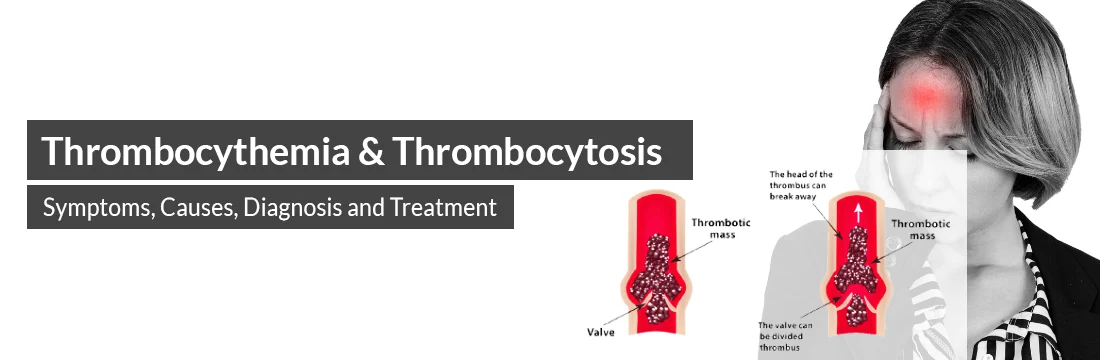
We will discuss in this blog the disease caused due to high platelet count in the blood(Thrombocythemia & Thrombocytosis) in detail.
Thrombocythemia and thrombocytosis both condition are both caused by the higher platelet count in the blood platelets are the small tiny cells produced in the bone marrow and released when your body gets injured these platelets get stuck together resulting in the formation of blood clots that help seal the wound, The normal platelet count ranges from 150,000-450,000 that is considered as a good healthy count requires during the blood clotting platelet count above the normal range can lead to the formation of blood clots in blood vessels that can block the blood flow through the body.
Thrombocythemia: Refers to high platelet count not caused due to the other health condition also called as primary thrombocythemia.
Thrombocytosis: refers to a high platelet count caused due to other health conditions also called as secondary thrombocytosis. It is more common than Thrombocythemia.
Symptoms of Thrombocythemia
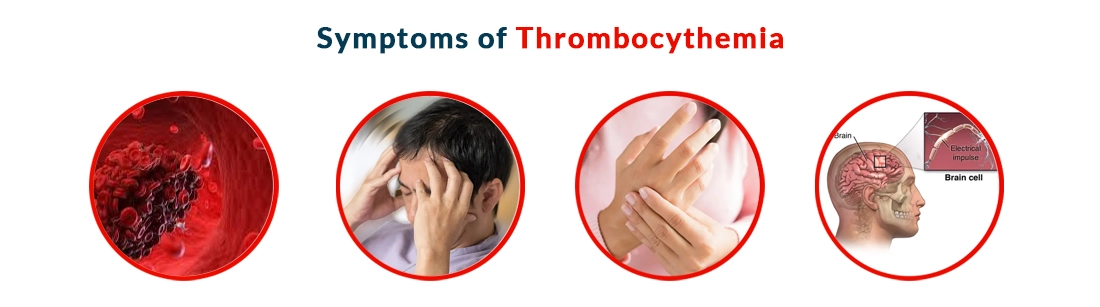
High platelet count in the blood usually does not have any early symptoms and this condition can be confirmed only during a routine blood test the symptoms include clotting and bleeding disorder
Blood clots
Thrombocytopenia often develops in the brain, hands, and feet and clots can develop anywhere in the body blood clots in the brain can lead to chronic conditions like Dizziness and headaches long-term can lead to transient ischemic attacks and strokes.
Other symptoms include:
- Confusion
- Migraines
- Seizures
- Numbness in hands and feet
- Upper body discomfort in one or both arms, your back, neck, jaw, or abdomen
- Shortness of breath and nausea
- Chest pain
- Pregnancy complications.
Bleeding
High platelet count can also lead to bleeding such as nose bleed, blood in stool and bleeding from the mouth and gums.
Bleeding can be due to many reasons when your body has any cut or injury and not enough platelets are available to clot the blood or due to abnormalities in the platelet functioning, or high platelet count in the blood may be due to a condition called Von Willebrand disease that affects how your blood clot.
Causes of Thrombocythemia & Thrombocytosis

Thrombocythemia
This condition is developed due to the high platelet count in the blood and may have both genetic and environmental causes, this condition is most often caused by changes in the genes responsible for making platelets in the blood, the genes include JAK2, CLAR and MPL as this condition is inherited this is passed from parents to their offspring
Primary Thrombocyhrtemia affects people over age 50-70 and it is more common in women than in men.
Thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis occurs when your blood platelet count is high due to any health condition this condition is less severe than thrombocythemia and lower risk of clots and bleeding, this condition is more common than thrombocythemia.
Medical conditions that can increase the risk of thrombocytosis include
- Anaemia: Anaemia is a disease caused by the deficiency of iron or haemoglobin in the blood due to which the body is not able to make enough Red blood cells(RBC) required for carrying out the oxygen throughout the body.
- Cancer: High platelet count can lead to cancerous conditions like ovarian cancer, lymphoma, gastrointestinal, breast cancer etc.
- Inflammations and infections: conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, tuberculosis and connective tissue disorder can raise the platelet count
- Splenectomy(Removal of the spleen): In severe conditions when your spleen overstores the platelets the spleen is removed which helps increase platelet count in blood possible complications include bleeding, infection and abnormal blood clots.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of thrombocythemia includes a blood test or checking the medical history of a patient or if a person has a history of passing down the disease(Inherited)
Your healthcare provider may suggest the following blood tests.
- Complete Blood count (CBC) test: This is a routine blood test that checks for the platelet count and other red blood cells.
- Blood smear: This test includes the microscopic examination of the blood smear under the microscope.
- Bone marrow test: This test checks for the bone marrow condition if it is healthy.
- Genetic testing: It checks for the mutation or changes in the genes that make your platelets.
Treatment
The symptoms of both conditions are analysed and if the condition is confirmed through proper diagnosis the doctor will give you suggestions regarding how to cure the condition and minimise the risk factors in the future People with thrombocythemia do not require any treatment but under certain conditions, it may require medication to treat the condition
Medication Includes
-
Anagrelide: This medicine is used to lower platelet counts Anagrelide also has side effects, such as fluid retention, palpitations, arrhythmias, heart failure, and headaches.
- Aspirin: This medicine helps prevent blood clots. It is mostly used by people with low blood risk of blood clots and if you have a high risk of blood clots, you may need to take both aspirin and hydroxyurea.
- Hydroxyurea: It is used to treat cancers and sickle cell disease by lowering the platelet count.
- Interferon alfa: It lowers platelet counts, but it may have serious Side effects like decreased appetite, nausea, diarrhoea, seizures, irritability, and sleepiness.
Other procedures to lower platelet count include
Plateletpheresis: It lowers the platelet count quickly during emergencies like stroke due to the primary Thrombocythemia
People with thrombocythemia may undergo blood transfusions in which a needle is used to insert an intravenous line that removes the platelets from your blood to lower down to its normal level
Conclusion
Thrombocythemia is one of the severe conditions that have potentially harmful effects on our body if not treated early it may lead to clotting and bleeding problems the higher platelet count in the body can be lowered down to its normal through special medicines, and surgery but first diagnose the condition through a blood test and get treated well by choosing the best diagnostic centre near you.
FAQs
What if My platelet count is high?
High platelet count is generally due to iron deficiency, spleen removal etc
What is the normal range of platelet count?
The normal platelet count range is 1,50,000 - 4,50,000 platelets/ microliter of the blood of a healthy person.
How can I download my report?
You can download the report from our website Ganesh diagnostic.com
What are the preparation required for this test?
No special preparation is required you only need to give a blood sample collection for lab testing.
















