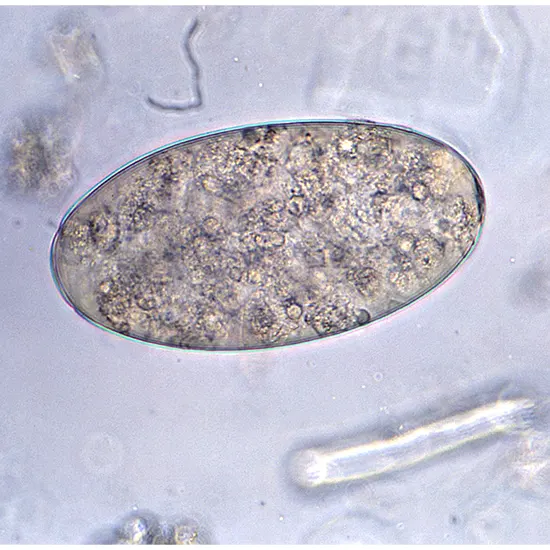
Fasciolopsis buski is a parasite that causes a variety of human symptoms. This parasite is most common in Southeast Asia, but has also been documented in other regions of the globe. Symptoms of infection can range from mild...
Fasciolopsis buski is a parasite that causes a variety of human symptoms. This parasite is most common in Southeast Asia, but has also been documented in other regions of the globe. Symptoms of infection can range from mild abdominal pain and diarrhea to severe anemia and liver damage.
This post explores the fascinating world of Fasciolopsis buski, including its life cycle, symptoms of infection, and options for prevention and treatment. You will have a better grasp of this parasite by the end of this essay, and you will be more equipped to prevent and cure infections in yourself and your loved ones.
What is Fasciolopsis buski?
Fasciolopsis buski is a parasitic flatworm common in Southeast Asia, especially in rural areas with poor sanitation. Also known as giant fluke due to its size, some specimens reach 7.5 cm long and 3 cm wide.
The life cycle of Fasciolopsis buski involves multiple hosts, including snails and freshwater plants. Parasite eggs are released in the faeces of infected individuals and can contaminate water sources such as ponds and paddy fields.
When these eggs hatch, they release larvae that infect the snail, where they develop into cercariae. The cercariae are then released into the water, where they can enter via the skin or be consumed along with tainted food or plants to infect people and other animals. When Fasciolopsis buschii enters the human body, it can cause various symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and malnutrition.
In severe cases, the parasite can cause intestinal obstruction and lead to life-threatening complications. Prevention of Fasciolopsis buski infection includes improved hygiene and sanitation practices such as: B.
Use clean water sources, wash vegetables properly, and practice good hand hygiene. Treatment usually includes drugs that target the parasite, such as praziquantel and triclabendazole.
Fasciolopsis buski infections are relatively rare in developed countries, however they continue to be a serious issue for global public health, particularly in places with inadequate hygienic conditions and access to medical care.
Understanding the life cycle and symptoms of this parasite is essential for effective prevention and treatment.
How is Fasciolopsis buski transmitted?
Fasciolopsis buski is a water-borne parasitic infection that occurs when humans ingest metacercarial cysts in contaminated freshwater plants. Cysts are found on the surface of aquatic plants and on the leaves of vegetables that have been watered with contaminated water. Eating these raw or undercooked plants and vegetables can lead to Fasciolopsis buski infection.
In addition to direct transmission through contaminated plants and vegetables, Additionally, tainted drinking water might spread fascioliopsis buski. The parasite can survive in water for up to 6 months and can be contracted by consuming contaminated water or food washed with contaminated water.
Fasciolopsis buski infection is not contagious and cannot be passed from person to person. Infection is transmitted only by ingesting cysts of the parasite that are excreted in the faeces of an infected person.
To prevent transmission of Fasciolopsis buski infection, it is recommended to avoid eating raw or undercooked aquatic plants and vegetables, particularly in regions where the parasite is widespread. Boiling, roasting, or steaming these plants and vegetables can also help kill potential cysts. Additionally, it's crucial to make sure that all food is prepared thoroughly and that drinking water is obtained from a reputable source.
Symptoms of Fasciolopsis buski infection
Fasciolopsis buski is a parasite that infects humans by eating contaminated water or vegetables. In the human body, worms can grow up to 75 mm long and live for several years.
In the early stages of infection, there may be no symptoms at all, but symptoms may appear as the worm grows and moves through the body. Common symptoms of Fasciolopsis buski infection include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and weight loss. In some cases, infections can cause anemia, jaundice, and liver damage.
In more severe cases, worms can cause bile duct blockages, leading to bile duct infections or cholangitis, which can cause fever, abdominal pain, and jaundice. In rare cases, infection can lead to life-threatening sepsis.
It is crucial to get medical assistance as soon as you can if you have any of these symptoms and have recently consumed contaminated water or veggies. Early detection and intervention can lessen the risk of complications and permanent harm.
Diagnosis of Fasciolopsis buski infection
Fasciolopsis buski symptoms are similar to those of other bowel illnesses, making the diagnosis of the infection challenging. A definitive diagnosis is therefore based on the detection of parasite eggs in the stool.
Diagnosis can be confirmed by stool examination using various techniques such as the Kato-Katz method, formalin ether enrichment, and direct wet examination.
If you suspect you have Fasciolopsis buski, it's important to see a doctor right away. A medical professional can perform the necessary tests to confirm the presence of parasites and advise on appropriate treatment.
Also, symptoms may not appear immediately after infection, and in some situations, it could be months before symptoms start to show. It is crucial to frequently get tested if you have travelled to a region where Fasciolopsis buski is endemic in order to detect it early and receive treatment if necessary.
Preventive measures against Fasciolopsis buski infection
Fasciolopsis buski, also known as the giant intestinal fluke, is a parasite that can seriously harm a person's health and lead to anaemia, starvation, and even death. Avoiding this infection altogether is the best course of action.
The most effective way to prevent Fasciolopsis buski infection is to avoid eating raw or undercooked aquatic plants such as water chestnuts, watercress, and bamboo shoots. These plants are the primary hosts for the larval stage of the parasite, and eating them can lead to infection.
Another important precaution is to avoid drinking contaminated water, especially from ponds, streams and rivers known to be infected with Fasciolopsis buski. It is also important to follow good hygiene and hygiene practices such as: B. Wash hands before eating, boil water before drinking, and prepare all food properly.
People who are at a high risk of contracting an infection, such as those who reside in endemic regions or whose line of work requires them to come into contact with polluted water, should have routine medical screening and treatment to stop infection. Or it can be detected early when it is easier to treat.
Overall, prevention is key to avoiding her Fasciolopsis buski infection, and taking the necessary precautions can protect her health and well-being.
Treatment options for Fasciolopsis buski
Fasciolopsis buski is a parasite that can cause serious harm to humans. If you suspect you have this parasite, it's crucial to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
The most effective treatment for Fasciolopsis buski is drug therapy. There are several anthelmintic drugs that can be used to kill parasites, such as praziquantel, bithionol, and niclosamide. These medications kill parasites by assaulting their nerve systems, paralysing them, and ultimately rendering them unconscious.
In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove large numbers of parasites from the body. This is especially true if the parasite has severely damaged the liver or other organs.Surgery may also be needed to remove the blockage caused by the parasite.
In addition to medication and surgery, it is important to follow good hygiene practices to prevent the spread of Fasciolopsis buski. This entails often washing your hands, staying away from water sources that may be polluted, and properly cooking all food before consuming it.
It's crucial to visit a doctor as soon as possible if you think you may have fasciolopsis buski. Proper treatment and preventive measures can effectively manage and control this parasitic infection.









