Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a rare genetic disorder that affects the thyroid gland. It is also known as type 1a pseudo hypothyroidism or Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO). This disorder is caused by a genetic mutation...
Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a rare genetic disorder that affects the thyroid gland. It is also known as type 1a pseudo hypothyroidism or Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO). This disorder is caused by a genetic mutation that affects the signaling pathway of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the body.
People with pseudohypoparathyroidism have high levels of TSH, but their thyroid gland does not respond normally to the hormone. As a result, they may exhibit symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and constipation, even though their thyroid gland is functioning normally.
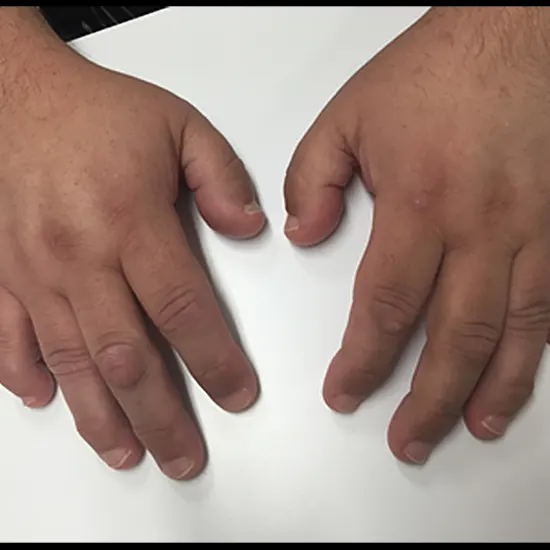
Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a complex disorder that can affect various parts of the body, including the bones, skin, and nervous system. People with this condition may have short stature, round face, short fingers, and other physical features.
Although there is no known treatment for pseudo hypothyroidism, hormone replacement therapy can help control its symptoms. To keep hormone levels within normal ranges and to guard against the disorder's consequences, regular monitoring is crucial.
When Thyroid Hormones Don't Work: The Causes of Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Genetic changes that disrupt the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) signaling system in the body are the root cause of pseudo-hypothyroidism.
Particularly, changes in the GNAS gene are responsible for this disease.
The alpha subunit of the stimulating G protein (Gs) is encoded by the GNAS gene.
The Gs protein plays a crucial role in the transmission of TSH signals to the thyroid gland.
The Gs protein is lacking or damaged pseudo hypothyroidism, which reduces the thyroid gland's responsiveness to TSH stimulation.
The pituitary gland's continued production of TSH to encourage the thyroid gland to generate thyroid hormones causes increased levels of TSH in the blood.
Pseudohypoparathyroidism Symptoms: Understanding the Warning Signs
The following list includes symptoms and signs of pseudohypoparathyroidism:
Hypocalcemia
Low calcium levels in the blood can cause twitching, cramping, and weakening of the muscles.
Hyperphosphatemia
High levels of phosphorus in the blood, known as hyperphosphatemia, can cause renal damage, bone discomfort, and fractures.
Hypothyroidism
Many persons with pseudohypoparathyroidism also experience symptoms of hypothyroidism, including fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold temperatures.
Short-stature
Pseudohypoparathyroidism can cause children to be smaller than usual in height.
Small jaw and round face
People with pseudohypoparathyroidism may have a round face.
Brachydactyly
The fourth and fifth fingers are shortened, which is brachydactyly, the disorder's defining characteristic.
Dental Problems
Patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism may have dental problems, such as misaligned or missing teeth.
Delayed Development
Children with pseudohypoparathyroidism may have delayed development and learning problems.
It is important to keep in mind that not everyone with pseudohypoparathyroidism will have all of these symptoms and that symptom severity can differ significantly from person to person.
Categorizing Psedohypoparathyroidism: Types and Symptoms
Type 1 and type 2 pseudo hypothyroidism are the two main varieties. The two categories differ in the following ways:
Type 1 pseudo hypothyroidism
It is commonly known as Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO), which is the most prevalent kind. It is brought on by changes in the GNAS gene that impair the Gs protein's functionality. Subtypes of type 1 Psedohypoparathyroidism can be identified based on the presence or absence of particular physical characteristics including short stature and a round face.
Type 2 pseudo hypothyroidism
It is brought on by mutations in the gene encoding for the receptor that binds thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the thyroid gland (TSHR). Despite the signaling route being intact, the thyroid gland itself cannot respond to TSH stimulation in type 2 pseudo hypothyroidism. Comparatively uncommon to type 1, type 2 pseudo hypothyroidism is not linked to physical characteristics like short stature and a round face.
It is significant to highlight that, even within the same type of condition, the symptoms and severity of pseudo-hypothyroidism can differ significantly between people. Clinical manifestations of the condition may differ depending on the particular genetic abnormalities that cause them.
Diagnosing Pseudohypoparathyroidism : Tests and Procedures
Clinical assessment, laboratory investigations, and genetic testing are all used to diagnose Pseudohypoparathyroidism. The following actions are routinely taken in the diagnosis of pseudo hypothyroidism:
Clinical assessment
A physician may assess a patient's symptoms, medical background, and results of a physical examination to see if they are consistent with pseudo-hypothyroidism.
Laboratory Tests
TSH, thyroid hormones, calcium, and phosphorus levels in the blood can all be determined through laboratory studies using blood samples. TSH levels are frequently increased in pseudo hypothyroidism, while thyroid hormone levels are normal. Phosphorus levels could be high and calcium levels could be low.
Genetic testing
Genetic mutations are the cause of pseudo hypothyroidism, hence genetic testing may be done to coToiagnosis. To check for mutations, this may include sequencing the TSHR and GNAS genes.
Imaging studies
To assess bone health and check for evidence of osteodystrophy, which is a typical feature of type 1 pseudo hypothyroidism, imaging studies such as X-rays or bone density scans may be carried out.
Differential diagnosis
It's critical to rule out other disorders like hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, and vitamin D deficiency that might produce the same symptoms.
It takes a combination of clinical assessment, laboratory investigations, and gene testing for Pseudohypoparathyroidism. Treatment can be started to manage symptoms and avoid problems once a diagnosis has been made.
Finding Relief : Effective Treatment Strategies for Pseudohypoparathyroidism
The course of treatment for pseudo hypothyroidism is determined by the kind and severity of the condition, the patient's symptoms, and their medical background. The following are some possible treatments:
Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation : Supplementing calcium and vitamin D can help people with pseudo hypothyroidism avoid bone problems because these nutrients may be deficient in their diets. Calcium and vitamin D supplements can help stop bone loss and lower the risk of fractures.
Thyroid hormone replacement : Thyroid hormone replacement treatment can be used to treat pseudo hypothyroidism, which is a condition in which the thyroid gland is underactive. To replace the hormones that the thyroid gland is not making, this includes taking pills containing synthetic thyroid hormones.
Symptom management : Additional therapies, such as physical therapy for muscle weakness or dental work for deformed teeth, may be employed to treat a particular symptom.
Pseudohypoparathyroidism patients should schedule Routine And Microscopy follow-up visits with their medical professionals to track their symptoms and modify their treatment as necessary. With the right care, some Urine Culture complications of pseudo hypothyroidism, like osteoporosis and kidney issues, can be avoided or treated.
Don't Let Psedohypoparathyroidism Rule Your Life - Fight Back Today









