In this blog, we will discuss about Meningitis a disease of the brain and spinal cord in detail
Meningitis is a disease caused by the inflammation of the tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord, also called as spinal meningitis, infectious diseases like viruses, fungi, bacteria or any kind of head injury can cause meningitis.
What are the Different types of Meningitis?
- Spinal meningitis: Commonly known as meningitis, it is the inflammation of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord
- Aseptic meningitis: In this, the fluid(CSF) surrounding your brain and spinal cord test negative for the bacteria indicating that the bacteria is not responsible for causing infection but may be due to viral infection
- Parasitic meningitis: Meningitis caused by parasitic infection also called as eosinophilic meningoencephalitis
- Primary amebic meningitis: caused by the Amoeba Naegleria fowleri
- Drug-induced aseptic meningitis: Drugs like Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics can cause
- Chronic meningitis: Prolonged meningitis that lasts for a month or more is called Chronic meningitis
- Acute meningitis: A condition in which the symptoms become severe. Often, bacterial meningitis is acute and is called acute meningitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms differ in babies as compared to children and adults, the symptoms include headache and neck stiffness, which can worsen if untreated
Symptoms of meningitis in children and adult
- Neck stiffness.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- photophobia(Sensitivity to light) .
- Confusion or altered mental state.
- Feeling Lethargic
- Extreme sleepiness.
- Lack of appetite.
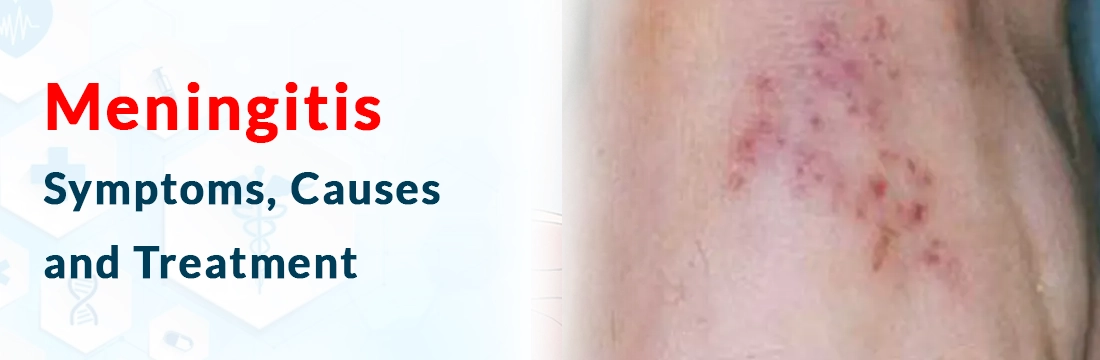
- Small round spots that look like a rash
Symptoms in Babies
- Bulging “soft spot” (fontanelle) on baby’s head.
- Poor eating.
- Sleepiness or trouble waking up from sleep.
- Low energy or slower responses (lethargy).
Causes
Causes of infections include Bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses, Non-infectious include diseases, certain medications and other conditions.
Causes of Bacterial Meningitis
- Streptococcus pneumonia.
- Group B Streptococcus.
- Neisseria meningitides.
- Haemophilus influenza.
- Listeria monocytogenes.
- E. coli.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Causes of Viral Meningitis
- Non-polio enteroviruses.
- Mumps.
- Herpesviruses (including those that cause mononucleosis, chickenpox and shingles).
- Measles.
- Influenza.
- Arboviruses, such as West Nile virus.
- Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.
Causes of Fungal Meningitis
Causes of Parasitic Meningitis
Causes of amebic meningitis
Causes of non-infectious meningitis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus).
- Certain medications, like NSAIDs and antibiotics.
- Head injuries.
- Brain surgery
How do you get meningitis?
- It can be passed from person to person, like a virus or bacteria.
- Through contaminated food and water.
- Fungal infection is caused if there is any fungus in the environment.
- Through non-infectious illnesses, like cancer or lupus.
- Any head injury or brain surgery.
- As a side effect of a medication.
Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of Meningitis can be done through physical examination in which your doctor will ask you about the symptoms and testing cerebrospinal fluid and will ask you about your travel history and will perform blood tests and stool examination if required.
Test to diagnose meningitis
Some tests your healthcare provider may use to diagnose meningitis include:
- Nasal or throat swab: In this, Your provider uses a soft-tipped stick (swab) to take a sample from your nose or throat to check for signs of infection.
- Lumbar puncture/spinal tap: Your healthcare provider inserts a needle into your lower back to collect a sample of your cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to test for any signs and infection
- Blood test: A Blood test will be performed to check for any kind of blood infection
- MRI and CT scan: Your healthcare provider can use a CT scan or MRI to take pictures of your brain and look for inflammation. This is sometimes called a brain scan.
- Stool sample examination. A lab test will be done to test your stool sample for signs of infection.
Management and Treatment
Meningitis can be treated by taking vaccines to enhance immunity against bacteria and infection, practising safe food handling and maintaining personal hygiene, your healthcare provider may recommend some antibiotics to reduce infection.
Vaccines
Vaccines against Bacteria: vaccines for meningococcal disease, pneumococcal disease, Haemophilus influenzae serotype b (Hib) and tuberculosis all help to protect you from bacterial infections that can lead to meningitis.
Vaccines against Viruses: Vaccines for chickenpox, influenza, measles and mumps help to protect you from viral infections that can lead to meningitis
Other Measures:
- Wash your Hands frequently
- Maintain Personal hygiene
- Cover your mouth and nose while sneezing, coughing
- Avoid contact with other people if you have any contagious disease
- Dont eat uncooked meat and seafood
- Wear a mask in dusty areas to avoid the risk of fungal infection
- A pregnant Lady can go for a test like Group B streptococcus which helps you to know if the baby has a high risk of infection for meningitis, Ask your healthcare practitioner for the test.
What is the Cost of a Meningitis test in India?
The cost of a Meningitis test typically ranges from Rs.5500-10000 but you can choose Ganesh Diagnostic in delhi which provides a Meningitis Package at a 50 per cent discount So get assistance and treatment from a team of well-experienced doctors at our centre, Book now
A note from Ganesh Diagnostics
Meningitis is an uncommon condition that can quickly become life-threatening. If you’re treated right away, you have a great chance of a full recovery. If you have symptoms of meningitis, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately, Get the best care and treatment with a top diagnostic centre and improve your well-being
People may Ask
What is Meningitis?
It is the infection of the soft tissue surrounding the Brain and spinal cord usually caused by Bacterial, viral and fungal infection
What can I expect if I have meningitis?
It depends upon when you get treated you can usually make a full recovery, though it can take a long time to feel completely well again.
How long does meningitis last?
Viral meningitis can go away on its own within about a week. Symptoms of bacterial or fungal meningitis may last a few days to a week or more after treatment. It can take weeks to months for complete recovery
What are the long-term effects of Meningitis
- Vision or hearing loss.
- Trouble with memory and concentration.
- Epilepsy.
- Movement and balance issues.
- Behavioral issues or learning difficulties in kids.
- Arthritis.
- Organ damage.
- Loss of fingers, toes or limbs due to sepsis









