Anaplasma may be a sort of microscopic organism of the alphaproteobacteria Rickettsiales, family Anaplasmataceae. Anaplasma species dwell in blood cells and lead to the malady anaplasmosis.
Anaplasma may be a sort of microscopic organism of the alphaproteobacteria Rickettsiales, family Anaplasmataceae.
Anaplasma species dwell in blood cells and lead to the malady anaplasmosis. The infection most commonly happens in ranges where competent tick vectors are inborn, counting tropical and semitropical ranges of the world for intraerythrocytic Anaplasma spp.
Anaplasma species are organically transmitted by Ixodes deer-tick vectors, and the prototypical species, A. marginale, can be mechanically transmitted by gnawing flies and iatrogenically with blood-contaminated disobedience. One of the major results of disease by bovine ruddy blood cells by A.
Marginale is the improvement of nonhaemolytic frailty, hence the nonattendance of hemoglobinuria, which permits clinical separation from another major tick-borne illness, bovine babesiosis, caused by Babesia bigemina.
Species of Anaplasma intrigued incorporate:
- Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma centrale in cattle
- Anaplasma ovis and Anaplasma mesaeterum in sheep and goats.
- Anaplasma phagocytophilum in pooches, cats, and steeds (see human granulocytic anaplasmosis)
- Anaplasma platys in pooches
- The Anaplasma sparouinense species is mindful of an uncommon zoonosis, the Sparouine anaplasmosis, recognized as it were in French Guiana, South America.This illness was portrayed from a surreptitious gold mineworker working deep in rainforest. Contamination of his ruddy blood cells drove to a serious weakening of his well being and required his hospitalization.
- Atomic writing appeared that Anaplasma sparouinense is particular to all known species and more hereditarily related to as of late depicted Anaplasma species causing contaminations in rainforest wild fauna of Brazil.
Anaplasmosis could be a tick-borne malady influencing ruminants, pooches, and steeds, and is caused by Anaplasma microbes. Anaplasmosis is an irresistible but not infectious malady. Anaplasmosis can be transmitted through mechanical and natural vector forms. Anaplasmosis can too be alluded to as "yellow sack" or "yellow fever" since the tainted creature can create an embittered see. Other signs of contamination incorporate weight misfortune, the runs, pallor of the skin, forceful behavior, and tall fever.
Morphology
There are numerous strains of Anaplasma marginale, all with contrasting morphology, antigenic properties, protein arrangement, and capacity to be transmitted by ticks. Major surface proteins (MSP) have been found to play a major part within the disease by Anaplasma marginale.
Out of the six MSP found on this species, three of the major surface proteins don't appear to contrast between all strains, those counting MSP1a, MSP4, and MSP5. The msp1a quality, which codes for MSP1a, is utilized as a marker for the distinguishing proof of Anaplasma marginale since it has appeared to be moderated within the duplication of rickettsia in cattle and ticks and has been appeared to be included in grip to bovine erythrocytes and tick cells.
Anaplasma phagocytophilum is a gram-negative bacterium that does not have lipopolysaccharides or peptidoglycan. The external layer does not have a capsule, and is coarse with sporadic periplasmic spaces. This species was initially included within the genus Ehrlichia (Ehrlichia phagocytophilum), but is presently included within the sort Anaplasma (Anaplasma phagocytophilum)
Transmission
Mechanical and organic vector transmission work in numerous ways but both lead to disease of the ruddy blood cells. Mechanical transmission happens in two ways, one when ruddy blood cells are immunized with the blood parasite through surgical equipment counting needles, dehorners, ear taggers, castrating blades, and tattoo disobedience. Another mechanical transmission mode is through the mouthparts of biting flies who carry an Anaplasma species of blood parasite.
Organic vector transmission is through ticks that carry a blood parasite able to cause anaplasmosis. The most common Anaplasmosis-causing tick is Ixodes scapularis, moreover known as the black-legged tick or the deer tick.Ticks who contain species of numerous distinctive Anaplasma species can transmit this disease through a nibble.
The blood parasite survives and can increase within the tick, and can sit torpid for months without being transmitted to any creature. When nibbled by a tick carrying a blood parasite, the blood parasite can at that point enter the modern have and cause contamination.
Signs and Indications
Signs and symptoms of anaplasmosis ordinarily start inside 1–2 weeks after the bite of a contaminated tick.
Tick chomps are more often than not painless, and numerous individuals don't remember being nibbled.
See your healthcare supplier in the event that you end up sick after having been bitten by a tick or having been within the woods or in regions with tall brush where ticks commonly live.
Early Ailment
Early signs and side effects (days 1-5) are usually mellow or direct and may incorporate:
- Fever, chills
- Serious cerebral pain
- Muscle throbs
- Queasiness, vomiting, diarrhea, misfortune of craving
Late Ailment
Once in a while, on the off chance that treatment is postponed or in case there are other therapeutic conditions present, anaplasmosis can cause extreme sickness. Incite treatment can diminish your chance of creating extreme sickness.
Signs and indications of extreme (late arrange) sickness can incorporate:
- Respiratory disappointment
- Dying issues
- Organ disappointment
- Death
Chance components for extreme ailment:
Postponed treatment
Age:
Being older puts you at hazard
Debilitated safe framework:
Individuals with debilitated safe frameworks (such as those accepting a few cancer medications, people with progressed HIV contamination, earlier organ transplants, or individuals taking some drugs) are at hazard for extreme ailment
Diagnosis and Testing
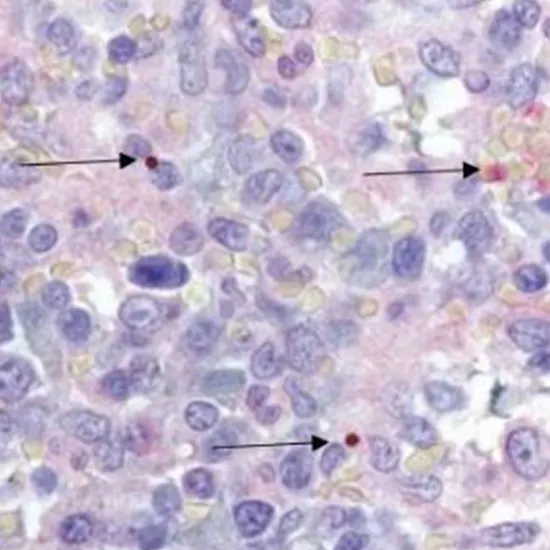
Your healthcare supplier can arrange certain blood tests such as CBC, Peripheral blood smear, Immunohistochemistry (IHC) etc. to hunt for prove of anaplasmosis or other ailments that cause comparable side effects.
Test results may take a few weeks.
In case your healthcare supplier considers you've got anaplasmosis, or other tickborne disease, he or she may prescribe antibiotics whereas you hold up for test comes about.
Treatment
The foremost common source of treatment is the utilize of tetracycline drugs (counting tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline, rolitetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline) and imidocarb. An infusion of tetracycline drugs can give ruminants insusceptibility to Anaplasma species for at least eight months. Imidocarb has appeared to be profoundly viable against Anaplasma marginale, but has been recognized as a possible carcinogen and isn't affirmed within the United States or Europe. Nations such as South Africa, Australia, Israel, and South America have utilized live immunizations containing irresistible Anaplasma centrale to anticipate disease of Anaplasma marginale.
Live antibodies are disallowed within the Joined together States, and there has been production of immunizations comprising of nonliving Anaplasma marginale pulled from infected bovine erythrocytes, which can give a few resistance but takes off cattle susceptible to other strains of Anaplasma marginale.Supportive therapy such as blood items and liquids may be vital.
Anticipation
Right now, no live or inactivated immunizations have been endorsed by the USDA that are viable against all strains of A. marginale. A few immunizations that depend on erythrocyte-derived antigen sources give immunity or avoid clinical illness, although these don't avoid cattle from being contaminated with A. marginale. Other implies of avoidance can incorporate testing all ruminants in a crowd and dispensing with any people who test positive for anaplasmosis, driving to an anaplasmosis-free crowd.
Vector control measures can too be used. Tick control is broadly utilized in a few nations, counting Africa, but seldom utilized within the United States due to the reality that this prevention method is labor-intensive and costly. In contrast, the control of flies is compelling and there are numerous ways to do this. Chemical operators can be used, sanitation methods (such as cleaning stalls/pens frequently, fertilizer administration, and securing nourish), as well as organic control by characteristic foes of flies (counting bees, vermin, parasitoids).
Ways to avoid iatrogenic transmission incorporate avoiding re-using of needles and sanitizing restorative hardware between employment. Antimicrobial treatment can moreover be utilized, in spite of the fact that it is more commonly used within the case of dynamic contamination.









