.webp)
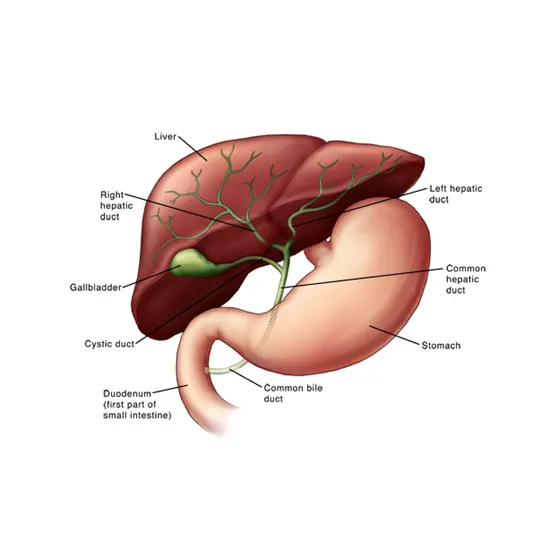
Gallbladder cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid. Gallbladder cancer is relatively rare, and it usually occurs in people...
Gallbladder cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid. Gallbladder cancer is relatively rare, and it usually occurs in people over the age of 65.
Types of gallbladder cancer
The types of gallbladder cancer include:
Adenocarcinoma : This is the most common type of gallbladder cancer and begins in the cells of glandular that line the inside of the gallbladder. It accounts for about 90% of cases.
Squamous cell carcinoma : This type of gallbladder cancer is rare and starts in the thin, flat cells that make up the lining of the gallbladder.
Adenosquamous carcinoma : This is a less common type of gallbladder cancer that contains both glandular and squamous cells.
Small cell carcinoma : This is a very rare and aggressive type of gallbladder cancer that starts in the nerve cells.
Undifferentiated carcinoma : This is a rare and aggressive type of gallbladder cancer that lacks the characteristics of specific cell types.
Stages of gallbladder cancer
The stages of gallbladder cancer are determined based on the size of the tumor, whether it has invaded nearby tissues or organs, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. The most commonly used system for staging gallbladder cancer is the TNM staging system, which stands for Tumor, Nodes, and Metastasis.
The stages of gallbladder cancer are
Stage 0 : This is also known as carcinoma in situ, which means the cancer is confined to the innermost lining of the gallbladder and has not spread to other tissues or organs.
Stage I : Cancer has grown into the connective tissue layer beneath the inner lining of the gallbladder, but has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Stage II : Cancer has invaded the muscle layer of the gallbladder or has spread to nearby organs, such as the liver, pancreas, or intestine.
Stage III : Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or has invaded nearby blood vessels or organs.
Stage IV : Cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the lungs, bones, or brain.
The treatment options and prognosis for gallbladder cancer depend on the stage of cancer, as well as other factors such as the patient's age, overall health, and whether cancer can be completely removed with surgery.
Symptoms of gallbladder cancer
Gallbladder cancer often doesn’t cause any symptoms in its early stage, and when symptoms do appear, they may be vague and easily mistaken for other diseases or conditions. However, as the cancer of the gallbladder progresses, the following symptoms occur:
Abdominal pain : It is the most familiar symptom of gallbladder cancer. This pain is usually located in the upper right side of the abdomen and may be severe and persistent.
Bloating : Some people with cancer of gallbladder cancer may experience bloating or a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Vomiting and Nausea : The symptoms such as nausea and vomiting can occur as a result of cancer blocking the bile ducts, which causes an accumulation of bile in the body.
Appetite Loss : People with cancer of gallbladder may experience an appetite loss problem even after taking a very little quantity of food.
Jaundice : It is a condition where your skin and eyes become yellowish because of an accumulation of bilirubin. The accumulation of bilirubin occurs when cancer blocks the bile ducts and prevents the liver from processing bilirubin properly.
Itchy Skin : Some individuals with gallbladder cancer experience itchy skin due to the build-up of bile salt in the skin.
Unexplained weight loss : Unexplained loss of weight occurs in patients with gallbladder cancer.
Causes of Gallbladder Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of gallbladder cancer development. The factors include:
Age : Cancer of the gallbladder occurs usually in older adults. It is usually diagnosed in patients of the age group of 65 years and more.
Gender : Compare to Men, women are more likely to develop gallbladder cancer.
Gallbladder disease : Individuals with gallbladder diseases may be at high risk of developing cancer of the gallbladder. Because gallbladder-related conditions such as gallstones or chronic gallbladder infections cause gallbladder inflammation, and irritation of the gallbladder and may increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Smoking : Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products may increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Family history : People with a family history of gallbladder cancer are at higher risk of developing the disease.
Diabetes : Individuals with any type of diabetes are at higher risk of being the candidate of cancer of gallbladder.
Chemical exposure : An exposure to specific type of chemicals like nitrosamines, likely to increase the chance of gallbladder cancer occurrence.
_1679742446.webp)
It is worth noting that if you have one or more of the mentioned above causes/ risk factors, that doesn’t mean you will develop the cancer of gallbladder. It can even affect the individual with no risk factor or no family history of gallbladder cancer.
Prevention of Gallbladder Cancer
However, there are several preventive measures you can take to reduce the development of gallbladder cancer such as:
Maintaining a healthy weight : Excessive weight increases the risk of gallbladder cancer. By taking a healthy diet and doing regular exercises you can manage your weight and lower the chance of occurrence of gallbladder cancer.
Consume a Healthy Diet : A healthy diet that is a high quantity of green vegetables, fruits, and whole grains but low in saturated fat helps in reducing the risk of developing cancer of the gallbladder.
Quit Smoking : Smoking cigarettes and using tobacco products increase the gallbladder cancer development risks. To prevent the occurrence of gallbladder cancer it's good to quit smoke.
Manage the gallbladder disease : The conditions such as gallstones, infection, and inflammation of the gallbladder increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. By managing gallbladder-related disease, you can reduce the possibility of the occurrence of Gallbladder cancer.
Limit exposure to chemicals : Exposure to certain chemicals, such as nitrosamines, may increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. If you work in an industry that exposes you to chemicals, then you must follow all safety guidelines to reduce your risk.
Get regular check-ups : Regular check-ups can help detect gallbladder cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you are at increased risk of developing gallbladder cancer, your healthcare provider may recommend regular screenings.
Benefits of early detection of gallbladder cancer
The benefits of early detection of gallbladder cancer cannot be overstated. When gallbladder cancer is detected early, it is more likely to be treatable and may be curable.
Some of the benefits of early detection include:
Better treatment options : If gallbladder cancer is detected early, there are more treatment options available, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. These treatments are more likely to be effective if the cancer is caught early.
Improved chances of survival : When gallbladder cancer is detected early, the chances of surviving the disease are much higher. In fact, the 5-year survival rate for people with early-stage gallbladder cancer is around 80%, compared to around 5% for people with advanced-stage cancer.
Less invasive treatments : If gallbladder cancer is detected early, less invasive treatments may be possible. For example, if the cancer is caught early enough, it may be possible to remove the gallbladder through a minimally invasive procedure known as laparoscopic surgery.
Reduced risk of complications : When gallbladder cancer is detected early, there is a lower risk of complications such as jaundice, infection, and liver failure.
Improved quality of life : Early detection and treatment of gallbladder cancer can help improve quality of life by reducing symptoms and allowing people to maintain their normal activities.
Diagnostic procedures for gallbladder cancer
There are several diagnostic procedures that may be used to diagnose gallbladder cancer. These include:
Blood tests : Blood tests such as Liver Function Test, Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) assay, CA 19-9 assay etc. may be used to detect elevated levels of certain proteins or enzymes that are associated with gallbladder cancer.
Biopsy : A biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from the gallbladder for examination under a microscope. This test can help confirm the presence of cancer cells in the gallbladder.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) : ERCP is a procedure that uses a long, flexible tube with a camera on the end to examine the bile ducts and gallbladder. This test can help identify blockages or abnormalities that may be indicative of gallbladder cancer.
Imaging tests : Imaging tests, such as abdominal ultrasound, CT whole abdomen scan, MR Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Scan and whole body pet scan, can be used to create detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures. These tests can help identify abnormalities, such as tumors or cysts, that may be indicative of gallbladder cancer.
The specific diagnostic procedures used will depend on the individual's symptoms, medical history, and other factors. If you are concerned about the possibility of gallbladder cancer, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider to determine which diagnostic tests may be necessary.
Conclusion
An early detection of gallbladder cancer can lead to better treatment options, improved chances of survival, less invasive treatments, reduced risk of complications, and improved quality of life. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about any concerns you may have and to undergo recommended screening tests if you are at increased risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Ganesh Diagnostic offers gallbladder cancer screening package for early detection of the gallbladder cancer. For any query regarding the diagnostic procedure or to schedule your appointment, you can contact to our healthcare executives 24x7.









