Fibroadenomas are generous breast tumors characterized by an admixture of stromal and epithelial tissue. Breasts are made of lobules (drain-creating organs) and conduits (tubes that carry the drain to the areola). These are...
Fibroadenomas are generous breast tumors characterized by an admixture of stromal and epithelial tissue. Breasts are made of lobules (drain-creating organs) and conduits (tubes that carry the drain to the areola). These are encompassed by glandular, sinewy, and greasy tissues. Fibroadenomas are created from the lobules. The glandular tissue and conduits develop over the lobule to create a strong knot.
Since both fibroadenomas and breast protuberances as a sign of breast cancer can show up comparable, it is prescribed to perform ultrasound examinations and conceivably tissue examination with ensuing histopathologic investigation to create a legitimate conclusion. Not at all like commonplace protuberances from breast cancer, fibroadenomas are simple to move, with clearly characterized edges. Fibroadenomas are some of the times called breast mice or breast mice owing to their tall portability within the breast.
Signs and symptoms
Fibroadenomas are kind tumors of the breast, most frequently display in ladies in their 20s and 30s. Clinically, fibroadenomas are ordinarily strong breast knots that are:
- Easy
- Firm or elastic
- Portable
- Solitaire-round with, smooth borders
Individuals who have a basic fibroadenoma have a marginally expanded hazard of creating harmful (destructive) breast cancer. Complex fibroadenomas may increase the chance of breast cancer Within the male breast, fibroepithelial tumors are exceptionally uncommon and are for the most part phyllodes tumors. Outstandingly uncommon case reports exist of fibroadenomas within the male breast, in any case, these cases may be related to antiandrogen treatment.
Causes
The cause of fibroadenoma is obscure (idiopathic). An association between fibroadenomas and regenerative hormones has been recommended which may clarify why they display themselves amid regenerative for a long time, increment in estimate amid pregnancy, and relapse post-menopause.
Higher admissions of natural products and vegetables, a higher number of live births, lower utilization of verbal contraceptives, and direct work out are related to lower recurrence of fibroadenomas.
Cytology
The illustrative findings on needle biopsy include endless stromal cells, which appear as exposed bipolar cores throughout the suction; sheets of relatively uniform-sized epithelial cells, which are typically organized in either a honeycomb pattern or antler-like pattern. These epithelial sheets tend to appear normal metachromatic blue on Diff-Quick recoloring. Froth cells and apocrine cells may be seen, even though these are less symptomatic highlights. The display pictures underneath illustrate these highlights.
Macroscopic
90% of fibroadenomas have a diameter of less than 3cm. In any case, these tumors have the potential to develop to a momentous measure, especially in youthful people. The tumor is round or ovoid, flexible, and nodular, and contains a smooth surface. The cut surface as a rule appears homogeneous and firm and is gray-white or tan in color. The pericanalicular sort (difficult) encompasses a whorled appearance with a total capsule, whereas the intracanalicular sort (delicate) has a deficient capsule.
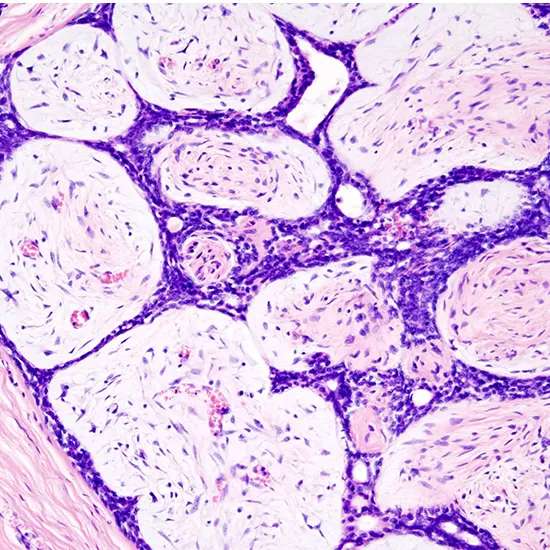
Microscopic
Breast fibroadenoma is a benign tumor made up of stromal and epithelial components that are proliferating neoplastically. There are two growth modes for this biphasic: intracanalicular and pericanalicular (stromal proliferation around epithelial structures) (stromal proliferation compressing the epithelial structures into clefts).
In contrast to malignant neoplasms, these tumors typically exhibit hypovascular stroma. Moreover, the epithelial proliferation characterizes duct-like gaps enclosed by a fibroblastic stroma and manifests as a single terminal ductal unit. Intact is the basement membrane.
An ultrasound, mammogram, clinical examination, and frequently a lump biopsy is used to detect fibroadenomas. A biopsy may be required for a person who has suspicious imaging findings to make a certain diagnosis. Fine-needle aspiration, core-needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy are the three different forms of biopsies. The breast mass's appearance, size, and location all influence the biopsy procedure.
Treatment
As it is normal for fibroadenomas to naturally diminish, the majority are just watched. Regular examinations are necessary for monitoring fibroadenomas to ensure that the breast tumor is not expanding and is not possibly malignant. Physical examinations every three to six months are included in checkups, along with optional diagnostic imaging every six to twelve months for a period of one to two years. Surgery is typically only advised if the fibroadenoma grows larger or results in more severe symptoms. If the preoperative clinical investigations indicate the need for this surgery, they are removed with a narrow margin of healthy breast tissue. If the lesion turns out to be a phyllodes tumor upon microscopic investigation, a tiny portion of healthy tissue must be excised.
Non-invasive Surgical Interventions
Cryoablation, percutaneous microwave ablation, and percutaneous radiofrequency ablation are a few non-invasive methods for the treatment of fibroadenomas. These techniques, which employ cutting-edge medical imaging, do not call for invasive surgery and have the potential for better cosmetic outcomes than traditional surgery.
Cryoablation
In 2001, the FDA approved cryoablation as a secure, efficient, and minimally invasive substitute for open surgical removal of fibroadenomas. Ultrasound imaging is employed during cryoablation to direct a probe into the mass of breast tissue. The aberrant cells are then killed off using extremely low temperatures, and eventually the body absorbs the destroyed cells back into itself. Using local anesthetic, the operation can be done as an outpatient procedure with far less scarring than open surgical procedures and no breast tissue deformation.
The following standards are suggested by the American Society of Breast Surgeons to determine whether a patient is a candidate for cryoablation of a fibroadenoma:
- Sonographically, the lesion must be discernible.
- Histological confirmation of the fibroadenoma diagnosis is required.
- The lesion should be less than 4 cm in diameter.
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) is a more recent technology that has shown excellent results in the total radiological eradication of malignancies in both malignant and benign breast cancers. By elevating the temperature in that region, an ultrasonic beam focused on a target in the breast causes tissue death and protein breakdown. Presently, radiation therapy is advised in some circumstances, although HIFU is not covered by the suggested protocols. Before using HIFU more frequently in fibroadenoma, additional research is needed to determine the technique's utility in this condition.
Epidemiology
Darker-skinned people and women from higher socioeconomic strata are more likely to develop fibroadenomas. It was discovered that the risk of fibroadenomas was negatively correlated with body mass index and the quantity of full-term pregnancies. The frequency of fibroadenomas is not known to be influenced by hereditary factors. The rate of occurrence of fibroadenomas in women has been reported in the literature to range from 7% to 13%.
Fibrocystic breast changes
Fibrocystic breast changes may be a condition of the breasts where there may be torment, breast sores, and breast masses. The breasts may be depicted as "knotty" or "doughy". Indications may compound amid certain parts of the menstrual cycle due to hormonal incitement. These are ordinary breast changes, not related to cancer.
These knots are smooth with well-characterized edges, and free moving regarding adjacent structures. These knots can now and then be darkened by inconsistencies within the breast related to the condition. They are frequently found within the upper, external areas of the breast (closest to the armpit) but can be found all through the breast. Ladies with fibrocystic changes may encounter a tireless or discontinuous throbbing or breast delicacy related to intermittent swelling. Breasts and areolas may moreover be delicate or itchy. Side effects take after an occasional drift closely tied to the menstrual cycle. Indications tend to top within the days to weeks recently each period and diminish a while later. At the top, breasts may feel full, overwhelming, swollen, and delicate to the touch.
Risk factors
Early onset of the first menstrual period and either having children later in life or not at all are risk factors. It is merely an example of typical breast changes and is not a sickness. Diagnosis involves ruling out breast cancer.
Education about the problem, wearing a bra that fits properly, and, if necessary, pain medication may all be part of management. Danazol or tamoxifen may occasionally be used as painkillers. Up to 60% of women are thought to be affected. Most frequently, people between the ages of 30 and 50.
Patho physiology
Although the exact cause of the ailment is not fully understood, it is believed to be linked to hormone-level fluctuations. The condition often subsides after menopause and is intimately connected to the menstrual cycle. Postmenopausal hormone substitution treatments have too detailed indications of fibrocystic breast changes demonstrating hormones may play a major part.
This condition is a collective handle, mostly caused by the ordinary hormonal variation amid a woman's month-to-month cycle. The foremost vital of these hormones incorporate estrogen, progesterone, and prolactin.
These hormones straightforwardly influence breast tissue by causing cells to develop and multiply. Other hormones such as TSH, affront, development hormone, and development variables such as TGF-beta apply both coordinate and circuitous impacts by intensifying or controlling cell development. Inveterate hormonal changes, in the long run, create little blisters and/or ranges of thick or fibrotic tissue over a long time. By the age of 30, multiple small blisters and breast torment may emerge. Bigger sores as a rule don't happen until after the age of 35. Over time, probably driven by abnormal development signals, such injuries may gather epigenetic, hereditary, and karyotypic changes such as altered expression of hormone receptors and misfortune of heterozygosity.
A few variations of fibrocystic breast changes may be recognized and may change in cause and hereditary inclination. Adenosis includes an anomalous check and thickness of lobular units, whereas other injuries show up to emerge from ductal epithelial roots.
There's proof that iodine insufficiency contributes to fibrocystic breast changes by improving breast tissue's affect ability to estrogen.
Diagnosis
This is often an avoidance determination, generally done based on the clinical introduction after administering out breast cancer. Areola liquid desire can be utilized as a classification blister sort strategy (and to a few degrees make strides in breast cancer chance expectation) but is occasionally utilized in the home. Biopsy or fine needle desires are occasionally justified.
Fibrocystic breast malady is fundamentally analyzed based on the indications, clinical breast exam, and physical exam. Amid this examination, the specialist looks for unordinary breast ranges, both outwardly and manually. Moreover, the lymph hubs found within the axilla and lower neck are examined. A total and precise restorative history is additionally supportive within the diagnosing preparation. If the patient's therapeutic history and physical exam discoveries are consistent with ordinary breast changes, no extra tests are required; something else will be inquired to return a couple of weeks afterward for reassessment. Women may identify lumps in their breasts amid self-examination; if this happens it is emphatically prompted to visit well-being proficiently and promptly.
Imaging
To set up whether the knot could be a sore or not, a few imaging tests may be performed, which may incorporate mammography, X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasound considerations. Mammography is usually the primary imaging test to be requested when bizarre breast changes are found amid a clinical breast examination. Asymptomatic mammography comprises an arrangement of X-rays that give clear and specific visualization of regions within the breast.
Ultrasounds and MRIs are commonly performed in conjunction with mammograms as they deliver clear pictures of the breast that recognize between strong masses and fluid-filled breast sores. These can better assess thick breast tissue, particularly in youthful patients under 30.
Biopsy
A breast biopsy is a test utilized to confirm the suspected diagnosis only after imaging tests have as now been performed and uncovered unusual-looking zones. The strategy consists in evacuating a test of breast tissue, which is at that point examined by a pathologist beneath a microscope. The specialist analyzing the tissue test will be able to conclude in case the breast changes are generous or threatening.
Four main sorts of methods for breast biopsy will be performed, including fine-needle, core-needle, stereotactic biopsy, and surgical approach. A fine-needle yearning biopsy is usually requested when the specialist is nearly certain that the protuberance could be sore. This test is generally performed in conjunction with an ultrasound which is supportive in directing the needle into a little or difficult-to-discover knot. The strategy involves embedding a lean needle into the breast tissue whereas the knot is palpated and seen live beneath sonographic ultrasound waves.
The core-needle biopsy is regularly performed beneath neighborhood anesthesia and in a physician's office. The needle utilized in this strategy is somewhat bigger than the one utilized in a fine-needle biopsy since the strategy is planning to expel a little barrel of tissue that will be sent to the research facility for an assistant examination.
A newer sort of breast biopsy method is the stereotactic biopsy which depends on a three-dimensional X-ray to direct the needle to a non-palpable mass. The biopsy is performed comparatively, by employing a needle to evacuate a tissue test, but finding the zone of the breast is done by X-raying the breast from two diverse points. A surgical biopsy is performed to expel the whole lump or a portion of it. It may be difficult and is done under neighborhood anesthesia.