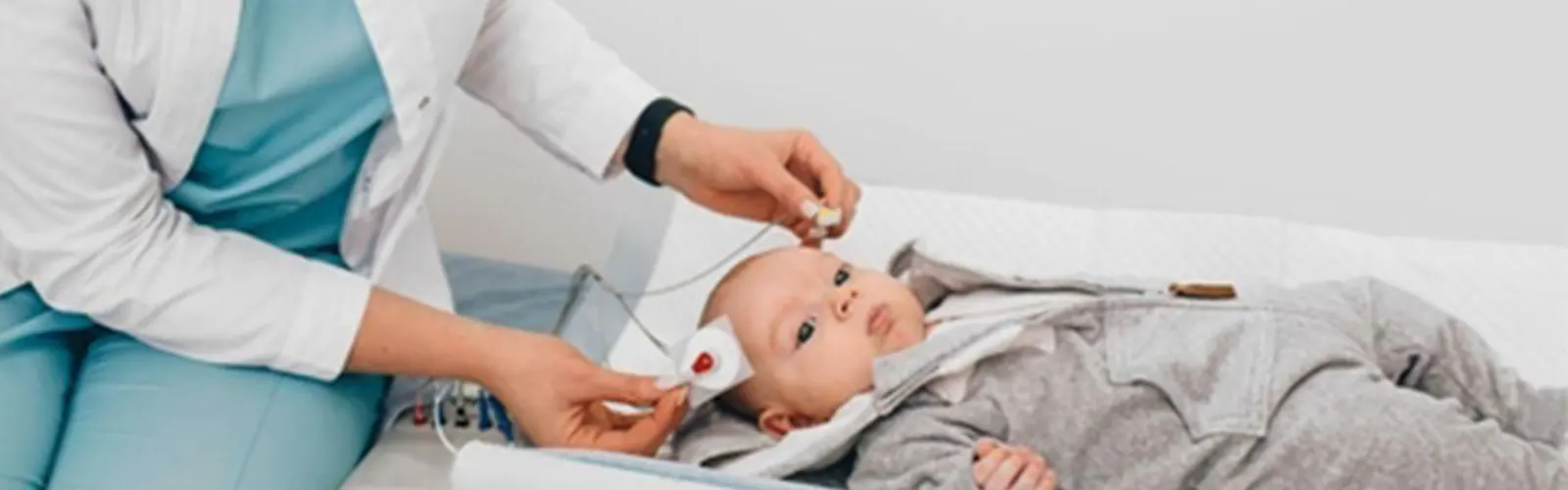
The Brainstem Sound-related Evoked Reaction (BAER) test, moreover known as the sound-related brainstem reaction (ABR) test, may be a diagnostic apparatus that's commonly utilized to assess hearing in newborn children,...
The Brainstem Sound-related Evoked Reaction (BERA) test, moreover known as the sound-related brainstem reaction (ABR) test, may be a diagnostic apparatus that's commonly utilized to assess hearing in newborn children, youthful children, and individuals who are incapable to supply solid criticism around their hearing.
The benefits of the BERA test incorporate
Objective estimation:
The BERA test is an objective degree of hearing that does not rely on a patient's subjective reaction. This makes it valuable for assessing hearing in individuals who are incapable of supplying solid criticism, such as newborn children and young children.
Early discovery of hearing misfortune
The BERA test can distinguish hearing misfortune in newborn children as youthful as a number of days ancient, permitting for early mediation and treatment.
Distinguishing proof of the sort and degree of hearing misfortune
The BERA test can recognize the sort and degree of hearing misfortune, which is vital in determining the fitting course of treatment.
Checking of hearing misfortune over time
The BERA test can be utilized to screen hearing misfortune over time and to assess the viability of treatment.
Non-invasive
The BERA test could be a non-invasive procedure that does not require any sedation or anesthesia, making it secure and simple to perform.
In general, the BERA test may be a profitable demonstrative device for assessing hearing in individuals of all ages, and can give critical data for the conclusion and treatment of hearing misfortune.