Rhinosporidiosis may be an inveterate granulomatous contamination of the mucous films that as a rule shows as vascular friable polyps that emerge from the nasal mucosa or outside structures of the eye.
Rhinosporidiosis may be an inveterate granulomatous contamination of the mucous films that as a rule shows as vascular friable polyps that emerge from the nasal mucosa or outside structures of the eye.
Rhinosporidiosis could be a persistent, localized granulomatous condition that presents with polyp-like injuries. The causative living being has been recognized by hereditary procedures as a part of the oceanic Protista. There are no test models and the living being cannot be refined. Illness has been detailed from numerous tropical nations, but 90% of detailed cases are from India and Sri Lanka.
The study of disease transmission
United States
Rhinosporidiosis cases within the United States are uncommon, but are more common in Texas and the Southeast. From 1896 through 2019, less than 50 cases have been detailed from the United States.
Worldwide
Rhinosporidiosis as a rule influences people in or from southern India and Sri Lanka. Cases have been detailed around the world, with an expanded rate in South America and Africa.
Pathophysiology
Rhinosporidiosis is an contamination that regularly is restricted to the mucosal epithelium. Disease as a rule comes about from a nearby traumatic vaccination with the living being. The infection advances with the neighbourhood replication of R and related hyperplastic development of tissue and a localized safe reaction.
Disease of the nose and nasopharynx is watched in 70% of people with rhinosporidiosis; infection of the palpebral conjunctivae or related structures (counting the lacrimal device) is watched in 15%.
Signs
- Pedunculated, or level sessile delicate tissue development
- Meaty appearance
- Pinpoint white or yellow spots
- Profoundly vascular and friable with free dying
- Proptosis
Indications
- Watering of eyes (visual injury)
- Conjunctivitis (visual injury)
- Ridiculous Tears (visual injury)
- Photophobia (visual injury)
- Itching (visual and nasopharynx injury)
- Trouble breathing (nasopharynx injury)
- Rhinorrhea (nasopharynx injury)
- Anosmia (nasopharynx injury)
- Epistaxis (nasopharynx injury)
- Trouble gulping (oropharynx injury)
Determination
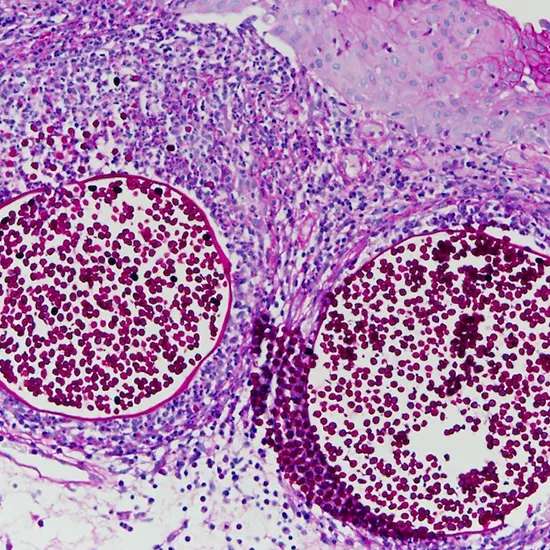
Histopathology is the authoritative way to affirm a conclusion of Rhinosporidiosis . On histopathology, obvious trophocytes and sporangia will be in several stages of advancement with encompassing penetration of provocative cells and hyperplasia of the mucosal tissue.
History
Patients showing with rhinosporidiosis may frequently have a history of swimming in stagnant water, have later travel or home in endemic areas, work close streams or are river-sand workers.
Physical Examination
Rhinosporidiosis happens when the endospores of R. taint the mucosa through a traumatised epithelium, driving to hyperplasia and growth of a delicate injury on the location of disease. It can ANA Elisashow in different areas within the body, but transcendently emerge within the nasal section, eyes and oropharynx.
Rhinosporidium polyps show up as a delicate tissue injury that's granular, beefy, and ruddy in colour with numerous yellowish to white stick head measured dabs that demonstrate underlying mature sporangia. Depending on the area, the injury can show as pedunculated or level.
Symptomatic methods
Authoritative determination of rhinosporidiosis depends on histological examination with immunohistochemistry. This frequently requires excisional biopsy, scratching of shallow injuries or fine needle desire. The histopathological areas will appear sporangia in different stages of maturation enclosed inside a lean divider.
The sporangia can run from 50-1000 μm in breadth with endospores interior that are around 5-10 μm. The overlying and encompassing tissue has fast development with the disease with hyperplasia of the tissue and free fibrovascular stroma. Resistant responses to the disease moreover comes about in penetration with lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells and PMNs.
- Differential conclusion
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Squamous or conjunctival papilloma
- Hemangioma
- Arteriovenous deformity
- Incessant contamination
- Oncocytoma
- Sebaceous adenoma
- Squamous carcinoma
- Foreign body
- Conjunctival sore
- Kindled pinguecula
Rhinosporidiosis disease is treated essentially with surgical intervention. Medical administration has once in a while been reported as an aide treatment to surgery.
Common treatment
The primary line treatment of rhinosporidiosis is surgical, and the strategy utilized is directed by the location of the injury. Within the lion's share of cases, add up to surgical excision is completed utilizing cautery. Electrocautery minimizes the dying from the profoundly vascular structure and limits the discharge of endospores into the adjacent mucosa. This may diminish the chance of repetition.
Therapeutic treatment with Dapsone and Amphotericin B is conceivable, but not well considered. Adequacy of these drugs are disputable, but may be utilized in disseminated infection. Dapsone has been utilized in some case reports FNAC but continuously as an aide to surgical treatment. As R. seeberi cannot be developed in vitro, medicate sensitivities are as of now obscure.
Restorative treatment
Therapeutic administration of rhinosporidiosis has not been unequivocally advised in reported cases. As of now, dapsone is an adjuvant sedate to surgery.
Surgery
Add up to extraction of the polyp or conjunctiva is prescribed, and electrocautery is most commonly utilized as it restricts free dying. In the event that there's lacrimal sac inclusion, a dacryocystectomy chest x-ray is ordinarily done. The method ought to expel the entirety of the whole sac, and post-operative Dapsone treatment is more often than not recommended.
In a review case series from India, 65% of all patients with lacrimal sac inclusion had localized illness. Amid removal of the polyp, spillage of the endospores into the encompassing mucosa may happen which can be contained by electrocautery.
Complications
Complications of rhinosporidiosis are moderately uncommon. Spread disease may happen driving osteolytic bone injuries which may be troublesome to recognize from backslide or reinfection in endemic districts.
Spread disease of the appendages can lead to bone devastation or disease of the brain and other destinations of the body. It is troublesome to treat and can lead to expanded horribleness. In expansion, nearby auxiliary CECT Chest bacterial diseases are noteworthy complications that can lead to horribleness as well. Repeat rates of visual rhinosporidiosis is lower than that of nasopharyngeal rhinosporidiosis.
Forecast
Despite the uncommon case of repeat, recovery or dispersal, the forecast is for the most part exceptionally favorable. It ordinarily takes after a generous, delayed course without treatment with restricted dismalness. Dismalness is ordinarily related when there is an auxiliary infection or dispersal.















