Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba, is the source of the uncommon but potentially fatal brain infection known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). This amoeba is typically found in dirt, untreated or improperly...
Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba, is the source of the uncommon but potentially fatal brain infection known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). This amoeba is typically found in dirt, untreated or improperly managed swimming pools or spas, as well as warm.
When N. fowleri enters the body through the nose and ascends to the brain, it causes inflammation and the degeneration of brain tissue, which results in PAM. The condition is particularly prevalent in the southern United States during the summer and often affects healthy youngsters and young adults who participate in warm freshwater activities such as swimming or diving.
Cause and Transmission of Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis pam. How does it occur?
Freshwater bodies like lakes, rivers, hot springs, and improperly managed swimming pools and water systems, is the cause of the uncommon and typically fatal brain infection known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM).
The most popular routes through which infection can spread that includes:
The virus spreads through physical contact, such as hand-shaking, kissing, or sexual contact, this is known as direct contact transmission.
Transmission through contaminated objects or surfaces, such as door handles, towels or kitchen utensils, is known as indirect contact transmission.
The transfer of a disease from one person to another is referred to as transmission. Depending on the particular disease, the method of transmission can change. For instance, sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) can be spread through sexual contact with an infected person, whereas respiratory infections like the common cold or flu can spread through coughs or sneezes.
Other probable transmission pathways include contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, ingestion of contaminated food or water, or exposure to contaminated bodily fluids. Ticks and mosquitoes, which are known to carry malaria and Lyme disease, can also transmit various diseases.
Indirect Contact : This method of transmission happens when a person contacts a phone, computer keyboard, doorknob, or other surface.
Droplets carrying the infectious agent are released into the air, which can lead to the spread of several diseases through the air. Others may breathe in these droplets, which could infect them.
Symptoms associated with Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis pam :
PAM symptoms can include the following and usually appear 1 to 9 days after infection of the amoeba:
- Headache
- Fever
- Nausea and diarrhoea
- Rigid neck
- Reduced appetite
- Seizures
- Confusion or fuzziness
- Hallucinations
Loss of coordination or balance Sensitivity to light
It can be challenging to distinguish these symptoms from those of other brain infections since they are so similar. If you have recently been swimming in warm freshwater or have been exposed to the amoeba in any other way, you should get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms.
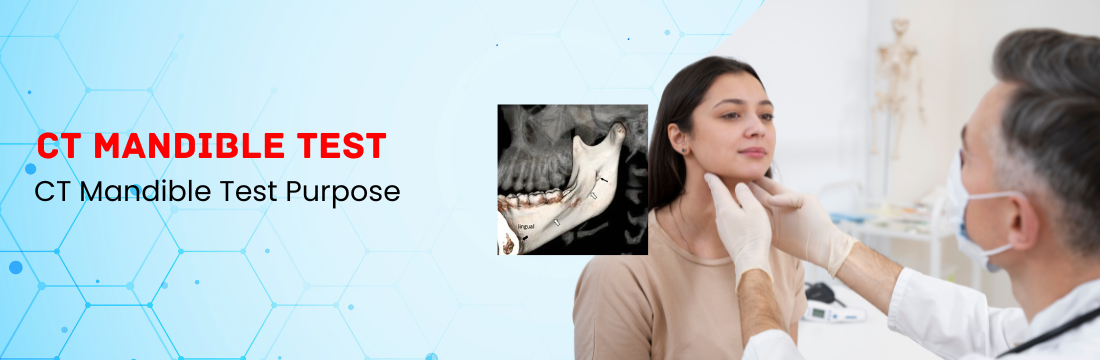
A doctor would often do a physical examination to rule out other conditions before prescribing diagnostic testing like an MRI or spinal tap to check for indications of inflammation. By finding the amoeba in a sample of spinal fluid or tissue, the diagnosis can be verified.
It is crucial to keep in mind that PAM is extremely uncommon and that many individuals exposed to the amoeba do not get the infection. To rule out PAM or other dangerous brain infections, however, if you develop any of the symptoms mentioned above after being exposed to warm freshwater, call your doctor straight once.
Treatment Options for PAM: What Are the Chances of Recovery?
A number of procedures are used to treat primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), with the goals of containing the infection, minimising inflammation, and offering supportive care. A step-by-step manual for treating PAM is provided below:
Confirming the diagnosis is the first step in the treatment of PAM. This entails a comprehensive physical examination as well as diagnostic procedures such a spinal tap, MRI, or CT scan. The Naegleria fowleri amoeba may also be diagnosed using cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Medication : The next step is to begin therapy with drugs once the diagnosis of PAM has been established. PAM is typically treated with antibiotics like rifampin and azithromycin, as well as antifungal medications like amphotericin B and fluconazole. These medications reduce inflammation in the brain while also focusing on the amoeba.
Supportive care : An important component of the therapy of PAM in addition to medication is supportive care. This may involve treatments including oxygen therapy, control of seizures, and hydration and electrolyte management. To control their symptoms, PAM patients may need hospitalisation and extensive care.
Monitoring : PAM patients need to be closely watched in order to gauge how well their treatments are working and to spot any potential problems. This may entail routine neurological examinations, monitoring of vital signs, and lab testing to evaluate kidney and liver function.
Rehabilitation : Patients who have survived PAM could need rehabilitation to assist them regain any lost function and to deal with any residual symptoms. Physical treatment, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation may all be included in this.
It is significant to emphasise that PAM treatment can be difficult, and the prognosis is still poor even with vigorous therapy. To increase the odds of survival, early detection and immediate treatment are essential.
Preventing PAM : Tips and Strategies for Avoiding Infection
The ideal strategy is to prevent primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), which can be fatal and is difficult to cure. Here are some recommendations and methods for preventing Naegleria fowleri infection:
Naegleria fowleri amoeba flourishes in warm, stagnant freshwater, especially in lakes and rivers during the summer. Avoid swimming or diving in such water. If the water temperature in these bodies of water is above 80 degrees Fahrenheit, avoid swimming or diving there.
When swimming or diving, use nose clips or plugs to help limit the chance of infection because the amoeba enters the body through the nose.
Try to keep your head above water when swimming or diving, or use a swim cap that is tightly fitted to lessen the quantity of water that enters your nose.
Keep the hot tubs and pools clean: Maintaining your hot tub or pool on a regular basis will help you avoid the growth of bacteria and other creatures that could serve as an amoeba's ideal habitat.
For nasal irrigation, only use sterile, distilled, or boiling water: Use sterile, distilled, or cooked water when using a neti pot or other nasal irrigation tool because tap water may contain the amoeba.
Learn about the dangers of PAM and teach others how to stay healthy by spreading awareness.
It is significant to remember that PAM is uncommon and that the majority of those who are exposed to the Naegleria fowleri amoeba do not become infected. However, by taking these precautions, you can lessen your chance of infection and safeguard your health.
To sum up, primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is an uncommon but severe infection that affects the brain and has a high mortality rate. Commonly found in warm freshwater, the Naegleria fowleri amoeba that causes PAM enters the body through the nose.
The greatest strategy for treating Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis is prevention, which can be achieved by taking steps like refraining from swimming or diving in warm freshwater, wearing nasal clips or plugs, and maintaining clean swimming pools and hot tubs.
If PAM symptoms appear, detecting them quickly and starting treatment are essential for increasing survival rates. Despite the fact that PAM still has a bad prognosis and a high death rate, it is crucial to be aware of the hazards and take precautions to prevent infection.