In this article we’ll get to know about the haemophilia and how to diagnose this condition .
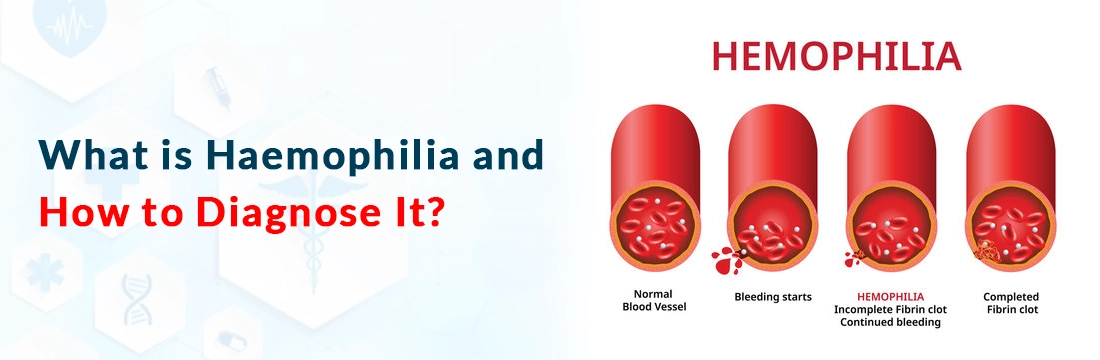
Haemophilia is a rare hereditary condition which prevents blood from clotting normally. Factor VIII, Factor IX, and Factor XI are the main blood clotting factors (plasma proteins) that are absent or present in insufficient quantities in this condition. In order for blood to clot, several proteins are necessary.
Haemophilia is typically caused by genetic mutations inherited from one or both parents. Haemophilia can, however, very rarely result from drug responses, cancer, autoimmune diseases, illnesses where the body's defences attack clotting factors, etc.
Because the clotting factor-producing genes are found on the X chromosome, it mainly affects men. Males only have one X chromosome, thus if it has a defective gene, they will develop haemophilia.
Females, on the other hand, have two X chromosomes. A defective gene on one chromosome is compensated by the other. As a result, female patients frequently have less or no symptoms.
What are the symptoms of haemophilia?
There can be many symptoms of haemophilia. Sometimes bleeding also occurs in the brain due to haemophilia, due to which the symptoms given below are shown.
- A severe headache
- Vomiting repeatedly
- Lethargic or drowsy
- Vision issue
- Sudden weakness or clumsiness
- seizure or convulsions
Other common symptoms of haemophilia are:
- heavy bleeding that doesn't seem normal from wounds or traumas, or during dental or surgical procedures
- Several deep or big bruises
- abnormal bleeding following immunizations
- Joint pain and edema,
- Nosebleeds without a known cause
- Blood in your stool or urine
- In young children, inexplicable agitation
How to diagnose the haemophilia
For diagnosing the haemophilia first the doctor will review your medical history and family history based on that assessment further confirmatory tests will be ordered for diagnosing the disease.If you have any of the symptoms given above, it means you may have haemophilia. There are different diagnostic tests to diagnose it, which are written below
- Physical examination: it is the first process for diagnosing haemophilia. Your healthcare provider will check for the signs of bruising and excessive bleeding and swollen joints.
- CBC blood test: complete blood count test is the mandatory test in case of suspicion of haemophilia as it give a overall picture of the red blood cells in a body, and it also tells about the level of clotting factor in a blood
- Clotting test : these tests are those which specifically tell about the clotting related properties of the blood these tests include prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) , this test tells about how much time the blood needs for clotting.
- X rays: this is performed to assess the damage caused by the bleeding
- Genetic test: this test is done to confirm the diagnosis and to find out the exact type of haemophilia
Conclusion
Haemophilia is a rare genetic disorder which can affect the person's ability to clot and can further aid in life threatening conditions as it can also lead to bleeding in the brain which is one of the most dangerous consequences of haemophilia. Get your haemophilia tested today with the ganesh diagnostic centre at discounted prices.
Frequently asked questions (people also ask)
How haemophilia occurs
Haemophilia is mainly caused by the absence of protein involved in clotting factor due to genetic mutation
How the doctors diagnose haemophilia
It can be diagnose with a series of blood test and genetic testing
How many types of haemophilia is there
There are total three types of haemophilia
- Haemophilia A
- Haemophilia B
- Haemophilia C
What are the symptoms of haemophilia
Haemophilia cause the abnormal bleeding, bruise, swollen joints etc
What is the most dangerous consequence of haemophilia
Bleeding in a brain is one of the most dangerous consequence of haemophilia.