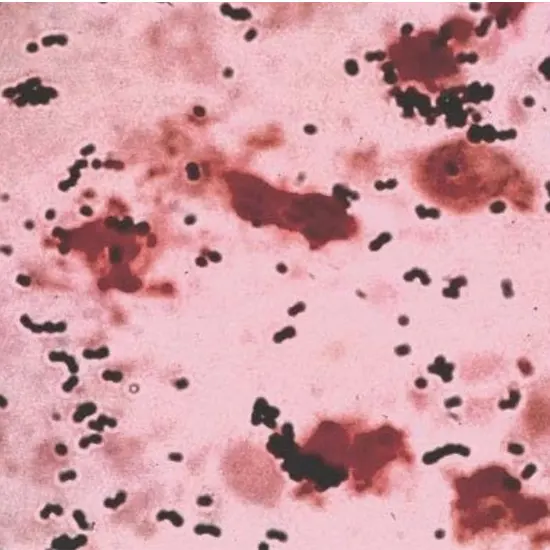
Streptococcus agalactiae, additionally recognised as Group B Streptococcus (GBS), is a kind of microorganism that is generally determined in the human body, especially in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts.
Streptococcus agalactiae, additionally recognised as Group B Streptococcus (GBS), is a kind of microorganism that is generally determined in the human body, especially in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts. In wholesome individuals, S. agalactiae is normally innocent and asymptomatic, however, it can cause serious infections in prone populations, such as newborns, pregnant women, and humans with weakened immune systems.
In pregnant women, S. agalactiae can cause infections of the urinary tract, amniotic fluid, and foetal membranes, which can lead to preterm labour, stillbirth, or neonatal sepsis. In newborns, S. agalactiae infections can reason sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis, which can be life-threatening.S. agalactiae is a necessary pathogen in the healthcare setting, and its prevention and administration require vigilant screening, splendid antibiotic prophylaxis, and instant cure of contaminated individuals.
What is Streptococcus agalactiae?
Streptococcus agalactiae, additionally recognized as Group B Streptococcus (GBS), is a kind of gram-positive microorganism that is generally discovered in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts of humans. In healthful individuals, S. agalactiae is normally innocent and asymptomatic, however, it can cause infections in prone populations such as newborns, pregnant women, and human beings with weakened immune systems.
S. agalactiae is a vital pathogen that can motivate serious infections such as urinary tract infections, amniotic fluid infections, foetal membrane infections, sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis. In pregnant women, S. agalactiae can be transmitted to the child in the course of transport and bone scans motivate extreme infections in the newborn. Therefore, it is vital to discover and display screen pregnant females for S. agalactiae colonisation and supply suitable antibiotic prophylaxis to stop the transmission of the microorganism to the baby
Epidemiological facts of Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) is a frequent human commensal bacterium that is determined in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts of 10-30% of wholesome adults.
The occurrence of GBS colonisation varies using geographical location, ethnicity, and different factors. In pregnant women, the incidence of GBS colonisation degrees from 10-30%, with greater prices stated in some populations.
Maternal GBS colonisation is the most necessary danger element for early-onset neonatal GBS disease, which takes place within the first 7 days of life and is related to excessive mortality rates.
Invasive GBS ailment is greater frequent in sure populations, inclusive of infants, aged adults, and persons with underlying scientific conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and immunodeficiency.
Invasive GBS ailment is additionally greater frequent in certain racial and ethnic groups, which include African Americans and Hispanics, in contrast to Caucasians.
In recent years, there has been a decline in the incidence of early-onset neonatal GBS disorder in many nations due to full-size screening and antibiotic prophylaxis for pregnant women.
However, the incidence of the onset of neonatal disorders and invasive ailments in nonpregnant men and women has remained secure or barely increased. Therefore, persevered surveillance and prevention efforts are fundamental to limiting the burden of GBS disease.
Explore the Pathophysiology of Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) is a pathogenic microorganism that can purpose a variety of infections in humans, such as urinary tract infections, amniotic fluid infections, foetal membranes infections, sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis.
The pathophysiology of GBS infections is complicated and entails a couple of mechanisms. GBS can produce a variety of virulence factors, along with tablet polysaccharides, lipoteichoic acid, floor proteins, and hemolysins, that assist the microorganism stay away from the host immune gadget and colonise host tissues.
Invasive GBS ailment takes place when the microorganism breaches the host's mucosal boundaries and enters the bloodstream, mainly to sepsis or different systemic infections.
The microorganism can additionally invade and injure host cells and tissues, mainly to organ dysfunction and different complications.GBS infections can additionally set off the host's immune response, mainly to the launch of cytokines and different inflammatory mediators.
In extreme infections, the host's immune response can come to be dysregulated and lead to systemic inflammation, organ damage, and sepsis.
The pathophysiology of GBS infections is additionally influenced by the host factors, consisting of age, sex, immune status, and underlying clinical conditions.
In particular, newborns and pregnant girls have an extended chance of GBS infections due to the immaturity of the neonatal immune gadget and the hormonal and anatomical adjustments that appear in the course of pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms of Streptococcus agalactiae
The signs and symptoms and signs of Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) contamination can range depending on the kind and severity of the infection, as well as the age and immune reputation of the affected individual.
In pregnant women, GBS infections may additionally no longer motivate any symptoms, however, can lead to issues such as
- Urinary tract infection
- Amniotic fluid infections,
- Foetal membrane infections
- Chorioamnionitis (infection of the foetal membranes).
These infections can cause:
- Fever
- Stomach pain
- Legs pain
- Uterine tenderness
- Preterm labour
In newborns, GBS infections can cause:
- Sepsis (bloodstream infection)
- Pneumonia (lung infection)
- Meningitis (brain and spinal twine infection)
- Encompass fever
- Terrible feeding
- Lethargy
- Irritability
- Respiratory distress
- Apnea
- Seizures
- Attributed rash or blisters
In nonpregnant adults, GBS infections can motivate
- Urinary tract infections
- Pores and skin and gentle tissue infections sepsis
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
The signs and symptoms and signs of GBS infections in adults can encompass
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Joint pain
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Confusion
- Seizures
It is vital to be aware that some persons with GBS infections can also now not have any signs and symptoms or might also have slight signs and symptoms that go unrecognised. Therefore, early detection and gorgeous therapy of GBS infections are indispensable to stop issues and enhance outcomes.
Diagnosis of Streptococcus agalactiae
The analysis of Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) contamination entails an aggregate of clinical, laboratory, and imaging studies.
In pregnant women, screening for GBS colonisation is normally carried out between 35 and 37 weeks of gestation with the usage of a vaginal and rectal swab. The swabs are cultured in the laboratory to realise the presence of GBS.
In the way of life is positive, prophylactic antibiotics are advocated at some stage in labour and shipping to decrease the threat of GBS transmission to the newborn.
In newborns and nonpregnant adults, the prognosis of GBS contamination is based totally on scientific signs and signs, as nicely as laboratory tests.
Blood cultures are the most frequent laboratory take a look at used to diagnose GBS bloodstream infections (sepsis), whilst cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cultures are used to diagnose GBS meningitis.
Other laboratory tests, such as urine cultures, respiratory cultures, and wound cultures, may additionally be used to diagnose different kinds of GBS infections.
Imaging studies, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, can also be used to diagnose GBS pneumonia or different kinds of GBS infections that contain organ structures different from the bloodstream or apprehensive system.
In addition to laboratory assessments and imaging studies, different diagnostic exams may also be used to consider the severity and extent of GBS infection.
These may additionally encompass whole blood counts (CBC), inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) or procalcitonin (PCT), and blood fuel analysis. Prompt and correct prognosis of GBS infections is necessary to inform fabulous therapy and forestall complications.
Complications of Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) infections can lead to a variety of complications, specifically if they are no longer straight away recognized and treated.
In pregnant women, GBS infections can lead to problems such as
- untimely rupture of membranes
- preterm labour
- chorioamnionitis (infection of the foetal membranes).
These problems can create the threat of
- foetal distress
- preterm delivery
- neonatal sepsis.
In newborns, GBS infections can cause serious issues such as
- sepsis (bloodstream infection),
- pneumonia (lung infection),
- Meningitis (brain and spinal wire infection).
These issues can lead to long-term
- Neurodevelopmental impairment,
- Listening loss,
- Imaginative
- Prescient problems.
- In extreme cases, GBS infections can be fatal, in particular in untimely or low beginning-weight infants.
- In nonpregnant adults, GBS infections can additionally motivate serious issues such as
- Sepsis
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- gentle tissue infections such as cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis.
These problems can lead to
- Septic shock
- Organ failure
- Even death
In addition to the immediate problems of GBS infections, some folks may also experience long-term problems such as persistent pain, disability, and a decreased life.
Therefore, it is essential to rapidly diagnose and deal with GBS infections to limit the hazard of problems and enhance outcomes.
Prophylactic antibiotics at some stage in labour and transport for pregnant females with GBS colonisation can assist forestall neonatal GBS infection and gorgeous antibiotic cure for newborns and nonpregnant adults with GBS contamination can assist forestall serious complications.
Treatment of Streptococcus agalactiae
The therapy of Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) infections relies upon the kind and severity of the infection, as nicely as the age and fitness popularity of the affected individual.
In pregnant girls who take a look at wonderful GBS colonisation, prophylactic antibiotics such as penicillin or ampicillin are advocated at some stage in labour and transport to decrease the danger of transmitting GBS to the newborn.
In newborns with GBS infection, antibiotics such as penicillin, ampicillin, or a mixture of antibiotics may additionally be used to deal with the infection.
The preference for antibiotics and period of remedy relies upon the severity and kind of infection, as well as the age and fitness repute of the infant.
In nonpregnant adults with GBS infection, antibiotics such as penicillin, ampicillin, or an aggregate of antibiotics are normally used to deal with the infection. The desire for antibiotics and period relies on the kind and severity of the infection, as well as the age and fitness fame of the affected individual.
In some cases, extra supportive care such as oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, and mechanical air flow may additionally be necessary.
It is essential to use fantastic antibiotics and the full path of therapy to ensure the eradication of the microorganism and forestall the improvement of antibiotic resistance.
In addition, prevention efforts such as screening for GBS colonisation in pregnant women, fabulous use of antibiotics, and adherence to contamination management measures in healthcare settings can assist in limiting the spread of GBS and stopping infection.
Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) is a kind of microorganism that can cause a variety of infections, mainly in pregnant women, newborns, and nonpregnant adults with weakened immune systems. Prompt and correct diagnosis, excellent antibiotic treatment, and prevention efforts such as screening and contamination management measures are essential to minimtold goldldingold gold of GBS and forestall issues.
Prevention is Key : Stop the Spread of Streptococcus agalactiae!