Tularemia, additionally regarded as rabbit fever or deer fly fever, is a probable life-threatening bacterial contamination brought on by using the bacterium Francisella tularensis.
Tularemia, additionally regarded as rabbit fever or deer fly fever, is a probable life-threatening bacterial contamination brought on by using the bacterium Francisella tularensis.
It is normally located in animals such as rabbits, rodents, and deer, however, can additionally be transmitted to human beings via contact with contaminated animals, insect bites, contaminated water or soil, or inhalation of contaminated aerosols.
Prevention measures consist of heading off contact with contaminated animals, carrying defensive apparel when in areas the ailment is prevalent, and the use of insect repellent to keep away from insect bites.
What is Tularemia?
Tularemia, additionally regarded as rabbit fever, is bacterial contamination induced through the bacterium Francisella tularensis. It is normally observed in animals such as rabbits, rodents, and deer, however, can additionally be transmitted to human beings via contact with contaminated animals, insect bites, contaminated water or soil, or inhalation of contaminated aerosols.
The signs of tularemia can range relying on the technique of transmission, however, encompass fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, joint pain, coughing, and swollen lymph nodes.
In extreme cases, tularemia can lead to problems such as pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis. Treatment for tularemia generally includes a route of antibiotics, and early therapy is indispensable to forestall serious complications.
Explore the Epidemiology of Tularemia:
Tularemia is an uncommon disease, and its incidence varies relying on the geographic vicinity and the populace studied.
In the United States, the annual incidence of tularemia is about 0.1 instances per 100,000 population, with the majority of instances taking place in the western and central areas of the country.
Tularemia is extra frequent in rural areas, the place human beings may additionally come into contact with contaminated animals or insect vectors.
Hunting, trapping, and different outside things can make the chance of tularemia bigger.
The sickness is also more frequent in guys than women, and in humans who are over 60 years of age.
Outbreaks of tularemia have passed off in a variety of components of the world, which includes Europe, Asia, and North America.
In some areas, outbreaks have been related to contaminated water or food, whilst in different areas, outbreaks have been linked to insect bites or publicity of contaminated animals.
Learn About the Pathophysiology of Tularemia
Tularemia is brought about via the bacterium Francisella tularensis, which can infect a range of animals which includes rabbits, rodents, and deer.
The microorganisms capable of living to tell the tale and multiply inside these animals, and can be transmitted to human beings through countless specific routes, together with direct contact with contaminated animals, ingestion of contaminated meals or water, inhalation of contaminated aerosols, or insect bites.
Once inside the human body, microorganisms can infect a range of tissues and organs, which includes the lungs, lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
Microorganisms are in a position to keep away from the immune gadget and replicate inside host cells, mainly to improve signs and symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and muscle aches.
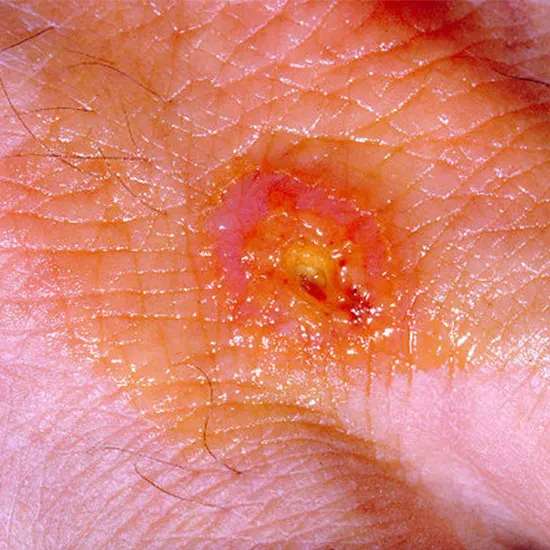
Tularemia can additionally cause the formation of small ulcers at the website of entry, such as a tick chew or a reduction from managing a contaminated animal.
These ulcers might also come to be painful and swollen and can lead to the improvement of regional lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes).
In extreme cases, tularemia can lead to issues such as pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis. The microorganism can additionally motivate harm to the liver, spleen, and different organs, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Treatment for tularemia usually includes a path of antibiotics, which can correctly kill the microorganism and forestall the improvement of extreme complications. An early cure is fundamental to forestall serious problems and ensure a full recovery.
Signs And Symptoms of Tularemia
The symptoms and signs of tularemia can fluctuate relying on the route of transmission and the severity of the infection.
Some frequent signs and symptoms of tularemia include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Joint pain
- Fatigue
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Abdominal pain Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
The signs of these issues can include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Low blood pressure
- Organ failure.
Diagnosis of Tularemia
Diagnosis of tularemia can be challenging, as the signs and symptoms can be similar to different bacterial infections.
However, there are quite a few checks that can be used to diagnose the disease, including:
Blood tests
Blood exams can be used to observe antibodies to Francisella tularensis, which can point out a modern-day or previous infection.
Culture
Culturing the microorganism from Bacteria Culture a patient's blood, tissue, or different bodily fluids can affirm the analysis of tularemia.
However, culturing the microorganism can be challenging and might also take various days to produce a result.
Polymerase chain response (PCR)
PCR is a molecular approach that can discover the presence of Francisella tularensis DNA in a patient's blood, tissue, or blood culture different bodily fluids. This takes a look at can grant a speedy and correct analysis of tularemia.
Skin test
Pores and skin take a look known as the tularemia antigen, which can be used to realize the presence of antibodies to Francisella tularensis in a patient's skin.
This check can be used to diagnose each present-day infection.
Imaging tests
Imaging checks such as X-rays or CT scans can also be used to consider the extent of any lung or organ involvement, especially in extreme cases.
It is necessary to seek clinical interest if you suspect you have been uncovered to tularemia or if you trip any signs of the disease.
Early analysis and therapy can forestall serious issues and ensure a full recovery.
Complications of Tularemia
Tularemia can lead to various complications, specifically if left untreated or if the contamination is severe.
Some of the doable issues of tularemia include:
Pneumonia
Tularemia can cause extreme respiratory symptoms, together with cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. In some cases, the contamination can lead to the improvement of pneumonia, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Meningitis
Tularemia can unfold to the membranes surrounding the intelligence and spinal cord, leading to the improvement of meningitis. This can motivate signs such as fever, headache, neck stiffness, and confusion.
Sepsis
In extreme cases, tularemia can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening circumstance that takes place when the body's response to contamination causes significant infection and organ damage.
Hepatitis
Tularemia can motivate irritation of the liver, mainly to the improvement of hepatitis. This can motivate signs such as stomach pain, nausea, and yellowing of the pores and skin and eyes.
Splenomegaly
Tularemia can cause the spleen to become enlarged, which can cause belly pain, fatigue, and anaemia.
Neurological complications
In uncommon cases, tularemia can cause neurological complications, which include seizures and encephalitis.
It is necessary to search for clinical interest if you suspect you have been uncovered to tularemia or if you have any signs and symptoms of the disease. Early prognosis and remedy can stop serious issues and make a full recovery.
Treatment of Tularemia
Tularemia can be dealt with antibiotics, generally for a length of 10-14 days. The kind of antibiotic prescribed will rely on the severity of the contamination and the patient's age and clinical history.
Some antibiotics that are regularly used to deal with tularemia include:
Streptomycin
This is the drug of choice for treating extreme tularemia infections, as it has the absolute best treatment rate.
Gentamicin
This is some other antibiotic that is superb in opposition to tularemia and can be used as a choice to streptomycin.
Doxycycline
This antibiotic is positive in opposition to tularemia and is regularly used to deal with moderate to reasonable infections.
Ciprofloxacin
This antibiotic is advantageous in opposition to tularemia and is frequently used to deal with slight to average infections.
Chloramphenicol
This antibiotic can be used to deal with tularemia, however, it is now not generally used due to its achievable facet effects. In addition to antibiotics, supportive care may additionally be necessary, specifically in instances the place the infection has brought on extreme signs or complications.
This might also encompass IV fluids, oxygen therapy, and therapy for any related prerequisites such as pneumonia or meningitis. It is essential to search for scientific interest if you suspect you have been Urine Routine and Microscopy uncovered to tularemia or if you have any signs of the disease. Early prognosis and cure can forestall serious issues and make certain a full recovery.
Tularemia is a bacterial contamination induced with the aid of Francisella tularensis that can be transmitted to human beings via contaminated animals, insect bites, or contaminated water and Urine Culture soil. The ailment can cause a variety of symptoms, from slight flu-like signs and symptoms to severe pneumonia and sepsis.
Taking measures to stop exposure, such as carrying shielding clothing when coping with animals and fending off ingesting untreated water, can additionally assist minimize the chance of infection.
Stay healthy, and stay informed about Tularemia!









