
When comparing cow milk to buffalo milk, there are several differences in nutrition and potential health benefits to consider. Here's a breakdown of the differences and which milk might be better suited for your dietary needs
Milk and dairy products are some of the most essential products required daily they are rich in calcium and strengthen the muscles and bones the milk is mainly derived from buffaloes, cow, goat etc and their nutritional profile varies depending upon the breed when we discuss the cow and buffalo milk both have their importance and consumed throughout the world with the cow milk consumed most although the nutrient profile of buffalo milk is highest it contains fats that make it less popular among the people willing to lose weight but there are many milk products like ice cream, yoghurt, cheese etc consumed widely due to their sweet taste and good texture, So let's discuss in this blog about Cow milk vs buffalo milk and differences in nutrition and which will be good for your health.
Sources of Buffalo and Cow Milk
Buffalo milk, belongs to a class of mammals, Bubalus bubalis, India and Pakistan are the major contributors that lead to around 80% of the total buffalo milk production worldwide. Diary buffaloes, seen in the Mediterranean and European continents, produce milk, mainly used to make cheese. Cow milk belongs to a family called Bovidae, usually of the species Bos taurus. Some of the major cow breeds that are reared In India are Sahiwal, Gir, Rathi, Tharparkar, and Red Sindhi etc.
Nutritional Profile: Buffalo milk Vs. Cow Milk
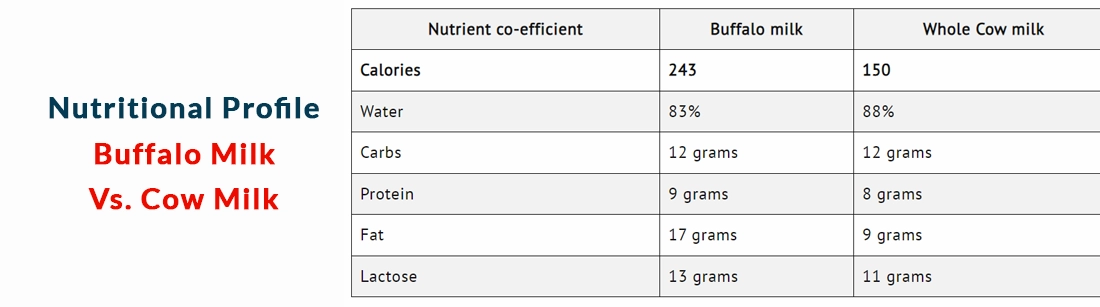
Cow’s milk is packed with nutrients that are filled with (87.4%) and milk solids (12.6%), including vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fat, and protein (casein and whey proteins). The primary carbohydrate is lactose. Buffalo milk contains proteins and unsaturated fatty acids, and is rich in antioxidants compared to cow milk Buffalo milk is highly viscous, which gives it a rich and creamy texture, which makes them perfect for making dairy products like butter, cream, yoghurt, cheese, and ice cream. Below is the table that shows the approximate nutrient and calorie values in 250ml of buffalo and cow milk.
|
Nutrient co-efficient |
Buffalo milk |
Whole Cow milk |
|
Calories |
243 |
150 |
|
Water |
83% |
88% |
|
Carbs |
12 grams |
12 grams |
|
Protein |
9 grams |
8 grams |
|
Fat |
17 grams |
9 grams |
|
Lactose |
13 grams |
11 grams |
The above table shows that buffalo milk contains more protein, fat, and lactose than cow milk. Milk with higher protein content aids in weight management by controlling appetite However, cow milk would be ideal if you are intolerant to lactose and want to decrease the fat intake The nutrient profile of Cow milk and buffalo milk is given in tabulated form below:
|
Nutrients |
Cow’s milk |
Buffalo’s milk |
|
Protein |
3.2-3.3% |
3.8-4% |
|
Fats |
3.5-4.5% |
6-7% |
|
Ash content |
0.72% |
0.82% |
|
Vitamin E |
2.1/100ml |
5.5/100ml |
|
Vitamin C |
0.94/100ml |
3.66/100ml |
|
Vitamin A |
0.14/100ml |
0.12/100ml |
|
Phosphorus |
29% of Daily Value (DV) |
41% of DV |
|
Magnesium |
6% of DV |
19% of DV |
|
Calcium |
32% of DV |
21% of the DV |
Buffalo milk also contains better amounts of vitamin A than cow milk converts beta-carotene (an antioxidant responsible for the yellow colour in cow milk ) into vitamin A
What Are the Health Benefits of Cow Milk and Buffalo Milk

Both cow milk and buffalo milk are packed with nutrients and have a positive impact on the overall health benefits. Buffalo milk can be stored for a longer duration due to its high peroxidase activity but cow milk needs to be consumed fresh within 1-2 days. The Health Benefits of both cow milk and buffalo milk are as follows:
Promotes bone health
Both cow and buffalo milk are rich in calcium that are required for bone growth and development. It also contains casein that improves bone density, bone health, and bone formation and prevents conditions like osteoporosis leads to low bone density, bone weakening, and increased risk of fractures. Buffalo milk contains 89%Casein and cow milk contains 80 % casein of total protein content.
Have Antioxidant properties
Milk is a very rich antioxidant agent that can neutralise the effect of free radicals and prevent oxidative stress that can cause harmful effects on the body. It also contains fat-soluble vitamins like vitamins A and Vitamin E in milk antioxidant properties, making them capable of helping fight many diseases. The antioxidant content in buffalo milk is between 56 and 58% and in cow milk is around 40-42%. Buffalo milk has good antioxidant properties compared to cow milk.
Controls Diabetes and improve heart health
Buffalo milk contains a high quantity of Whey protein and beta-lactoglobulin helps reduce high blood pressure levels they do so by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzymes that increase blood pressure. Buffalo milk also contains potassium that helps lower Blood pressure and the presence of unsaturated fatty acids in buffalo milk helps in lowering the cholesterol level preferred by diabetic people overall improving the High-density Lipoprotein(HDL) and heart health.
Conclusion
As both cow and buffalo milk provide many health benefits to us but going through this blog, we can conclude that Buffalo milk is more beneficial when compared to cow milk as it has rich antioxidant properties and also contains a good amount of fat and protein that aids in weight management and controls the appetite, But if you are lactose intolerant cow milk is the best choice, So consume it accordingly and keep yourself safe and disease free.
FAQs
Why buffalo milk is favoured most?
It contains a good amount of protein, minerals, fats and vitamins that help in controlling the appetite and also has an antioxidant capacity of around 58% making it suitable for consumption.
What if I am lactose intolerant?
If you are lactose intolerant prefer cow milk as it can be digested easily and also provides valuable nutrients to your body.
Which Milk is preferred for Diabetic patients?
Buffalo milk is preferred as it contains beta-lactoglobulin helps reduce high blood pressure levels they do so by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzymes that increase blood pressure thereby reducing the risk of hypertension and promoting heart health.










