Stomach cancer (gastric cancer) is a cancer that develops in the lining of the stomach. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated.
Stomach cancer (gastric cancer) is a cancer that develops in the lining of the stomach. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated.
Types of stomach cancer
There are several types of stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, which can be classified based on the location of the tumor in the stomach and the type of cells that make up the tumor.
The primary types of stomach cancer include:
Adenocarcinoma: This is the most common type of stomach cancer, accounting for about 95% of all cases. It develops from the glandular cells that line the inner surface of the stomach.
Lymphoma: This is a rare type of stomach cancer that develops from the lymphatic tissue in the stomach. It accounts for about 4% of all stomach cancers.
A gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): This is a rare type of stomach cancer that develops from the specialized cells that control the movement of food through the digestive system. It accounts for about 1% of all stomach cancers.
Carcinoid tumor: This is a rare type of stomach cancer that develops from the hormone-producing cells in the stomach. It accounts for less than 1% of all stomach cancers.
Squamous cell carcinoma: This is a rare type of stomach cancer that develops from the cells that make up the lining of the stomach. It accounts for less than 1% of all stomach cancers.
Stages of stomach cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is staged based on the size and extent of the tumor, as well as the degree of spread to nearby lymph nodes and distant organs. The most common staging system for stomach cancer is the TNM system, which takes into account the following factors:
T stage : This refers to the size and extent of the primary tumor.
N stage : This refers to the degree of spread to nearby lymph nodes.
M stage : This refers to the presence or absence of distant metastasis (spread of cancer to other organs).
Using this system, the stages of stomach cancer can be classified as follows:
Stage 0 : Also known as carcinoma in situ, this stage refers to cancer cells that are confined to the inner layer of the stomach lining and have not spread to other tissues.
Stage I : Cancer has invaded deeper layers of the stomach lining, but has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Stage II : Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or through the muscle layer of the stomach wall, but has not yet spread to distant organs.
Stage III : Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes and through the muscle layer of the stomach wall, and may also involve nearby structures such as the pancreas or spleen.
Stage IV : Cancer has spread to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, or bones.
The treatment and prognosis of stomach cancer depend on the stage of cancer at the time of diagnosis, as well as other factors such as the patient's age and overall health. Early detection and treatment offer the best chance of a good outcome.
Symptoms of stomach cancer
Stomach cancer may not cause any symptoms in the early stages, but as the disease progresses, the following symptoms may occur:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Feel full even after consuming a very small quantity of food
- Blood in the stool
- Fatigue
Causes of stomach cancer
There are various causes/ risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing stomach cancer disease. These include:
_1679721004.webp)
Age : Individuals of age group more than 50 are at higher risk of having stomach cancer.
Gender : Compare to women, men are more likely to develop stomach cancer.
Helicobacter pylori infection : This is a bacterial infection that can cause stomach inflammation and increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
Family history : If a close relative has had stomach cancer, your risk of developing the disease is increased.
Smoking : Smoking increases the risk of developing many types of cancer, including stomach cancer.
Diet : A diet high in smoked, salted, or pickled foods and low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
Benefits of early detection of stomach cancer
Early detection of stomach cancer can offer several benefits, including:
Better treatment options : When stomach cancer is detected early, it may be possible to treat cancer with surgery, which offers the best chance for a cure. In some cases, other treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy may also be used.
Improved prognosis : The earlier stomach cancer is detected, the better the chance of a good outcome. When stomach cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, the five-year survival rate can be as high as 90%.
Reduced risk of complications : Stomach cancer can cause a range of complications, including bleeding, obstruction of the digestive system, and malnutrition. Early detection and treatment can help reduce the risk of these complications.
Reduced need for aggressive treatment : If stomach cancer is not detected until it has advanced, aggressive treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy may be necessary. Early detection may make it possible to use less aggressive treatments or to avoid these treatments altogether.
Peace of mind : Regular screening for stomach cancer can provide peace of mind, knowing that any potential cancer will be detected early and treated promptly.
Overall, early detection of stomach cancer can improve outcomes, reduce the need for aggressive treatment, and provide peace of mind for patients and their families. Regular screening is recommended for individuals at high risk of developing stomach cancer, such as those with a family history of the disease or a history of certain gastrointestinal conditions.
Prevention of stomach cancer
There is no sure way to prevent stomach cancer, but there are several steps that may help reduce the risk of developing the disease, including:
- Adding healthy diet that includes fruits and vegetables in your routine.
- Quitting smoking.
- Treating and preventing Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Getting regular exercise.
- Limiting alcohol consumption.
- Undergoing regular screening if you are at high risk for stomach cancer.
Diagnosis of stomach cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and various tests.
Physical examination : During a physical exam, a doctor will examine the abdomen for any lumps or masses.
Medical history : A doctor will ask about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and family history of cancer.
Blood Test : Blood tests are performed to know about the functioning of the organs. Because poor organ functioning is an indication of cancer spreading to that particular organ. So, LFT, KFT, and complete hemogram tests are usually recommended.
Imaging tests : Imaging tests such as an X-Ray barium, CT abdomen scan, MRI abdomen scan, Ultrasound abdomen and ultrasound Pelvis, and Whole Body PET scan may be used to produce detailed images of the stomach and surrounding tissues.
Endoscopy : An endoscopy involves passing a thin, flexible tube with a camera down the throat and into the stomach to examine the lining of the stomach and take biopsies if needed.
Biopsy : A tissue sample is taken from the stomach during an endoscopy or surgery and examined under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present.
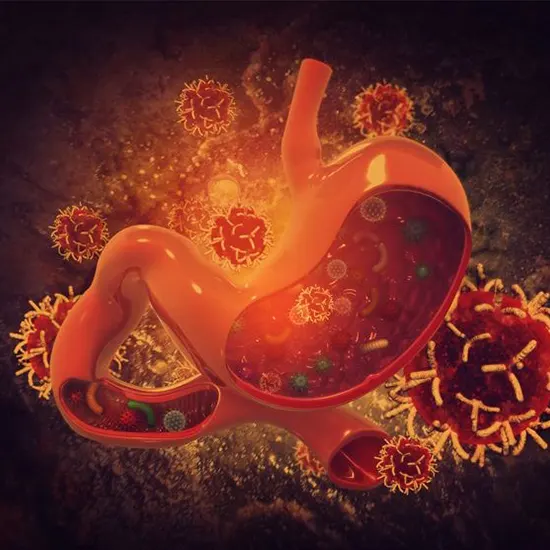
Once a diagnosis of stomach cancer is confirmed, further tests may be done to determine the stage of cancer and the extent of its spread. Treatment options will depend on the stage and location of cancer.
Conclusion
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a type of cancer that occurs when cancer cells develop in the lining of the stomach. It is 5th most common cancer type and the 3rd leading cause of cancer-related deaths over the globe. It often develops slowly over several years and can go unnoticed in the early stages. Some common symptoms of stomach cancer include nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, bloating, and weight loss.
The exact cause of stomach cancer is not known, but certain factors can increase the risk of developing it, such as a family history of the disease, smoking, and a food high in salt and pickled foods. Treatment for stomach cancer depends on the stage and location of cancer. Prevention of stomach cancer involves maintaining a healthy diet that is low in processed and smoked foods, quitting smoking, and getting regular check-ups if you have a family history of the disease.
Ganesh Diagnostic offers a comprehensive stomach cancer screening package for the early detection of stomach cancer and for determining the risks of developing cancer. If you are having any queries regarding the stomach cancer and diagnosis package, please feel free to communicate with our healthcare executives.









