Contrast-based MRI, also known as contrast-enhanced MRI or MRI with contrast, is a type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that uses a special dye or contrast agent to enhance the images produced by the scan.
Contrast-based MRI, also known as contrast-enhanced MRI or MRI with contrast, is a type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that uses a special dye or contrast agent to enhance the images produced by the scan.
The contrast agent is a substance that is injected into the patient's bloodstream before or during the MRI scan. It helps highlight specific areas of the body that may be difficult to see on a regular MRI. Although the cost is a bit higher than normal MRI scan price, it’s still important to go for it many- a- times.
The contrast agent used in MRI scans is typically a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA), which is a type of metallic compound that contains the rare earth element gadolinium. Gadolinium is highly magnetic, and when it is injected into the patient's bloodstream, it interacts with the magnetic field produced by the MRI machine. This creates a signal that can be detected by the scanner, allowing the machine to produce detailed images of the body's internal structures.
Indications for Contrast-Based MRI
Contrast-based MRI is used for a variety of reasons, including:
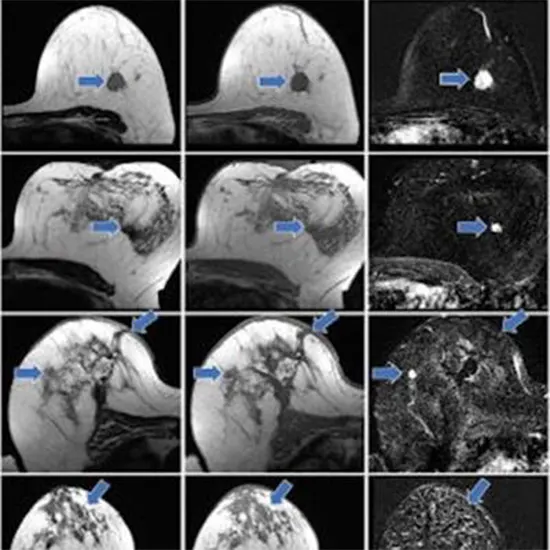
Tumor Detection - Contrast-based MRI can help detect tumors in the brain, breast, liver, and other areas of the body that may be difficult to see on a regular MRI. The contrast agent helps highlight the abnormal tissue, making it easier for doctors to identify and diagnose the tumor.
Inflammation and Infection - Contrast-based MRI can also help detect areas of inflammation or infection in the body, such as in the joints or organs. The contrast agent helps identify areas of increased blood flow, which can indicate inflammation or infection.
Vascular Abnormalities - Contrast-based MRI can be used to visualize the blood vessels in the body, helping detect any abnormalities such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and other vascular diseases.
Liver and Kidney Function - Contrast-based MRI can help evaluate liver and kidney function, as the contrast agent is filtered through these organs and can reveal any abnormalities.
Cardiac Imaging - Contrast-based MRI can be used to image the heart, allowing doctors to evaluate its structure and function. This can be helpful in diagnosing conditions such as heart disease, arrhythmias, and congenital heart defects.
Contra- Indications of Contrast Based MRI
While contrast-based MRI is generally safe, there are certain situations in which it may not be recommended due to the potential risks or complications. These situations are referred to as contraindications and include:
Allergy to the Contrast Agent - Patients who have previously had an allergic reaction to gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) or any of the other ingredients in the contrast agent should not undergo contrast-based MRI.
Kidney Disease - Patients with severe kidney disease or those who are on dialysis may not be able to receive contrast-based MRI, as the contrast agent can potentially cause further kidney damage.
Pregnancy - Contrast-based MRI is generally not recommended for pregnant women, especially during the first trimester, as there is a theoretical risk of harm to the developing fetus.
Breastfeeding - Women who are breastfeeding should not undergo contrast-based MRI, as the contrast agent can pass into breast milk and potentially harm the infant.
Acute Inflammatory Response - Patients with an acute inflammatory response, such as an infection or inflammation, may not be able to undergo contrast-based MRI until the condition is resolved.
Heart Conditions - Patients with certain heart conditions, such as severe heart failure or unstable angina, may not be able to undergo contrast-based MRI due to the potential risks.
Certain Medical Devices - Patients with certain medical devices, such as a pacemaker or cochlear implant, may not be able to undergo contrast-based MRI due to the potential for the magnetic field to interfere with the device.
It is important to inform the healthcare provider of any medical conditions, allergies, or medications ultrasound before undergoing a contrast-based MRI. They can determine whether the procedure is safe and appropriate for the patient and provide alternative imaging options if needed.
In some cases, the risks of the contrast-based MRI may outweigh the benefits, and the healthcare provider may recommend alternative imaging methods, such as non-contrast MRI or ultrasound. It is important to follow the ct scan healthcare provider's recommendations and discuss any concerns or questions before undergoing any medical procedure.
Preparing for Contrast-Based MRI
Before a contrast-based MRI, the patient will need to undergo some preparation, which may include:
Fasting - If the scan is being done on the abdomen, the patient may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for several hours prior to the scan.
Medical History - The patient will need to provide their medical history to the healthcare provider, including any medications they are taking, any allergies they may have, and any previous reactions to contrast agents.
Removing Metal - The patient will need to remove any metal objects from their body, such as jewelry, watches, or hairpins, as metal can interfere with the MRI scan.
Changing Clothes - The patient may need to change into a hospital gown to avoid any clothing containing metal during the scan.
What Happens During the Contrast-Based MRI
Your Position: During the contrast-based MRI, the patient will lie on a narrow table that slides into the MRI machine. The machine is shaped like a tunnel and can be intimidating for some patients. The patient will be given earplugs or headphones to block out the loud tapping and knocking noises produced by the MRI machine.
Procedure: A healthcare professional will then insert a needle into the patient's vein and inject the contrast agent into their bloodstream. The contrast agent may cause a warm sensation in the body, but this is normal and typically passes quickly.
Scanning: The MRI scan will then begin, and the patient will need to remain still throughout the procedure. The scan can take anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the type of images needed.
Risks and Side Effects of Contrast-Based MRI
Contrast-based MRIis generally considered safe, and serious side effects are rare. However, some patients may experience mild to moderate side effects, including:
Nausea - Some patients may feel nauseous or experience a metallic taste in their mouth after receiving the contrast agent.
Allergic Reaction - A small percentage of patients may have an allergic reaction to the contrast agent, which can cause hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
Kidney Damage - In rare cases, the contrast agent can cause damage to the kidneys, particularly in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
Headache - Some patients may experience a mild headache after the MRI scan.
Patients who have pre-existing kidney disease or who are taking certain medications, such as metformin, may be at a higher risk of experiencing kidney damage from the contrast agent. It is important to inform the healthcare provider of any medical conditions or medications before the MRI scan.
Conclusion
Contrast-based MRI is a valuable diagnostic tool that can help healthcare providers detect and diagnose a wide range of medical conditions. The contrast agent helps highlight specific areas of the body, making it easier for doctors to identify abnormalities that may be difficult to see on a regular MRI.
While the procedure is generally safe, patients should be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with contrast-based MRI. It is important to discuss any medical conditions or Nuclear Medicine medications with the healthcare provider free ambulance before the scan and to report any side effects or concerns immediately following the procedure.
Overall, contrast-based MRI can provide healthcare providers with valuable information to help diagnose and treat medical conditions, and can provide patients with peace of mind knowing they are receiving the best possible care.









