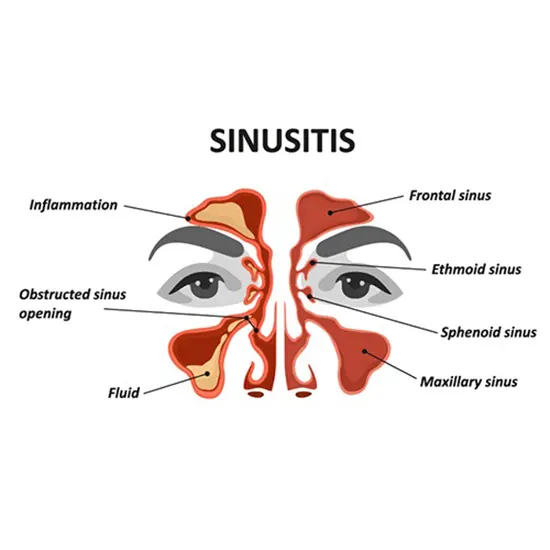
The sinuses are the bony cavities between the eyes, behind the cheekbones, and on the forehead. The sinuses around the nose are air-filled cavities of the nasal cavity and called paranasal sinuses. They are four in number,...
Introduction
The inflammation of the tissue lining the sinuses is termed as sinusitis
What is a Sinus?
The sinuses are the bony cavities between the eyes, behind the cheekbones, and on the forehead. The sinuses around the nose are air-filled cavities of the nasal cavity and called paranasal sinuses. They are four in number, named according to the bones they are located.
- Frontal
- Maxillary - largest among them and most prone to infections.
- Ethmoid
- Sphenoid
The function of the lateral cavities is the subject of much debate, but few if they are summarized-
- The immune defense of the nasal cavity is made stronger.
- Humidifies inhaled air
- It forms mucus that keeps the inside of your nose moist, which keeps all the pollutants out of the nasal cavity.
Normal sinuses are filled with air. However, when they become clogged and filled with liquid, microorganisms can grow and inflict an infection.
Prevalence
An estimated 35 million people per year in the United States are affected by sinusitis, and accounts for close to 16 million office visits per year. It is more commonly seen in females, and the highest incidence is between the ages 45 to 64 years.
Who is at Risk?
People with the following Risk factors:
- Asthma
- Bad immune features
- Laryngitis
- Bronchitis
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- A deviated nasal septum
- Sensitivity to Aspirin
- A fungal infection
- Tumors
- Allergic condition that affects your sinuses
- Active or passive smoking , both are equally responsible.
Causes
Various Viruses, bacteria, and fungi, can cause sinusitis.
Bacteriology: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, and anaerobic bacteria (Prevotella and Porphyromonas, Fusobacterium and Peptostreptococcus spp.)
Viral Infection: most sinusitis occurs due to Rhinovirus, Coronavirus influenza viruses, and parainfluenza viruses are the most common causes of sinusitis.
Fungal Infection - some fungi are also confirmed to cause sinusitis, some of them are Fungal balls (mycetoma) and saprophytes.
Pollutants like smoke.
CHEMICALS may trigger the building of mucus (e.g. pollen, dust, etc.)
NASAL INFECTIONS
Swimming infected water enters the sinuses through the ostium.
Trauma like Compound fractures or penetrating injuries.
Dental Infections: usually from the tooth in close approximation to the maxillary sinus like maxillary molars and premolars.
Structural Problems within the Sinuses. For instance growths on the lining of the nose and sinuses are known as nasal polyps. and deviated septum.
Smoking
Weak Immunity or taking medications that weaken your immune system.
Enlarged Tumor
Types
There are many types of sinusitis based on time period:
- Acute sinusitis. It can start immediately and last 2 to 4 weeks. It presents with cold-like symptoms such as a runny nose, nasal congestion
- Subacute sinusitis generally continues for 4 to 12 weeks.
- Chronic sinusitis is said when symptoms occur for more than 12 weeks.
- Recurrent sinusitis which occurs several times a year.
- Pansinusitis affects all sinuses in the head.
Signs and symptoms of sinusitis? Usually, signs and symptoms depend on the time period lapsed but some common symptoms of sinus infections include:
- Pain in the upper jaw
- Postnasal drip (mucus dripping down the throat).
- A runny nose with thick mucus stuffy nose.
- Facial pressure ( mostly around the nose, eyes, and forehead).
- Moving your head or bending over can make this worse
- Tooth pressure or pain.
- Increased body temperature
- Halitosis (halitosis) or a bad taste in the mouth.
- Cough
- Headache.
- Malaise
Acute Sinusitis (2-4 Weeks)
An upper respiratory tract infection frequently precedes acute sinus mucosa inflammation. The majority of instances of acute sinusitis begin with a typical cold caused by a virus. Colds can inflame the sinuses and produce sinusitis symptoms. If the cold-induced inflammation results in a bacterial infection.
As mucus accumulates in the sinuses and is unable to flow into the nose, it provides a source of nourishment for germs. Acute sinusitis can occasionally cause brain infections and other dangerous consequences. The inflammation which is induced by the cold and nasal difficulties causes the thickening of the mucous membranes of the sinuses, which can lead to the trapping of air and mucus behind the narrowing of the sinuses.
Clinical manifestations of acute sinusitis- This condition causes:
- Discomfort or pressure in the maxillary region (cheek, jaw, gums, and teeth),
- As well as reddish, edematous, and sore cheeks
- Bending down or coughing aggravates the pain.
- Frontal Sinusitis: This condition can cause discomfort or pressure in the frontal sinus cavity. The patient always whines of frontal headache and pain over the forehead. The discomfort is acute in the morning and progressively fades by midday when the infectious material drains from the sinus.
- Ethmoid Sinusitis: The pain is restricted to the bridges of the nose.
- Sphenoid Sinusitis: it produces pain or pressure behind the eyes .
Diagnosis of Acute Sinusitis?
Healthcare providers usually detect sinusitis based on symptoms and medical history. The doctor checks your ears, nose, and throat for swelling, discharge, or congestion. They use an endoscope (a small lighted instrument) to see inside their nose.
Your general physician can also make referrals to specialists, such as: ENT Certain tests to diagnose acute sinusitis
Certain tests that doctors order to diagnose sinus infections include:
- History taking
- X-ray examination
- Anterior and posterior rhinoscopy. Imaging.
- A computed tomography (CT) scan is used to get a better understanding of what is happening in your sinuses.
- Allergy test. If you have chronic sinusitis, your doctor can test for allergies that may be causing it.
- Biopsy. Rarely, a healthcare provider may take a sample of tissue from the nose for testing.
Treatment of acute sinusitis
Various treatment options for sinusitis, depending on the symptoms and on the time period they have been present. Following are some ways to treat a sinus infection at home:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) prescribed cold and allergy medicines.
- Rinses with nasal saline.
- drink lots of water.
- If sinus symptoms do not improve after 10 days, the health care provider may prescribe
- Antibiotics. If the doctor thinks that a bacterial infection is responsible, he may prescribe antibiotics.Antibiotics only help with bacterial infections, most commonly prescribed are-
- Augmentin (amoxicillin/clavulanate).
- Amoxicillin.
- Doxycycline.
- Levofloxacin.
- Painkillers In order to relieve discomfort and pain , pain alleviating drugs like ibuprofen and paracetamol is usually suggested
- Oral or topical decongestants.- These drugs help in decreasing the amount of mucus produced.commonly used are Xylometazoline nasal drops .
- Antibiotics. If the doctor thinks that a bacterial infection is responsible, he may prescribe antibiotics.Antibiotics only help with bacterial infections, most commonly prescribed are-
Chronic Sinusitis (more than 12 weeks)
Since the lining has been swollen for more than 12 weeks, the membranes of both the nose and paranasal sinuses get thickened. Chronic sinusitis is typically the outcome of unresolved acute sinusitis. Polyps in the nose are growths which appear as grapes that protrude into the sinuses or nasal passages, which maje drainage of the sinuses and passage of air via the nose even more difficult.
Clinical Implications of chronic sinusitis:
- Persistent nasal blockage
- Nasal congestion caused by excessive nasal discharge
- Edema of the nasal mucous membrane
- Reduced mucociliary clearance
- Sore throat and throat dryness
- Facial discomfort
- Headache
- Night time coughing
- Asthma symptoms that were previously minimal or under control worsen.
- Thick green or yellow discharge
- Epistaxis
- Sensation of face fullness or tightness .
Certain Tests Used to Diagnose Chronic Sinusitis
- Nasal endoscopy. As the name suggests a small camera-like device is used to view the sinus.nasal swab. Your doctor may use a soft stick to take a sample of fluid from your nose and then check for viruses and other bacteria that may be causing your symptoms.
- Biopsy of the mucous membranes
- Allergy test
- MRI scan
Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis
Usually, the health care providers prescribe the same medications as acute ones but with increased doses and time periods of Antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotics for 3-4 weeks are given
Painkillers, In order to relieve discomfort and pain, pain-alleviating drugs like ibuprofen and paracetamol, are usually suggested as Oral or topical decongestants.
Steroids- sometimes in order to reduce swelling of the lining of the sinuses, intranasal steroids are used, in severe cases, oral steroids are given.
Bioelectronic sinus device. This works with the aid of the use of microcurrents to stimulate nerve fibers in your sinuses. They are Sold as over-the-counter drugs.it enables to lessen sinus inflammation, pain, and congestion.
Surgery- In recurrent cases, surgeries can be done to relieve blockage and correct the anomalies some of them are listed -
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: The main goal of FESS is to restore sinus ventilation and mucociliary removal Small fiberoptic endoscopes are passed through the nasal cavity into the sinus cavity.
- External Spheno-Ethmoidectomy: It is a surgical procedure in which diseased mucosa from the ethmoid oral cavity is removed. A small incision is made to remove the diseased mucosa in the lateral sinus.Then a bundle of nasal and ethmoid mucosa.
- Nasal antrostomy: Maxillary antrostomy is a surgical procedure to enlarge the sinus opening allowing the here to heal.
- Antrum Puncture: Under the inferior turbinate, the trochar and cannula are placed around half an inch from the turbinate. The trochar entered the antral cavity after penetrating the nasoantral wall. The trochar is withdrawn, and the cannula is correctly inserted into the sinus cavity. The sinus cavity is irrigated with sterile nasal saline during this operation. The discharge exits the sinus by the natural ostium. Following the operation, a local anesthetic is administered, the cannula is removed, and the nose is cleansed.
- Intranasal Antrostomy: It is a procedure performed in which a permanent window near the maxillary floor helps in discharge drainage.
- Caldwell Luc surgery: Incision in the upper gum is given ,to open in the anterior wall of the antrum, excision of the whole sick maxillary sinus mucosa, and drainage into the inferior or middle meatus through a big window in the lateral nasal wall.
- Balloon Sinuplasty: This method,similar to balloon angioplasty which is used to unclog coronary arteries, employs balloons in an attempt to expand sinus openings in a less invasive manner.
Home Remedies
Although medicines usually help, many cases of sinusitis can be relieved on their own, without any medical treatment. Some treatments can be done at home too , some of them are using a
- Use a humidifier in rooms .
- steam taken from a bowl of warm water.can be taken
- The steam vapors taken in ease congested and swollen nasal passages.
- Application of warm heat.
- Try a nasal saline solution,they don't contain any medicine (saline is salt water), they can help keep your nasal passages moist.
- irrigating the nose with saline helps in clearing out mucus. They help in thinning of the mucus, which reduces the blockage in your sinuses.
Prevention
You may assist avoid sinus infections by doing everything you can to be healthy and keep others well, such as:
- Wash your hands.
- Get prescribed immunisations, such as influenza and pneumococcal vaccines.
- Stay distant from those who are suffering from colds or other upper respiratory illnesses.
Prognosis
A lot of cases of bacterial sinusitis can be cured as an outpatient with a favorable outcome. Frontal or sphenoid sinusitis with high amounts of air-fluid may necessitate hospitalization and intravenous (IV) antibiotics. Individuals who look to be immunocompromised or toxic necessitate hospitalization.
Complications
Acute sinusitis issues are uncommon, and serious issues are rare. If they occur, problems would possibly include:
- Chronic sinusitis. Acute sinusitis might also be a flare-up of a long-term hassle recognized as continual sinusitis. This continued sinusitis extends more than 12 weeks called chronic sinusitis. Meningitis. This infection motivates swelling of the fluid and membranes present around your brain and spinal cord.
- Others. Rarely, it can move to the bones causing osteomyelitis r pores and skin which causes cellulitis
- Vision problems. If the infection spreads to your socket of the eye, it can lead to decreased imaginative vision or even blindness, is usually everlasting
How Long Is It Contagious?
If a virus is a cause you may have been infected, days earlier than you bought the infection. Most viruses can unfold for simply a few days, however now and again you may want to ignore it for a week or more.









