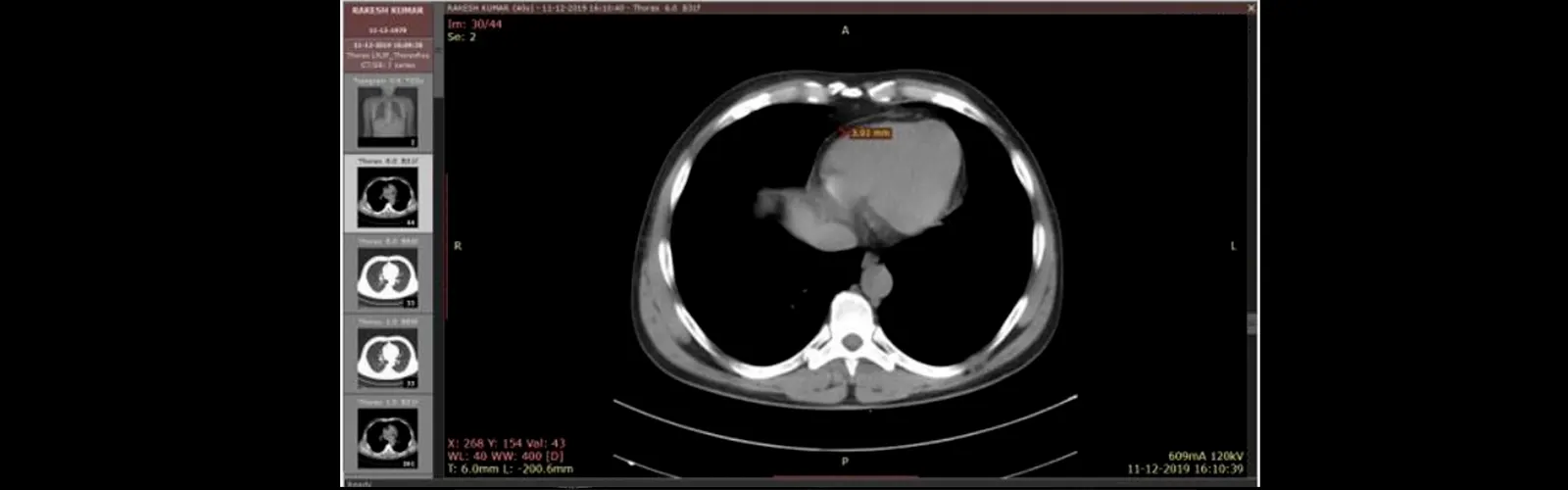
Non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) of the chest is a medical imaging procedure that uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the chest without the use of a contrast agent. NCCT chest can be useful...
Non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) of the chest is a medical imaging procedure that uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the chest without the use of a contrast agent. NCCT chest can be useful in the staging of cancer, which is the process of determining the extent of cancer spread in the body.
Here are some ways NCCT chest can play a role in the staging of cancer:
Identification of primary tumor: NCCT chest can help identify the primary tumor in cases where cancer has originated in the lungs. The size, location, and extent of the tumor can be assessed using an NCCT chest, which can help guide treatment decisions such as surgery or radiation therapy.
Evaluation of lymph nodes: NCCT chest can also be used to evaluate the lymph nodes in the chest, which can indicate whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. Enlarged or abnormal lymph nodes can be identified using an NCCT chest, which can help determine the stage of cancer and guide treatment decisions.
Assessment of distant metastases: NCCT chest can help identify the presence of distant metastases, which is when cancer has spread to other parts of the body such as the liver, bones, or brain. NCCT chest can detect the presence of lung nodules, which can indicate whether the cancer has spread to the lungs. This information can help determine the stage of the cancer and guide treatment decisions.
Overall, the NCCT chest can be a valuable tool in the staging of cancer, particularly in cases where cancer has originated in the lungs or has spread to the lungs. By providing detailed images of the chest, NCCT scans can help identify the primary tumor, evaluate lymph nodes, and assess the presence of distant metastases, which can guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.









