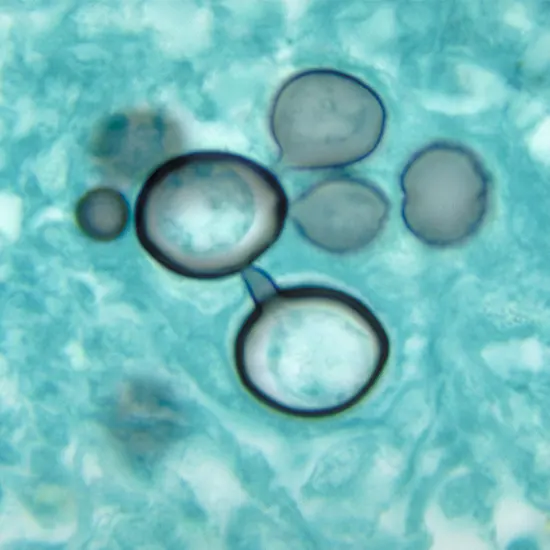
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is a systemic fungal contamination prompted by the dimorphic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, which is endemic to Latin America, especially Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Argentina.
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is a systemic fungal contamination prompted by the dimorphic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, which is endemic to Latin America, especially Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Argentina.
PCM notably impacts the lungs and mucous membranes,s, however, it can additionally unfold to different organs such as the skin, lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and central anxious system.
PCM principally impacts people who work in rural areas, such as farmers and miners, who come into contact with the fungus in the soil. It is additionally greater frequent in guys than in girls and is generally identified in folks aged between 30 and 50 years old.
PCM can exist as a moderate or extreme disease, relying on the immune repute of the affected individual.
What is Paracoccidioidomycosis?
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is a fungal contamination induced by the dimorphic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.
PCM chiefly impacts the lungs and mucous membranes, however, it can additionally unfold to other organs such as the skin, lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and central anxious system.
Preventive measures such as sporting protecting apparel and keeping off publicity to contaminated soil are additionally essential in lowering the hazard of infection.
Explore the Epidemiology of Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is a fungal contamination that is endemic to Latin America, in particular Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Argentina.
The specific incidence of PCM is tough to determine due to the fact of underreporting and misdiagnosis, however, it is estimated that there are around 10,000 new cases of PCM every 12 months in Brazil alone.
PCM specifically influences men and women who work in rural areas, such as farmers and miners, who come into contact with the fungus in the soil.
It is more frequent in guys than in girls and generally impacts folks aged between 30 and 50 years old.
The incidence of PCM has been declining in some areas, in all likelihood due to improved awareness, beforehand diagnosis, and elevated therapy options.
However, in some regions, the incidence stays high, and PCM is nonetheless a widespread public fitness concern.
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are at an improved chance of growing extreme varieties of PCM.
In these cases, PCM can grow hastily and lead to life-threatening issues such as respiratory failure and meningitis.
Overall, the epidemiology of PCM highlights the significance of preventive measures such as carrying shielding apparel and keeping off publicity to contaminated soil in at-risk populations, as well as early prognosis and therapy in those who improve the infection.
Learn about the Pathophysiology of Paracoccidioidomycosis:
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is precipitated via the dimorphic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.
The fungus exists in the soil in its saprophytic form, which is composed of hyphae and conidia.
When these conidia are inhaled, they can seriously change into the pathogenic yeast shape in the host's tissues.
The yeast structure of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis is characterized by using its giant measurement (8 to eighty microns), a couple of budding, and thick-walled cells that can withstand the host's immune system.
The fungus can adhere to host cells, penetrate the respiratory epithelium, and disseminate hematogenously to different organs such as the skin, lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and central frightened system.
PCM is principally a granulomatous disease, which means that it is characterised using the formation of granulomas, which are collections of immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes, that encompass the fungus and strive to incorporate the infection.
However, in some cases, the granulomas can end up necrotic and lead to tissue damage.
The severity of PCM relies upon the immune popularity of the affected individual.
In healthful individuals, the immune response is generally enough to manipulate the infection, and the sickness may additionally continue to be asymptomatic or exist as a slight respiratory illness.
However, in folks with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, the fungus can hastily disseminate and lead to extreme disease, consisting of continual lung sickness and doubtlessly life-threatening problems such as respiratory failure and meningitis.
Overall, the pathophysiology of PCM highlights the complicated interaction between the host's immune response and the pathogenic traits of the fungus.
Signs and Symptoms of Paracoccidioidomycosis:
The symptoms and signs and symptoms of Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) can differ depending on the severity of the infection, the immune repute of the affected individual, and the organs involved.
The most frequent presentation of PCM is a continual respiratory sickness that can mimic tuberculosis or different lung diseases. Symptoms may also include:
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Sputum production
- Wheezing
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
In addition to respiratory symptoms, PCM can additionally cause pores and skin lesions that may additionally be ulcerated or nodular, specifically in areas of the physique uncovered to the soil, such as the toes and legs.
Other viable signs and symptoms of PCM can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen)
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Headache
- Vishal changes
- Confusion
Severy varieties of PCM, in particular in folks with weakened immune systems, can lead to probably life-threatening issues such as respiratory failure, meningitis, and sepsis.
It's essential to say that some men and women with PCM may also be asymptomatic or have moderate symptoms, and the sickness PUS Routine can also solely be detected by the way of imaging research or at some point using laboratory tests.
Diagnostic Methods for Paracoccidioidomycosis
The analysis of Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) can be difficult due to the non-specific nature of the signs and the similarities with other respiratory and systemic infections.
An aggregate of scientific evaluation, laboratory testing, and imaging research is commonly required for a correct diagnosis.
Some of the diagnostic assessments normally used for PCM include:
Serology
Serological exams can notice antibodies to Paracoccidioides brasiliensis in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). These assessments are fairly unique however might also now not be touchy in the early degrees of the infection.
Direct microscopy
Samples of sputum, pores and skin lesions, or different tissues can be examined below the microscope for the presence of attribute fungal elements, such as hyphae, yeast cells, and budding cells.
Direct microscopy is fast and inexpensive, however, its sensitivity may also be low, especially in instances of continual infection.
Culture
Tissue samples can be cultured on fungal media to develop the fungus. This approach is pretty touchy and specific, however, it can take up to 4 weeks to acquire results.
Polymerase chain response (PCR)
PCR-based exams can observe fungal DNA in medical specimens with excessive sensitivity and specificity. PCR can be carried out on sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), or tissue samples.
Imaging studies
Chest X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans can become aware of abnormalities in the lungs, lymph nodes, or different organs.
This imaging research can assist in information on the prognosis and reveal the response to treatment. It's necessary to be aware that the prognosis of PCM requires an excessive index of suspicion, especially in people residing or working in endemic areas.
Complications of Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) can lead to a variety of complications, specifically in persons with weakened immune structures or those with a superior disease.
Some of the feasible issues of PCM include:
Chronic lung disease
PCM can motivate persistent lung disease, which can lead to shortness of breath, decreased lung function, and a decreased exceptional of life.
Disseminated disease
In extreme cases, PCM can disseminate from the lungs to different organs, such as the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, skin, and central anxious system, leading to organ failure and doubtlessly life-threatening complications.
Meningitis
PCM can lead to meningitis, which is an infection of the shielding membranes that encompass the talent and spinal cord. Meningitis can cause signs such as headache, fever, neck stiffness, confusion, and seizures.
Respiratory failure
In uncommon cases, PCM can lead to respiratory failure, which is a life-threatening circumstance that requires immediate clinical intervention.
Secondary bacterial infections
PCM can weaken the immune gadget and extend the hazard of secondary bacterial infections, in particular in humans with the superior disease.
Skin lesions
PCM can motivate pores and skin lesions that can also be ulcerated or nodular, mainly in areas of the physique exposed to soil, such as the feet and legs. These lesions can be painful and disfiguring and can enlarge the danger of secondary infections.
Malnutrition
PCM can cause weight loss and malnutrition, which can in addition weaken the immune gadget and amplify the hazard of complications.
Treatment Options for Paracoccidioidomycosis
The therapy of Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) generally includes the use of antifungal medicinal drugs to cast off the fungal infection.
The preference for antifungal remedy and the length of remedy relies on the severity of the infection, the organ involved, and the immune popularity of the affected individual.
Azoles
Itraconazole is the most generally used azole for the therapy of PCM. It can be taken orally for numerous months to 12 months relying on the severity of the infection. Other azoles that can be used consist of fluconazole and posaconazole.
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is a robust antifungal medicine that can be used for extreme or disseminated instances of PCM. It can be given intravenously or as liposomal training to reduce aspect effects.
Sulfonamides
Sulfonamides, such as sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, can be used in a mixture with different antifungal medicines to deal with PCM.
Surgery
Surgery can also be fundamental in uncommon instances of PCM where there are complications, such as abscesses, masses, or strictures.
Supportive care
Supportive care, which includes vitamin support, oxygen therapy, and administration of complications, can also be quintessential in extreme instances of PCM.
It's vital to observe that the cure for PCM can be challenging, in particular in folks with weakened immune structures or those with superior disease.
Close monitoring and follow-up with healthcare companies are integral to make sure the effectiveness of the cure and to decrease the danger of complications.
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM) is a systemic fungal contamination that specifically impacts folks in Central and South America. Preventive measures, such as fending off publicity to soil and sporting defensive apparel and footwear, can assist decrease the chance of infection.
Stay vigilant against Paracoccidioidomycosis, and stay healthy!















