identifying any anomalies that may be related to an infection with the Hendra virus.
A laboratory test called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can identify the genetic material (RNA) of the Hendra virus in blood or tissue samples. This examination can establish whether the virus is present in the body.
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, a lab test that can identify antibodies to the Hendra virus in blood samples.
Isolation of the virus: Isolation of the virus entails producing the Hendra virus in a lab environment, which can establish the virus's existence in the body.
Serology is a blood test that can identify Hendra virus antibodies in blood samples.
Immunohistochemistry: In immunohistochemistry, tissue samples are stained with Hendra virus-detectable antibodies. This examination can prove that the virus is present in tissue samples.
It's crucial to keep in mind that not all healthcare facilities may offer these procedures, and certain tests may MRI require several days for findings to be received. Seek emergency medical assistance if you believe you may have been exposed to the Hendra virus or if you are exhibiting symptoms.
Treatment of Hendra virus
The therapy of the disease is centred on supportive care to assist control symptoms and prevent complications because there is presently no particular treatment or cure for Hendra virus infection. Here is a step-by-step manual for treating Hendra virus infection:
Seek emergency medical assistance if you believe you may have been exposed to the Hendra virus or if you are showing symptoms.
If you are found to have the Hendra virus, you will be isolated in order to stop the virus from spreading.
Supportive care will be given to manage symptoms, and may take the form of
- Giving oxygen therapy to people who are having respiratory problems.
- IV fluid administration to avoid dehydration.
- Administering drugs to treat symptoms such as pain, fever, and others.
- Keeping track of vital indications including heart rate and blood pressure.
- Hospitalisation: Individuals with severe Hendra virus infections may need to be admitted for enhanced supportive treatment in an intensive care unit (ICU).
- Avoid complications: Those who have contracted the Hendra virus may be at risk of getting pneumonia or encephalitis.
- To avoid or treat these consequences, preventative steps can be performed, such as giving out antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
Impact of Hendra Virus
A deadly and highly contagious virus, the Hendra virus typically affects horses but can also infect humans when they come into touch with sick animals or their bodily fluids. The Hendra virus can have a negative influence on economic activity as well as the health of humans and animals.
Therefore, the effect of the Hendra virus on public health is a major worry, and work is still being done to create efficient vaccines and treatments for both horses and people. In order to stop further outbreaks of the virus, additional steps are being taken, such as strict quarantine regulations and increased biosecurity practices.
The Hendra virus can have severe effects on both animal and human health, but the measures being made to stop it are also eerily beautiful. The tenacity of those creating vaccines and cures, as well as the concern and commitment of those trying to stop current outbreaks and prevent new ones, are examples of the human spirit at action.
It serves as a reminder that despite the toughest and deadliest viruses, we can band together to defend other living things and guarantee everyone has a better future. Despite the sadness and loss brought on by the Hendra virus, the reaction to this global menace is marked by a sense of hope and unanimity.









