Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a highly spreadable virus that causes a skin infection called molluscum contagiosum. MCV is a component of the poxvirus family and is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact or by...
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a highly spreadable virus that causes a skin infection called molluscum contagiosum. MCV is a component of the poxvirus family and is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact or by touching contaminated objects. The virus primarily involves children, sexually active adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
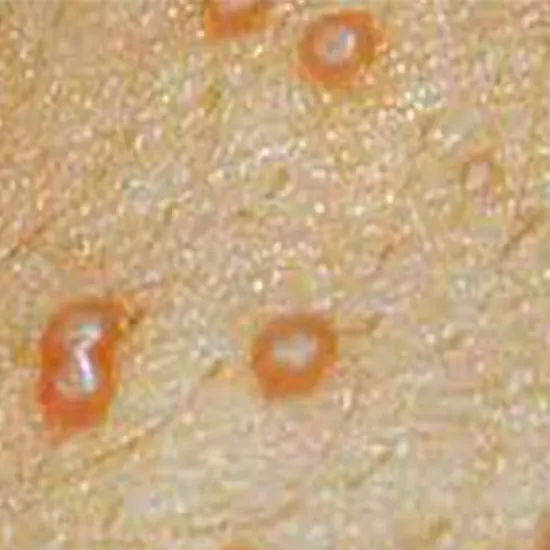
The infection causes the formation of small, raised, and painless bumps or lesions on the skin, typically on the face, neck, arms, and hands. These bumps can range in size from 2 to 5 mm and can be pink, white, or skin-colored. They often have a central indentation and a waxy or pearly appearance.
Molluscum contagiosum is usually a self-limited disease. However, treatment may be necessary to prevent the spread of the virus or to manage symptoms in people with weakened immune systems. Treatment options include physical removal of the lesions, topical antiviral medications, and cryotherapy (freezing the lesions).
Prevention measures include avoiding direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects, practicing good personal hygiene, and avoiding sexual contact with infected individuals. Vaccines against molluscum contagiosum are currently under development.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is primarily transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual. The virus can also be transmitted through touching contaminated objects, such as towels, clothing, toys, and gym equipment. Sexual contact with an infected individual can also lead to the transmission of MCV.
The risk of acquiring molluscum contagiosum is higher in children and sexually active adults, as they are more likely to come into close contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects.
Risk factors for acquiring molluscum contagiosum include:
1. Direct skin-to-skin connection with a contaminated individual
2. Sharing contaminated objects
3. Participation in contact sports or activities
4. Weakened immune system due to a medical condition or medication
5. Sexual connection with a contaminated person
Prevention measures include avoiding direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects, practicing good personal hygiene, and avoiding sexual contact with infected individuals. Vaccines against molluscum contagiosum are currently under development.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) typically presents with small, raised, and painless bumps or lesions on the skin, which are typically present on the face, neck, arms, and hands. These bumps can range in size from 2 to 5 mm and can be pink, white, or skin-colored. They often have a central indentation and a waxy or pearly appearance.
The lesions are usually firm and dome-shaped, and they may be surrounded by a pink or red rash. The bumps can occur singly or in clusters and may spread to other areas of the body through scratching or by coming into contact with the fluid from the bumps.
Molluscum contagiosum can also cause itching, especially as the lesions begin to heal.
In people with weakened immune systems, the lesions may be larger, more numerous, and more persistent, and they may be more likely to occur on the face, trunk, and genital area.
It's crucial to remark that not everyone infected with MCV will develop manifestations, and some people may only have a few lesions, while others may have many. Additionally, the incubation period for the virus can range from 2 weeks to 6 months, which means that symptoms may not appear immediately after infection.
Diagnosis of Molluscum Contagiosum Virus
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection of the skin caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is typically made by a visual examination of the affected area. The characteristic symptom of the condition is the appearance of small, raised, and round bumps on the skin, which can be flesh-colored, pink, or white. These bumps often have a central dimple or indentation and may be itchy, sore, or tender.
If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, a healthcare provider may perform a biopsy or a scraping of the affected area to confirm the presence of the virus. This is done by examining the skin cells under a microscope or using a specialized diagnostic test.
It is important to note that molluscum contagiosum can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions such as warts, chickenpox, or even skin cancer. Therefore, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment for Molluscum Contagiosum Virus
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral contamination of the pores and skin induced via the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is usually made via a visible examination of the affected area. The attribute symptom of the situation is the look of small, raised, and spherical bumps on the skin, which can be flesh-colored, pink, or white. These bumps frequently have a central dimple or indentation and may additionally be itchy, sore, or tender.
If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, a healthcare company may additionally function a biopsy or a scraping of the affected vicinity to verify the presence of the virus. This is accomplished employing analyzing the pores and skin cells underneath a microscope or the usage of a specialized diagnostic test.
It is vital to be aware that molluscum contagiosum can once in a while be wrong for different pores and skin prerequisites such as warts, chickenpox, or even pores and skin cancer. Therefore, it is essential to seek advice from a healthcare issuer for a correct prognosis and fabulous treatment.
Prevention and Control Measures
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a frequent viral pore and skin contamination that is without difficulty unfolded via skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated objects. To forestall MCV, you can take the following measures:
1. Avoid skin-to-skin contact with contaminated individuals: MCV is distinctly contagious, so keep away from direct skin-to-skin contact with humans who have energetic MCV lesions.
2. Practice suitable hygiene: Wash your arms regularly and keep away from sharing non-public gadgets such as towels, clothing, or toys that may also be contaminated with the virus.
3. Keep your pores and skin easy and dry: Keeping your pores and skin smooth and dry can assist forestall the virus from spreading.
4. Avoid scratching the affected area: Scratching the affected region can unfold the virus to different components of your body.
5. Practice protected sex: MCV can unfold through sexual contact, so the use of condoms throughout sexual recreation can assist decrease the threat of infection.
6. Boost your immune system: A wholesome immune machine can assist forestall and combat off MCV. Eating a healthful diet, getting sufficient sleep, and decreasing stress can all assist increase your immune system.
If you suspect that you have been uncovered to MCV or have developed symptoms, such as small, raised, pearly, or flesh-colored bumps on your skin, seek advice from a healthcare expert for prognosis and treatment.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis for Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is normally good, as the contamination is generally self-limited and resolves within 6-12 months in most cases. However, the length of the contamination can be longer in some people, especially in those with weakened immune systems.
Complications of MCV are rare, however, they can manifest in sure populations, such as:
1. Secondary bacterial infections: Scratching or choosing the MCV lesions can lead to secondary bacterial infections of the skin.
2. Eczema: MCV lesions can motivate eczema, a circumstance in which the pores and skin turn inflamed, itchy, and dry.
3. Disfigurement: MCV lesions can show up on the face or different seen areas of the physique and may also motivate embarrassment or self-consciousness.
4. Immune-compromised individuals: In humans with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or organ transplant recipients, MCV can be extra extreme and long-lasting.
It is vital to are seeking scientific interest if you advance any issues or have a weakened immune system. Your healthcare issuer can also propose cure alternatives to assist control the signs and stop additional complications.
Current Lookup and Developments
There is an ongoing lookup into the prevention, diagnosis, and therapy of Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Some cutting-edge lookup and trends include:
1. Vaccines: Researchers are working to increase a vaccine that can stop MCV infection. Early research has proven promising consequences in animal models, however, similarly, lookup is wished to take a look at the security and efficacy of the vaccine in humans.
2. Topical treatments: Topical treatments, such as imiquimod and cantharidin, have proven efficacy in treating MCV lesions. However, there is a want for the extra lookup to decide the most useful dosing and period of treatment.
3. Immunomodulators: Immunomodulatory agents, such as cidofovir, have proven promise in treating MCV infections in immune-compromised individuals. However, extra research is wanted to decide the most beneficial dosing and security of these agents.
4. Diagnosis: Researchers are investigating new techniques for diagnosing MCV infections, such as PCR-based assays and imaging techniques. These strategies might also assist enhance the accuracy of analysis and limit the want for invasive diagnostic procedures.
5. Epidemiology: Researchers are analyzing the epidemiology of MCV, inclusive of the occurrence of contamination in one-of-a-kind populations and the hazard elements for infection. This data can assist inform prevention techniques and cure guidelines.
Overall, ongoing lookups and traits in the subject of MCV are desired at enhancing the lookups, diagnosis, and cure of this frequent viral infection.








.webp)







