Carcinoma could be a threat that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma could be cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or external surfaces of the body and emerges from cells starting within the endodermal, mesodermal, or ectodermal germ layer amid embryogenesis.
Cancer happens when a single better cell amasses transformations and other changes within the DNA, histones, and other biochemical compounds that make up the cell's genome. The cell genome controls the structure of the cell's biochemical components, the biochemical responses that happen inside the cell, and the organic intelligence of that cell with other cells. Certain combinations of transformations within the given begetter cell eventually result in that cell (too called a cancer stem cell) showing several irregular, harmful cellular properties that, when taken together, are considered characteristic of cancer, counting:
the capacity to proceed to partition never-ending, creating an exponentially (or near-exponentially) expanding number of modern harmful cancerous "girl cells" (uncontrolled mitosis);
the capacity to enter ordinary body surfaces and boundaries, and to bore into or through adjacent body structures and tissues (nearby invasiveness);
the capacity to spread to other locales inside the body (metastasize) by entering or entering into the lymphatic vessels (territorial metastasis) and/or the blood vessels (removed metastasis).
If this preparation of ceaseless development, neighborhood intrusion, and territorial and far-off metastasis isn't stopped using a combination of incitement of immunological guards and restorative treatment intercessions, the result is that they have encompasses a persistently expanding burden of tumor cells all through the body. Inevitably, the tumor burden progressively meddling with ordinary biochemical capacities carried out by the host's organs, and passing eventually results.
Carcinoma is but one frame of cancer—one composed of cells that have created the cytological appearance, histological engineering, or atomic characteristics of epithelial cells. A better carcinoma stem cell can be shaped from any of several oncogenic combinations of changes in a totipotent cell, a multipotent cell, or a develop separated cell.
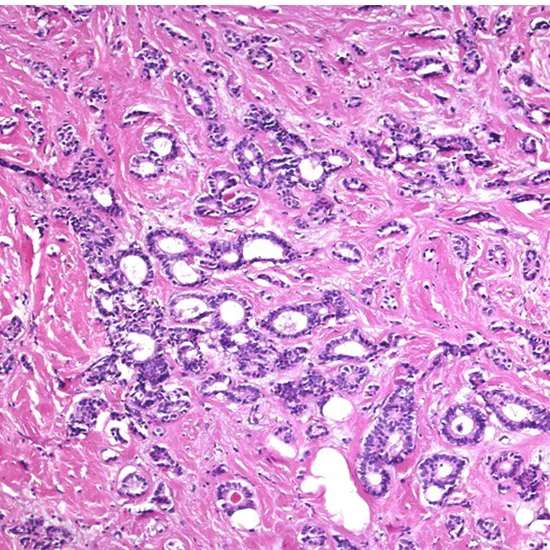
Tubular Carcinoma
Tubular carcinoma may be a subtype of intrusive ductal carcinoma of the breast. More seldom, tubular carcinomas may emerge within the pancreas or kidney. Most tubular carcinomas start within the drain duct of the breast and spread to sound tissue around it.
Tubular carcinoma may be a sort of obtrusive ductal carcinoma where all the cancer cells see tube-shaped beneath a magnifying lens. Tubular carcinoma is uncommon and more often than not forceful. Typically the tumors are little and do not develop exceptionally quickly.
Tubular carcinoma could be a sort of IDC that creates within the drain conduits of the breast. The tumors tend to be little, as a rule, 1 centimeter or less in distance across. Tubular carcinoma gets its title from the tiny, tube-shaped structures that make up the tumors.
Tubular carcinomas are as a rule seen on mammography as sporadically molded masses with central densities and spiculated edges, and most tubular carcinomas can be recognized on sonography as hypoechoic masses with ill-defined edges and back acoustic shadowing. The middle age of the TC gather was 47 a long time (extend, 36-74 a long time), and the middle tumor estimate was 0.9 cm (run, 0.3-4.5 cm). Fractional mastectomy was performed in 65 cases (92.8%), though five patients (6.1%) underwent add up to mastectomy.
Tubular carcinomas are not a common shape of breast cancer. Tubular carcinoma is uncommon in men. The normal age for a determination for women is around 50 a long time ancient. Foundation: Tubular carcinoma could be a less forceful shape of breast cancer which encompasses 1-4% of obtrusive breast cancer. Earlier ponders have appeared a nearly 100-year survival rate for tubular carcinoma compared to the 89.2% five-year survival of all breast cancers.
Tubular breast cancer may be a sort of obtrusive ductal breast cancer that accounts for less than 2% of all breast cancers. Like other sorts of obtrusive ductal cancer, tubular breast cancer starts within the drain conduit of the breast time recently spreading to the tissues around the conduit. Papillary and tubular carcinomas speak to two exceptional subcategories of breast carcinoma more often than not analyzed in elderly patients. Intraductal papillary carcinomas generally develop inside expanded conduits, with intermittent inclusion of adjoining conduits to make a little non-solid mass
Tubule arrangement: This score speaks to the percentage of cancer cells that are shaped into tubules. Organize 2 cancer may be a bit more genuine than arrange 1 cancer, but with early treatment, patients can be cured of the infection.
The recurrence rate is additionally low if treated quickly. Current treatment cures more than 50% of patients with organized I renal cell cancer, but patients with arranged IV infections have exceptionally destitute results. All patients with recently analyzed renal cell cancer are candidates for clinical trials, when conceivable.
Staging
Staging of carcinoma alludes to the method of combining physical/clinical examination, the obsessive survey of cells and tissues, surgical methods, research facility tests, and imaging considers in a coherent design to get data around the estimate of the neoplasm and the degree of its attack and metastasis. Carcinoma organization is the variable that has been most reliably and firmly connected to the forecast of the danger.
Carcinomas are as a rule arranged with Roman numerals. In most classifications, Organize I and Arrange II carcinomas are affirmed when the tumor is little and/or has spread to neighborhood structures as it were. Organize III carcinomas ordinarily have been found to have spread to territorial lymph hubs, tissues, and/or organ structures, whereas Arrange IV tumors have as of now metastasized through the blood to far-off locales, tissues, or organs.
In a few sorts of carcinomas, Arrange carcinoma has been utilized to depict carcinoma in situ, and mysterious carcinomas are recognizable as they were using an examination of sputum for threatening cells (in lung carcinomas).
In later organizing frameworks, substages (a, b, c) are getting to be more commonly utilized to way better characterize bunches of patients with a comparable guess or treatment alternatives.
The criteria for staging can vary significantly based on the organ framework in which the tumor emerges. For case, the colon and bladder cancer organizing framework depends on the profundity of attack, arranging of breast carcinoma is more subordinate to the measure of the tumor, and in renal carcinoma, organizing is based on both the measure of the tumor and the profundity of the tumor attack into the renal sinus. Carcinoma of the lung features a more complicated arranging framework, taking into consideration several estimates and anatomic factors.
The UICC/AJCC TNM frameworks are most regularly used.[clarification required] For a few common tumors, in any case, classical arranging strategies (such as the Dukes classification for colon cancer) are still utilized.
Grading
Grading of carcinomas alludes to the business of criteria planning to semi-quantify the degree of cellular and tissue development seen within the changed cells relative to the appearance of the ordinary parent epithelial tissue from which the carcinoma determines.
Grading of carcinoma is most regularly done after a treating doctor and/or specialist gets a test of suspected tumor tissue utilizing surgical resection, needle or surgical biopsy, coordinate washing or brushing of tumor tissue, sputum cytopathology, etc. A pathologist at that point analyzes the tumor and its stroma, maybe utilizing recoloring, immunohistochemistry, stream cytometry, or other strategies. The pathologist classified the tumor semi-quantitatively into one of three or four grades.
Grade 1, or well-differentiated:
there is a striking resemblance to the normal parent tissue, or there is one that is extremely similar, and the tumour cells are easily recognised and categorised as a specific malignant histological entity.
Grade 2, or moderately differentiated:
there is a considerable resemblance to the parent cells and tissues, but abnormalities can commonly be seen and the more complex features are not particularly well-formed
Grade 3, or poorly differentiated:
there is very little resemblance between the malignant tissue and the normal parent tissue, abnormalities are evident, and the more complex architectural features are usually rudimentary or primitive
Grade 4, or undifferentiated carcinoma:
With little discernible production of glands, ducts, bridges, stratified layers, keratin pearls, or other prominent traits consistent with a more highly differentiated neoplasm, these carcinomas have little in common with the respective parent cells and tissues.
Although there is a definite and convincing statistical correlation between carcinoma grade and tumor prognosis for some tumor types and sites of origin, the strength of this association can be highly variable. It may be stated generally, however, that the higher the grade of the lesion, the worse its prognosis.
Pathogenesis
The accumulation of mutations and other alterations in the DNA, histones, and other biochemical components that make up a cell's genome in a single progenitor cell is what causes cancer. The structure of a cell's biochemical components, internal biochemical reactions, and connections with other cells are all governed by the genome of that cell.A specific combination of mutations in each progenitor cell ultimately causes that cell (also known as a cancer stem cell) to exhibit many abnormal and malignant cellular characteristics thought to be characteristic of cancer, including will be:
- Ability to continuously divide and produce exponentially (or near-exponentially) increasing numbers of new malignant cancerous "daughter cells" (uncontrolled mitosis).
- Ability to penetrate normal body surfaces and barriers and perforate adjacent body structures and tissues (local invasiveness);
- Ability to spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body by penetrating or invading lymphatic vessels (local metastasis) and/or blood vessels (distant metastasis).
If this process of ongoing growth, local invasion, and local and distant metastasis is not halted by a combination of immunological defense stimuli and therapeutic intervention, the systemic tumor cell host burden will continually increase. Ultimately, tumor burden gradually disrupts the normal biochemical functions performed by the host's organs, ultimately leading to death.
Carcinoma is but one frame of cancer—one composed of cells that have created the cytological appearance, histological design, or atomic characteristics of epithelial cells. A better carcinoma stem cell can be shaped from any of several oncogenic combinations of changes in a totipotent cell, a multipotent cell, or a develop separated cell.
Invasion and Netastasis
The trademark of a dangerous tumor is its inclination to attack and penetrate nearby and adjoining structures and, inevitably, spread from the location of its beginning to non-adjacent territorial and removed locales within the body, a prepare called metastasis. If unchecked, tumor development and metastasis, in the long run, make a tumor burden so incredible that they have surrendered. Carcinoma metastasizes through both the lymph hubs and the blood.
Mutation
Entirety genome sequencing has built up the change recurrence for entire human genomes. The transformation recurrence within the entire genome between eras for people (parent to child) is almost 70 unused changes per era.
Carcinomas, be that as it may, have much higher transformation frequencies. The specific recurrence depends on tissue sort, whether a mismatch DNA repair insufficiency is displayed, and introduction to DNA harming specialists such as components of tobacco smoke. Fish and Amos have summarized the transformation frequencies per megabase (Mb) in a few carcinomas, as appeared within the table (alongside the demonstrated frequencies of transformations per genome).
Pathology
Even though tubular carcinoma has been considered a special-type tumor,[a] recent trend has been to classify it as a low-grade, intrusive NOS carcinoma since there's a ceaseless range from immaculate tubular carcinomas to blended NOS[b]carcinomas with tubular highlights, depending on the rate of the injury that shows tubular highlights.
Histology
They are as a rule low-grade. Elastosis has been famous as common but isn't displayed in all cases.
The histologic highlights of tubular carcinoma are the multiplication of well-differentiated organs or tubules, orchestrated in a tumultuous and frequently outspread design, with organs expanding unpredictably into adjoining sinewy stroma and fat tissue.
Prevalence
Alter Predominance has already been disputable, with conflicting reports from considers announcing either exceptionally moo predominance or a tall prevalence. With the expanding accessibility of screening mammography, be that as it may, tubular carcinomas are being analyzed prior, and later ponders propose tubular carcinomas speak to between 8% and 27% of all breast cancers.
Prognosis
A few shapes of carcinoma can be cured with early location and early treatment. For occurrence, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) contains a 100% five-year survival rate. This implies that individuals with BCC are fair as likely to be lively five years after conclusion as somebody without a BCC conclusion.
What is the treatment for Organize 1 carcinoma?
In a few cases, arrange 1 cancer treatment involves chemotherapy, radiation treatment, solutions, surgery, or a combination of approaches.
Is invasive carcinoma curable?
When caught and treated early, the forecast for localized intrusive ductal carcinoma is nice with a 5-year survival rate of about 100%. If cancer has spread to adjacent tissue or metastasized to other regions of the body the 5-year survival rate drops.
How is tubular breast cancer treated?
Surgery to the lymph hubs. Tubular breast cancer is less likely to spread to the lymph hubs beneath the arm than most other sorts of breast cancer.
- Radiotherapy.
- Hormone (endocrine) therapy
- Chemotherapy Focused on (natural) treatments.
















