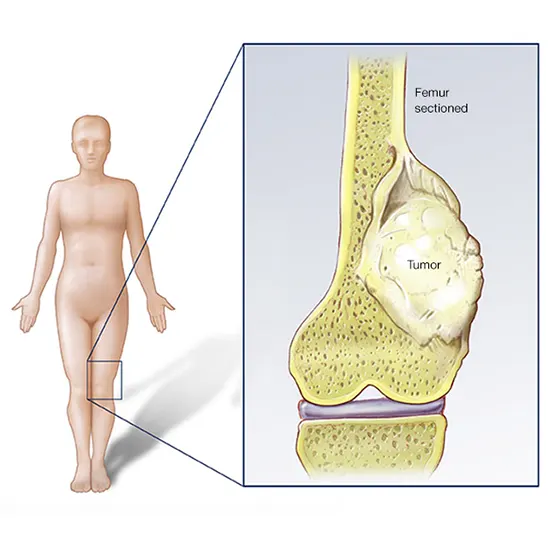
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the foremost common essential threatening bone tumor. It is additionally the third most common sort of cancer influencing children and teenagers after lymphomas and brain tumors. OS cells determine from...
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) (or essentially bone cancer) might be a cancerous tumor in a bone.
Particularly, it is a forceful dangerous neoplasm that emerges from primitive changed cells of mesenchymal root (and hence a sarcoma) which shows osteoblastic differentiation and produces dangerous osteoid.
Osteosarcoma is the foremost common histological frame of essential bone sarcoma. It is most predominant in young people and youthful adults.
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the foremost common essential threatening bone tumor. It is additionally the third most common sort of cancer influencing children and teenagers after lymphomas and brain tumors. OS cells determine from mesenchymal ancestry and can create osteoid substances and/or youthful bone.
The hazard of osteosarcoma is most elevated for those between the ages of 10 and 30, particularly amid the young development spurt. This proposes there may be a connection between fast bone development and the chance of tumor arrangement. The chance goes down in center age but rises once more in more seasoned grown-ups (more often than not over the age of 60)
Signs and Symptoms
Numerous patients begin with complaints of torment which will be more awful at night may be discontinuous and of changing concentration and may have been happening for a long time. Youngsters who are dynamic in sports often complain of torment within the lower femur, or instantly underneath the knee. If the tumor is expansive, it can display as overt restricted swelling. In some cases, a sudden fracture is the primary side effect since the influenced bone isn't as solid as ordinary bone and may break unusually with a minor injury. In cases of more deep-seated tumors that are not as near to the skin, such as those starting within the pelvis, restricted swelling may not be apparent.
Causes
A few research groups are exploring cancer stem cells and their potential to cause tumors in conjunction with genes and proteins causative in numerous phenotypes. Radiotherapy for disconnected conditions may be an uncommon cause.
A little supernumerary marker chromosome or a mammoth pole chromosome is displayed within the tumor cells of moo review OS counting moo review central OS and parosteal OS (see underneath Variations section), carry different possibly pro-cancerous qualities, and are thought to contribute to the advancement of these OS.
Familial cases where the cancellation of chromosome 13q14 inactivates the retinoblastoma quality is related to a tall chance of osteosarcoma advancement. Bone dysplasias, including Paget's malady of bone, sinewy dysplasia, enchondromatosis, and innate different exostoses, increase the hazard of osteosarcoma.
Li–Fraumeni disorder (germline TP53 change) could be a predisposing factor for osteosarcoma improvement. Rothmund–Thomson disorder (i.e. autosomal passive affiliation of intrinsic bone abandons, hair and skin dysplasias, hypogonadism, and cataracts) is related to the expanded hazard of this illness. Large doses of Sr-90, nicknamed bone searcher, increase the hazard of bone cancer and leukemia in creatures and are presumed to do so in people. There's no clear affiliation between water fluoridation and cancer or deaths due to cancer, both for cancer in common additionally particularly for bone cancer and osteosarcoma.
The arrangement of research concluded that the concentration of fluoride in water does not relate to osteosarcoma. The convictions concerning the affiliation between fluoride introduction and osteosarcoma stem from a think by the US National Toxicology Program in 1990, which showed uncertain proof of affiliation between fluoride and osteosarcoma in male rats. But there's still no strong proof of the cancer-causing tendency of fluoride in mice. Fluoridation of water has been practiced around the world to improve citizens' dental well-being. It is additionally regarded as a major well-being success. Fluoride concentration levels in water supplies are controlled, such as the United States National Security Organization controls fluoride levels to not be more noteworthy than 4 milligrams per liter. Water supplies as of now have characteristic fluoride, but numerous communities chose to include more fluoride to the point that it can reduce tooth decay.
Fluoride is additionally known for its capacity to cause unused bone formation. However, assist inquire appears to be no osteosarcoma dangers from fluoridated water in humans. Most of the investigations included counting several osteosarcoma patients’ cases in specific ranges which have different concentrations of fluoride in drinking water. The measurement analysis of the information appears no significant contrast in events of osteosarcoma cases with completely different fluoridated regions. Another critical investigation included collecting bone tests from osteosarcoma patients to determine fluoride concentration and compare them to bone tests of recently analyzed dangerous bone tumors. The result is that the middle fluoride concentrations in bone tests of osteosarcoma patients and tumor controls are not altogether different. Not as if fluoride concentration in bones, Fluoride exposures of osteosarcoma patients are moreover demonstrated to be not essentially diverse from sound people.
Mechanism
Osteosarcomas tend to happen at the locales of bone development, apparently since expansion makes osteoblastic cells in this locale inclined to procure transformations that seem to lead to a change of cells (the RB quality and p53 quality are commonly included). The tumor may be localized after the long bone (commonly within the metaphysis). Most regularly it influences the proximal conclusion of the tibia or humerus or the distal conclusion of the femur. Osteosarcoma tends to influence districts around the knee in 60% of cases, 15% around the hip, 10% at the shoulder, and 8% within the jaw. The tumor is strong, difficult, and sporadic ("fir-tree," "moth-eaten", or "sun-burst" appearance on X-ray examination) due to the tumor spicules of calcified bone transmitting at right points. These right points frame what is known as a Codman triangle, which is characteristic but not symptomatic of osteosarcoma. Encompassing tissues are penetrated.
Microscopically
The characteristic of osteosarcoma is the nearness of osteoid (bone arrangement) inside the tumor. Tumor cells are exceptionally pleomorphic (anaplastic), a few are monsters and various atypical mitoses. These cells create osteoid portraying sporadic trabeculae (nebulous, eosinophilic/pink) with or without central calcification (hematoxylin biophilic/blue, granular)—tumor bone. Tumor cells are included within the osteoid framework. Depending on the highlights of the tumor cells shown (whether they take after bone cells, cartilage cells, or fibroblast cells), the tumor can be subclassified. Osteosarcomas may display multinucleated osteoclast-like monster cells.
Diagnosis
X-rays are the introductory imaging of choice to analyze osteosarcoma. A few characteristics of osteosarcoma on X-rays are sunburst appearance and Codman triangle (rise of hard cortex by the tumor that caused modern bone arrangement). CT filter is accommodating in characterizing the hard life structures, the judgment of the hard cortex, recognizing pathologic break, and surveying solidification (laying of modern bone materials) and calcification of the cartilage. On the other hand, delicate tissue and medullary depth are superior images by an MRI filter.
Most times, the early signs of osteosarcoma are caught on X-rays taken amid scheduled dental check-ups. Osteosarcoma as often as possible is created within the mandible (lower jaw); appropriately, dentists are prepared to hunt for signs that will recommend osteosarcoma. Indeed even though radiographic discoveries for this cancer change significantly, one more often than not sees a symmetrical extension of the periodontal tendon space. A dental practitioner who has reason to suspect osteosarcoma or another fundamental clutter would at that point allude to a Verbal & Maxillofacial specialist for a biopsy. A biopsy of the suspected osteosarcoma exterior of the facial locale ought to be performed by a qualified orthopedic oncologist. The American Cancer Society states: "Likely in no other cancer is it as critical to performing this strategy appropriately. A disgracefully performed biopsy may make it troublesome to spare the affected appendage from removal." It may moreover metastasize to the lungs, basically showing up on the chest X-ray as single or different circular knobs most common at the lower locales.
Variants
- Osteoblastic, chondroblasts,
- Fibroblastic OS
- Telangiectatic OS Little cell OS
- Low-grade central OS
- Periosteal OS
- Parosteal OS
- Auxiliary OS
- High-grade surface OS
- Extraskeletal OS
Treatment
A total radical, surgical, en alliance resection of cancer, is the treatment of choice in osteosarcoma. Although around 90% of patients can have limb-salvage surgery, complications, especially contamination, prosthetic extricating, non-union, or nearby tumor repeat may cause the requirement for advanced surgery or removal.
Mifamurtide is utilized after a persistent has had surgery to evacuate the tumor and alongside chemotherapy to murder the remaining cancer cells to decrease the chance of cancer repeating. Moreover, the alternative to having rotationplasty after the tumor is taken out exists.
Patients with osteosarcoma are best overseen by a therapeutic oncologist and an orthopedic oncologist experienced in overseeing sarcomas. The current standard treatment is to utilize neoadjuvant chemotherapy (chemotherapy given sometime recently after surgery) taken after surgical resection. The rate of tumor cell rot (cell passing) seen within the tumor after surgery gives a thought of the guess conjointly lets the oncologist know in case the chemotherapy regimen ought to be modified after surgery.
Standard treatment may be a combination of limb-salvage orthopedic surgery when conceivable (or removal in a few cases) and a combination of high-dose methotrexate with leucovorin protect, intra-arterial cisplatin, adriamycin, ifosfamide with mesna, BCD (bleomycin, cyclophosphamide, dactinomycin), etoposide, and muramyl tripeptide. Rotationplasty may be utilized. Ifosfamide can be utilized as adjuvant treatment on the off chance that the corruption rate is low.
Despite the victory of chemotherapy for osteosarcoma, it has one of the least survival rates for pediatric cancer. The most excellent detailed 10-year survival rate is 92%; the convention utilized is an aggressive intra-arterial regimen that individualizes treatment based on arteriographic response. Three-year event-free survival ranges from 50% to 75%, and five-year survival ranges from 60% to 85+% in a few considers. By and large, 65–70% of patients treated five a long time back will be lively today. These survival rates are generally midpoints and shift significantly depending on the person's rot rate.
Filgrastim or pegfilgrastim offer assistance with white blood cell checks and neutrophil tallies. Blood transfusions and epoetin alfa help with frailty. Computational examination on a board of osteosarcoma cell lines recognized unused shared and particularly helpful targets (proteomic and hereditary) in osteosarcoma, whereas phenotypes appeared in an expanded role of tumor microenvironments.
Prognosis
The prognosis is separated into three groups.
Stage I
Osteosarcoma is uncommon and incorporates parosteal osteosarcoma or low-grade central osteosarcoma. It has a great forecast (>90%) with a wide selection.
Stage II
The forecast depends on the location of the tumor (proximal tibia, femur, pelvis, etc.), an estimate of the tumor mass, and the degree of corruption from neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Other obsessive components such as the degree of p-glycoprotein, whether the tumor is cxcr4-positive, or Her2-positive are too imperative, as these are related to far-off metastases to the lung. The guess for patients with metastatic osteosarcoma makes strides with longer times to metastases (more than 12 months to 4 months), a little number of metastases, and their respectability. It is way better to have fewer metastases than a long time to metastases. Those with a longer length of time (more than 24 months) and few knobs (two or fewer) have the best guess, with a two-year survival after the metastases of 50%, five-year of 40%, and 10-year of 20%. On the off chance that metastases are both neighborhood and territorial, the guess is more awful. Beginning the introduction of organize III osteosarcomas with lung metastases depends on the resectability of the essential tumor and lung knobs, the degree of the rot of the essential tumor, and possibly the number of metastases. In general survival, guess is almost 30%. Passings due to dangerous neoplasms of the bones and joints account for an obscure number of childhood cancer passes. Mortality rates due to osteosarcoma have been declining at approximately 1.3% per year. Long-term survival probabilities for osteosarcoma have progressed drastically amid the late 20th century and approximated 68% in 2009.
Epidemiology
Osteosarcoma is the eighth-most common shape of childhood cancer, comprising 2.4% of all malignancies in pediatric patients, and almost 20% of all essential bone cancers.
Incidence rates for osteosarcoma in U.S. patients under 20 a long time of age are evaluated at 5.0 per million per year within the common populace, with a slight variation between people of dark, Hispanic, and white ethnicities (6.8, 6.5, and 4.6 per million per year, separately). It is somewhat more common in guys (5.4 per million per year) than in females (4.0 per million per year)
It originates more regularly within the metaphyseal region of tubular long bones, with 42% happening within the femur, 19% within the tibia, and 10% within the humerus. Around 8% of all cases happen within the cranium and jaw, and another 8% within the pelvis.
Around 300 of the 900 individuals analyzed within the United States will die each year. A moment crest in rate happens within the elderly, more often than not related to a basic bone pathology such as Paget's infection of the bone.