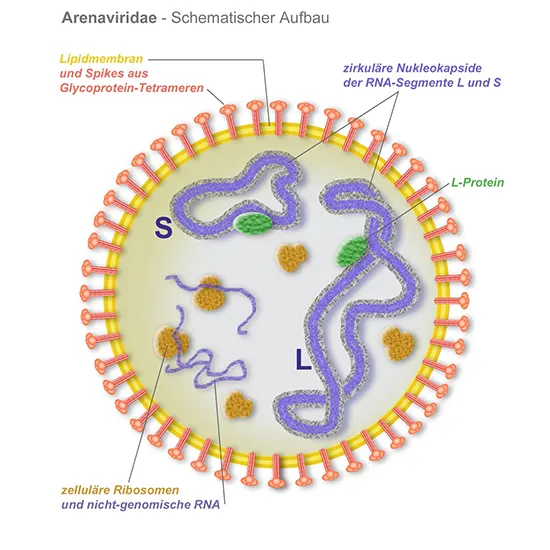
Junin virus is a pathogenic virus that belongs to the household Arenaviridae, and it is the causative agent of Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF). The virus was once first recognized in 1958, in the Junin Province of Argentina,...
Junin virus is a pathogenic virus that belongs to the household Arenaviridae, and it is the causative agent of Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF). The virus was once first recognized in 1958, in the Junin Province of Argentina, therefore the title Junin virus.
AHF is a doubtlessly deadly sickness that can cause extreme signs such as fever, malaise, muscle aches, gastrointestinal symptoms, hemorrhagic manifestations, and neurological symptoms.
The virus is transmitted to human beings via publicity to the urine or faeces of contaminated rodents, especially Calomys musculus. The sickness is endemic to positive areas of Argentina, with sporadic outbreaks taking place every few years. There is presently no particular therapy or vaccine for the Junin virus, making it a massive public fitness problem in affected areas.
What is Junin Virus?
Junin virus is a pathogenic virus that belongs to the Arenaviridae family, and it is the causative agent of Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF). The virus was once first recognized in 1958, in the Junin Province of Argentina, and it especially impacts people and rodents.
It is transmitted to people through publicity to the urine, saliva, or faeces of contaminated rodents, chiefly Calomys musculus. Junin virus can cause an extensive range of symptoms, along with fever, malaise, muscle aches, gastrointestinal symptoms, hemorrhagic manifestations, and neurological symptoms.
Explore the Epidemiological Facts of Junin Virus
Junin virus is particularly discovered in certain areas of Argentina, which include the provinces of Buenos Aires, Cordoba, La Pampa, San Luis, and Santa Fe.
The virus is transmitted to human beings through publicity to the urine and faeces of contaminated rodents, notably Calomys masculine, which is the main reservoir for the virus.
People who live or work in rural areas or are worried about agriculture, such as farmers and farm workers, are in higher danger of infection.
The ailment is endemic to the affected regions, and sporadic outbreaks of Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF) take place every few years.
The incidence of AHF has reduced over the years, thanks to elevated surveillance, management of rodent populations, and public fitness schooling campaigns.
However, outbreaks nevertheless occur, and the disorder remains a sizable public fitness difficulty in affected areas. There have additionally been reviews of imported instances of AHF in different countries, commonly in humans who have travelled to the affected areas in Argentina or who have had contact with contaminated individuals.
Various Causes of Junin Virus
Junin virus is brought on via contamination with the Junin virus, which is a member of the Arenaviridae family. The virus especially infects rodents, in particular the Calomys musculus species, which serves as the most important reservoir for the virus.
The virus is transmitted to human beings through publicity to the urine, saliva, or faeces of contaminated rodents. This can manifest through direct contact with contaminated surfaces or objects, inhalation of aerosolized rodent excreta, or consumption of contaminated meals or water.
Person-to-person transmission can additionally occur, especially through contact with blood or different bodily fluids of contaminated individuals. This can appear at some stage in clinical techniques or through contact with contaminated individuals, such as household individuals or healthcare workers.
The virus can cause Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF), which can vary from slight to extreme and doubtlessly fatal. The severity of the disorder can differ relying on the individual's immune machine response and different factors.
There is presently no precise cure or vaccine for the Junin virus, making prevention, manipulation of rodent populations, and public fitness schooling campaigns vital for lowering the chance of infection.
Pathophysiology of Junin Virus
Junin virus is an enveloped RNA virus that notably ambitions endothelial cells and macrophages. Once the virus enters the body, it replicates in these cells and causes harm to the endothelial lining of blood vessels, resulting in expanded vascular permeability and leakage of fluid into the surrounding tissues.
This leads to the attributed hemorrhagic manifestations of Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF), such as bleeding from the gums, nose, and gastrointestinal tract. In addition to endothelial damage, the Junin virus additionally causes harm to the immune system, in particular to the lymphoid tissue and lymphocytes, mainly to immunosuppression.
This can make sufferers extra inclined to secondary bacterial infections, which can in addition complicate the route of the disease. The virus additionally motivates injury to different organ systems, such as the liver, kidney, and respiratory systems. In extreme cases, sufferers can strengthen a couple of organ failures, which can be fatal.
The pathophysiology of Junin virus contamination is complicated and includes an aggregate of direct viral damage, immune-mediated damage, and coagulation abnormalities. Further, lookup is wanted to completely apprehend the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Junin virus contamination and AHF.
How is Diagnosis of Junin Virus Done?
Diagnosis of Junin virus contamination is usually primarily based on medical symptoms, records of publicity to contaminated rodents, and laboratory testing.
Because early signs and symptoms of Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF) are comparable to those of many different viral illnesses, a thorough scientific record and bodily examination are essential for ruling out different possible causes.
Laboratory testing for the Junin virus consists of serological tests, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which can notice antibodies to the virus in a patient's blood.
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain response (RT-PCR) can additionally be used to notice viral RNA in blood or tissue samples.
In addition to these diagnostic tests, different laboratory exams may additionally be carried out to consider the severity of the disease, such as a Prothrombin time, Activated partial thromboplastin time, Clotting time, whole blood count, liver characteristic tests, and coagulation studies.
It is vital to notice that laboratory checking for Junin virus contamination is generally solely carried out in specialized laboratories, and samples need to be treated cautiously to keep away from illness and ensure the accuracy of results.
Clinical administration of sufferers suspected of having AHF have to be guided by skilled healthcare experts with information on the analysis and cure of viral hemorrhagic fevers.
Possible Complications of Junin Virus
Complications of Junin virus infection, which causes Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF), can be extreme and probably life-threatening.
Some of the problems that can take place with AHF include
Hemorrhagic manifestations
Patients with AHF can ride bleeding from a variety of sites, which include the gums, nose, and gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to anaemia, shock, and even death.
Neurological symptoms
In extreme instances of AHF, sufferers can ride neurological signs such as confusion, seizures, and coma.
Multiple organ failure
AHF can cause harm to a couple of organ systems, such as the liver, kidneys, and respiratory systems. This can lead to a couple of organ failures, which can be fatal.
Secondary bacterial infections
Patients with AHF are at risk of creating secondary bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, which can complicate the path of the disorder and enlarge the chance of death. It is essential to observe that issues of Junin virus contamination can differ depending on the individual's immune gadget response, age, and underlying fitness conditions.
Patients with extreme or intricate AHF require intensive supportive care, which may also encompass hospitalization, intravenous fluids, blood transfusions, and different remedies to control signs and forestall complications.
Treatment Options Available for Junin Virus
There is presently no unique treatment or vaccine for Junin virus contamination or Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF).
Management of sufferers with AHF is principally supportive, aimed at treating signs and symptoms and stopping complications.
Patients with extreme or intricate AHF require hospitalization in an isolation ward, a place where they can be monitored carefully and acquire intensive supportive care.
Supportive care may additionally consist of intravenous fluids, blood transfusions, oxygen therapy, and remedy for secondary bacterial infections.
Patients with extreme bleeding can also require transfusions of clotting elements or platelets.
Experimental remedies for AHF are being developed, which include the use of antiviral tablets and monoclonal antibodies, however, these remedies are nevertheless in the early tiers of improvement and have no longer been authorized for movements medical use.
Prevention of Junin virus contamination is essential, and management of rodent populations, perfect storage and disposal of food, and private defensive measures, such as carrying gloves and masks, can assist limit the danger of infection.
Public fitness training campaigns are additionally vital for elevating cognizance of the disorder and promotion of prevention measures in affected communities.
In conclusion, the Junin virus is a viral contamination that is transmitted to people via contact with contaminated rodents or their excreta.
Prevention of Junin virus contamination is essential, and public fitness schooling campaigns and management of rodent populations are essential for lowering the chance of infection.
Racing Against Time : Let's Fight against Junin Virus!
















