Book E-Cadherin Appointment Online Near me at the best price in Delhi/NCR from Ganesh Diagnostic. NABL & NABH Accredited Diagnostic centre and Pathology lab in Delhi offering a wide range of Radiology & Pathology tests. Get Free Ambulance & Free Home Sample collection. 24X7 Hour Open. Call Now at 011-47-444-444 to Book your E-Cadherin at 50% Discount.
E-cadherin, also known as epithelial cadherin, is a transmembrane protein that plays a crucial role in cell-cell adhesion in epithelial tissues. It is a calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecule that is expressed on the surface of most epithelial cells.
E-cadherin is a member of the cadherin superfamily of transmembrane proteins, which mediate cell-cell adhesion by forming homophilic interactions with cadherins on adjacent cells. The extracellular domain of E-cadherin binds to the extracellular domain of another E-cadherin molecule on an adjacent cell, forming a stable adhesive interaction.
E-cadherin is important for maintaining the structural integrity of epithelial tissues and plays a critical role in the regulation of epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. Loss of E-cadherin expression or function has been implicated in the progression of various cancers, including breast, gastric, and prostate cancer.
The CDH1 gene in humans encodes the protein known as cadherin-1, also known as epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin), which is distinct from cadherin, which is an APC/C activator protein. [5] Cancers of the stomach, breast, colon, thyroid, and ovary are all associated with mutations. Also known as CD324 is CDH1 (cluster of differentiation 324). It is a gene that suppresses tumours.
Masatoshi Takeichi, whose work on adherent epithelial cells began in 1966, is credited with discovering cadherin cell-cell adhesion proteins. [8] His research first focused on the regulation of lens fibre differentiation by retinal cells in chicken embryos, which he studied at Nagoya University. Takeichi first gathered medium (CM) used to develop neural retina cells before suspending lens epithelial cells in it. In contrast to cells in his usual medium, he noticed that cells floating in the CM media exhibited delayed attachment. His fascination with cell adhesion led him to investigate attachment under many circumstances, including those involving protein, magnesium, and calcium. Throughout the 1970s, there was limited knowledge of the precise roles.
E-cadherin is measured or analyzed in various ways to assess its expression or function in different biological and medical contexts.
A traditional cadherin superfamily member is cadherin-1. Five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail make up the encoded protein, which is a calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein. Gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid, and ovarian cancers are associated with mutations in this gene. By accelerating proliferation, invasion, and/or metastasis, loss of function is thought to speed up the progression of cancer. This protein's cytoplasmic domain is essential for internalization, and its ectodomain mediates bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells. The identified transcript variants are the result of splice site mutations.
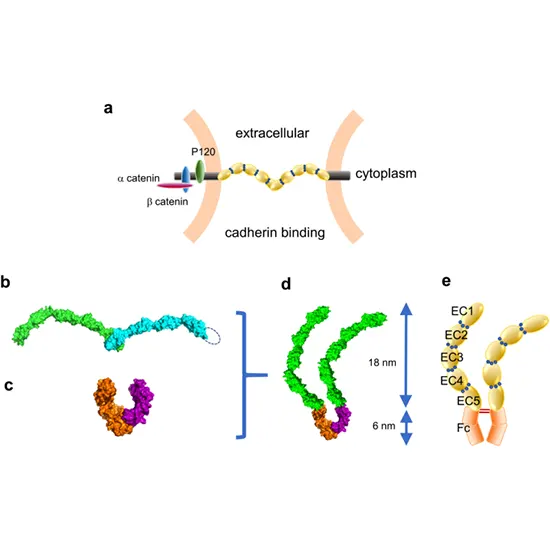
The most extensively researched member of the cadherin family and a crucial transmembrane protein in adherens junctions is e-cadherin (epithelial). Adherens junctions are made up of E-cadherin as well as the intracellular proteins p120-catenin, beta-catenin, and alpha-catenin. Collectively, these proteins govern intercellular communication and stabilize epithelial tissues. Five cadherin repeats (EC1–EC5) make up the extracellular domain of E-cadherin, together with a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain that has undergone extensive phosphorylation. The function of E-cadherin depends on the binding of beta-catenin, which is dependent on this area. [17] Alpha-catenin and beta-catenin can attach to each other. Actin-containing cytoskeletal filaments are regulated by alpha-catenin. Cell-to-cell contacts in epithelial cells that contain E-cadherin are frequently seen next to filaments of the cytoskeleton that contain actin.
Growth signals are suppressed by E-cadherin adhesions, which sets off a kinase cascade that prevents the transcription factor YAP from entering the nucleus. On the other hand, increasing mechanical stretch to put E-cadherins under increased strain or reducing cell density (decreasing cell-cell adhesion) encourages cell cycle entry and YAP nuclear localization.
Edit E-cadherin has been discovered to play a part in epithelial morphogenesis and branching, including when epithelial buds are formed. In terms of biology, branching is a crucial characteristic that enables tissues, such as pancreatic buds and salivary glands, to optimise useful surface areas. There is evidence to suggest that
For the creation and maintenance of multicellular organization, cell migration is essential. Many cell migration processes are involved in morphogenesis, including the movement of epithelial sheets during gastrulation, the migration of neural crest cells, and the migration of the posterior lateral line primordium. It is understood that cells that start internalizing at the embryo's dorsal surface mobilize to extend the axis and guide the progenitors of the posterior prechordal plate and notochord. The ability of "follower cells" to help the leading cells in the right direction determines how cells can orient themselves during this process.
The sample required for E-cadherin analysis or measurement depends on the specific method used. Here are some examples of sample types that may be used for E-cadherin analysis:
Tissue biopsy : E-cadherin expression can be analyzed by immunohistochemistry using tissue biopsy samples. This method involves staining thin sections of tissue with antibodies specific to E-cadherin.
Cell culture : E-cadherin expression can be analyzed in cultured cells using techniques such as western blotting, flow cytometry, or immunofluorescence microscopy. These methods require the isolation of cells from the tissue of interest and culturing them in appropriate conditions.
Blood or serum : E-cadherin levels can be measured in blood or serum using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or other similar methods. This type of analysis may be useful for monitoring E-cadherin levels in cancer patients or for evaluating the response to therapy.
The cost of E-cadherin near me in Delhi ranges from INR 1000 to INR 5400.
| Test Type | E-Cadherin |
| Includes | E-Cadherin Test (Oncology) |
| Preparation | |
| Reporting | Within 24 hours* |
| Test Price |
₹ 1313
|

Early check ups are always better than delayed ones. Safety, precaution & care is depicted from the several health checkups. Here, we present simple & comprehensive health packages for any kind of testing to ensure the early prescribed treatment to safeguard your health.