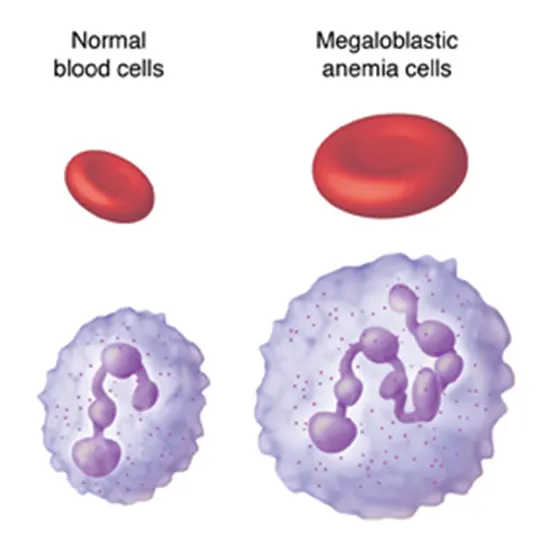
A condition in which the blood doesn't have sufficient sound ruddy blood cells. Frailty comes about from a need for ruddy blood cells or broken ruddy blood cells within the body. This leads to a diminished oxygen...
Anemia
A condition in which the blood doesn't have sufficient sound ruddy blood cells. Frailty comes about from a need for ruddy blood cells or broken ruddy blood cells within the body. This leads to a diminished oxygen stream to the body's organs.
Megaloblastic Anemia
Megaloblastic iron deficiency may be a sort of macrocytic frailty. Frailty may be a ruddy blood cell deformity that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic frailty comes about from the hindrance of DNA blend amid ruddy blood cell production. When DNA amalgamation is disabled, the cell cycle cannot advance from the G2 development organized to the mitosis (M) organize. This leads to proceeding cell development without division, which presents as macrocytosis. Megaloblastic iron deficiency includes a or maybe moderate onset, particularly when compared to that of other anemias. The imperfection in ruddy cell DNA amalgamation is most regularly due to hypovitaminosis, particularly vitamin B12 lack or folate insufficiency. Misfortune of micronutrients may moreover be a cause.
Megaloblastic frailty not due to hypovitaminosis may be caused by antimetabolites that harm DNA generation straightforwardly, such as a few chemotherapeutic or antimicrobial operators (for case azathioprine or trimethoprim).
The neurotic state of megaloblastic is characterized by numerous expansive youthful and broken ruddy blood cells (megaloblasts) within the bone marrow conjointly by hypersegmented neutrophils (characterized as the presence of neutrophils with six or more flaps or the nearness of more than 3% of neutrophils with at least five lobes).[4] These hypersegmented neutrophils can be detected within the fringe blood
What is another title for megaloblastic frailty? Megaloblastic anemia could be a frame of macrocytic iron deficiency. Macrocytic iron deficiency may be a blood disorder that causes your bone marrow to form strangely large red blood cells. It's moreover a sort of vitamin insufficiency or iron deficiency.
Malignant iron deficiency may be a sort of megaloblastic frailty in which the body isn't able to assimilate vitamin B12 due to a need for a natural appearance in stomach discharges. The natural calculation is required for the body to assimilate vitamin B12.
What sort of RBC is megaloblastic iron deficiency? Megaloblasts are expansive nucleated ruddy blood cell (RBC) antecedents with noncondensed chromatin due to a disabled DNA blend. Macrocytes are extended RBCs (ie, cruel corpuscular volume [MCV] > 100 fL/cell). Macrocytic RBCs happen in an assortment of clinical circumstances, numerous disconnected from megaloblastic development.
The indications displayed in each person can shift incredibly. Extra common symptoms include throbs and pains, muscle shortcomings, and trouble breathing (dyspnea). People with megaloblastic frailty may to create gastrointestinal abnormalities including runs, queasiness, and misfortune of craving.
Causes
Vitamin B12 insufficiency:
- Achlorhydria-induced malabsorption
- Insufficient admissions
- The insufficient inherent figure, a particle delivered by cells within the stomach that's required for B12 retention (vindictive frailty or gastrectomy)
Coeliac infection
Natural competition for vitamin B12 by diverticulosis, fistula, intestinal anastomosis, or contamination by the marine parasite Diphyllobothrium latum (angle tapeworm)
- Specific vitamin B12 malabsorption (congenital—juvenile megaloblastic iron deficiency 1—and drug-induced)
Constant pancreatitis
- Ileal resection and bypass Nitrous oxide anesthesia (more often than not requires rehashed occasions).
Folate lack:
- Liquor addiction
- Lacking admissions
Expanded needs:
- pregnancy, newborn child, fast cellular expansion, and cirrhosis Malabsorption (intrinsic and drug-induced) Intestinal and jejunal resection (backhanded) Insufficient thiamine and components (e.g., chemicals) capable of irregular folate digestion system.
Combined Lack:
- vitamin B12 & folate.
Acquired Pyrimidine Union Clutters:
- Orotic aciduria Acquired DNA Amalgamation Disarranges
Poisons and Drugs:
- Folic corrosive adversaries (methotrexate) Purine amalgamation opponents (6-mercaptopurine, azathioprine) Pyrimidine enemies (cytarabine) Phenytoin
- Nitrous Oxide
- Erythroleukemia
- Innate hereditary transformations of the Methionine synthase quality
- Di Guglielmo's disorder is Inherent dyserythropoietic iron deficiency.
Copper lacks coming about from an abundance of zinc from curiously tall verbal utilization of zinc-containing denture-fixation creams is a cause.
Pathophysiology
There's a deformity in DNA blend within the quickly isolating cells and to a lesser degree, RNA and protein amalgamation are too impeded. In this manner, lopsided cell multiplication and disabled cell division happen because of captured atomic development so the cells appear nuclear-cytoplasmic asynchrony.
Within the bone marrow, most megaloblasts are devastated earlier to enter the fringe blood (intramedullary hemolysis). A few can elude the bone marrow (macrocytes) to fringe blood, but they are devastated by the reticuloendothelial framework (extramedullary hemolysis).
Diagnosis
The gold standard for the determination of Vitamin B12 lack may be a moo blood level of Vitamin B12. A moo level of blood Vitamin B12 may be a finding that ordinarily can and ought to be treated by infusions, supplementation, or dietary or way-of-life counsel, but it isn't a conclusion.
Hypovitaminosis B12 can result from several components, counting those recorded over. For assurance of cause, advanced persistent history, testing, and experimental treatment may be clinically indicated.
An estimation of methylmalonic corrosive (methylmalonate) can give a circuitous strategy for in part separating Vitamin B12 and folate lacks. The level of methylmalonic corrosive isn't hoisted in folic acid lack. Coordinate estimation of blood cobalamin remains the gold standard since the test for raised methylmalonic corrosiveness isn't particularly sufficient. Vitamin B12 is one fundamental prosthetic bunch to the protein methyl malonyl-coenzyme A mutase. Vitamin B12 insufficiency is but one among the conditions that can lead to the brokenness of this chemical and a buildup of its substrate, methylmalonic corrosive, the raised level of which can be recognized within the pee and blood.
Due to the need for accessible radioactive Vitamin B12, the Schilling test is present to a great extent an authentic artifact. [citation needed] The Schilling test was performed in the past to assist in determining the nature of vitamin B12 insufficiency. An advantage of the Schilling test was that it frequently included Vitamin B12 with the intrinsic figures.
Blood findings
The blood film can point towards vitamin lack: Diminished ruddy blood cell (RBC) tally and hemoglobin levels.
Expanded cruel corpuscular volume (MCV, >100 fL) and cruel corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
Ordinary cruel corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC, 32–36 g/dL)
Diminished reticulocyte number due to pulverization of delicate and anomalous megaloblastic erythroid forerunner.
The platelet count may be decreased.
Neutrophil granulocytes may appear as multi-portioned cores ("decrepit neutrophil"). Usually thought to be due to diminished generation and a compensatory delayed life expectancy for circulating neutrophils, which increment numbers of atomic fragments with age. [citation required]
Anisocytosis (expanded variety in RBC estimate) and poikilocytosis (unusually molded RBCs).
Macrocytes (bigger than ordinary RBCs) are displayed.
Ovalocytes (oval-shaped RBCs) are shown. Howell-Jolly bodies (chromosomal remainders) too show.
Blood chemistries will moreover appear:
- An expanded lactic corrosive dehydrogenase (LDH) level. The isozyme is LDH-2 which is normal for the serum and hematopoietic cells. Expanded homocysteine and methylmalonic corrosive in Vitamin B12 lack.
- Expanded homocysteine in folate lack.
- Typical levels of both methylmalonic corrosive and add up to homocysteine run the show of clinically critical cobalamin insufficiency with virtual certainty.
- Bone marrow (not ordinarily checked in a persistent suspected of megaloblastic iron deficiency) appears megaloblastic hyperplasia.
Who is at risk for megaloblastic anemia?
People who don't eat meat, eggs, or dairy may have an expanded hazard of megaloblastic iron deficiency due to a need for vitamin B12. A 2014 survey detailed an 80% predominance of vitamin B12 insufficiency in populaces in India and Hong Kong, where veggie lovers don't regularly eat B12-fortified nourishments or utilize supplements.
What is the hemoglobin level for megaloblastic frailty?
An assessment for megaloblastic frailty is regularly incited by CBC. CBC discoveries may incorporate frailty (hemoglobin 100 fL).
What is the administration of megaloblastic frailty?
Folate Treatment In expansion, the quiet ought to devour a folate-enriched eat less. The measurement run for folate is 1 to 5 mg every day; 1 mg/d is the regular dose for adults with megaloblastic frailty, whereas a better dose is shown in hemolysis, malabsorption, liquor addiction, and exfoliative dermatitis.
What is MCV in megaloblastic frailty?
Macrocytic frailty with expanded cruel corpuscular volume (MCV), characterized as more than 100 fL, is the trademark of megaloblastic frailty, but leukopenia and thrombocytopenia are too regularly shown.
Why do platelets diminish in megaloblastic frailty?
It may result from many instruments such as marrow hypoplasia (diminished megakaryocytes), incapable thrombopoiesis (ordinary to expanded megakaryocytes), and expanded annihilation of platelets (expanded megakaryocytes)
Why does MCV increment in megaloblastic iron deficiency?
The foremost common cause of macrocytic iron deficiency is megaloblastic frailty, which is the result of impeded DNA union. Even though DNA amalgamation is disabled, RNA amalgamation is unaffected, driving a buildup of cytoplasmic components in a gradually separating cell. This comes about in a larger-than-normal cell.
Which natural product is wealthy in vitamin B12?
Bananas are a cheap, solid, and nutrient-dense natural product that can effortlessly end up a portion of everyone’s slim down. It is one of the leading natural products rich in vitamin B12. Bananas moreover contain fiber and potassium. It makes a difference to oversee blood weight, diminishing push, and calming obstruction and ulcer issues.
Why is MCH typical in megaloblastic frailty?
Abandons in atomic development, as seen in megaloblastic anemias due to folate or B12 insufficiency, result in huge oval erythrocytes (macroovalocytes) with an ordinary hemoglobin substance. The MCV and MCH are expanded, whereas the MCHC remains typical.
What is the relationship between MCV and B12?
The MCV can be utilized to form the determination of B12 lack more--or less--probable. A hoisted MCV legitimizes the estimation of serum B12. The MCV ought to not be used as the as it were parameter in administering the diagnosis of B12 insufficiency.
What is the avoidance of megaloblastic iron deficiency?
Anticipation of megaloblastic iron deficiency may not be conceivable, but you'll be: able to make changes within your way of life. eat vegetables and natural products that contain vitamin B-12 and folic corrosive; not drinking liquor, stop smoking, diminish drinking liquor.
Which iron deficiency MCV is expanded?
Macrocytic iron deficiency may be a sort of frailty where the normal ruddy blood cell volume is bigger than ordinary. Macrocytic frailty is assisted sub-categorized as megaloblastic or non-megaloblastic.
What is the foremost common cause of tall MCV?
Tall cruel corpuscular volume (MCV), moreover known as macrocytosis, is related to vitamin B12 and folic corrosive insufficiency, liver malady, hyperglycemia, liquor addiction, smoking propensities, and other pathologic conditions.
Why does MCH increase in macrocytic iron deficiency?
High MCH scores are commonly a sign of macrocytic iron deficiency. This condition happens when the blood cells are as well enormous, which can be a result of not having sufficient vitamin B12 or folic corrosive within the body. High MCH scores may too be the result of the taking after liver illnesses.
What is the treatment for MCV lack?
The primary line of treatment for many individuals is correcting supplement deficiencies. This will be done with supplements or foods like spinach and ruddy meat. You will be able to require supplements that include folate and other B vitamins. You will to require vitamin B-12 infusions in case you do not retain verbal vitamin B-12 appropriately.
What vitamins influence MCV?
The comes about uncovering that vitamin B12 deficiency would increment MCV. Out of 868 patients who were vitamin B12 insufficient 10.36% had tall MCV (>100 fL). 13.13% had moo MCV (<80 fL) and 76.49% were with typical values of MCV (80 - 100 fL)
Is macrocytic frailty caused by liver infection?
There are a few potential obsessive components that clarify why macrocytic iron deficiency is related to the seriousness of liver impedance. To begin with, patients with progressed liver harm are more likely to have vitamin B12 or folate insufficiencies, which straightforwardly result in macrocytic iron deficiency.
What are the side effects of tall MCV?
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) may be esteem related to your ruddy blood cells. A normal MCV score is between 80 and 95. If the MCV goes up to an extraordinary 125, it may demonstrate vitamin B12, folate lacks, or cold agglutinin disease.
What are the indications of high MCV and MCH?
If you've got more MCH esteem, you'll encounter the taking-after indications: shortness of breath, chest torment, quick pulse, weariness, or shortcoming, and exceptionally pale or yellowish skin. cerebral pain.
What disease causes low MCV?
Low MCV implies that RBCs are littler than typical and may demonstrate microcytic iron deficiency. This condition may be caused by press insufficiency, lead harming, or thalassemia, a hereditary condition that causes your body to have less hemoglobin than typical.
Does low MCV cause liver infection?
Results may indicate that MCV levels are tall, or that ruddy blood cells are as well expansive, or moo, which implies that ruddy blood cells are littler than normal. More MCV levels may demonstrate a condition like liver illness or a vitamin lack, whereas moo MCV levels are commonly related to iron insufficiency iron deficiency.









